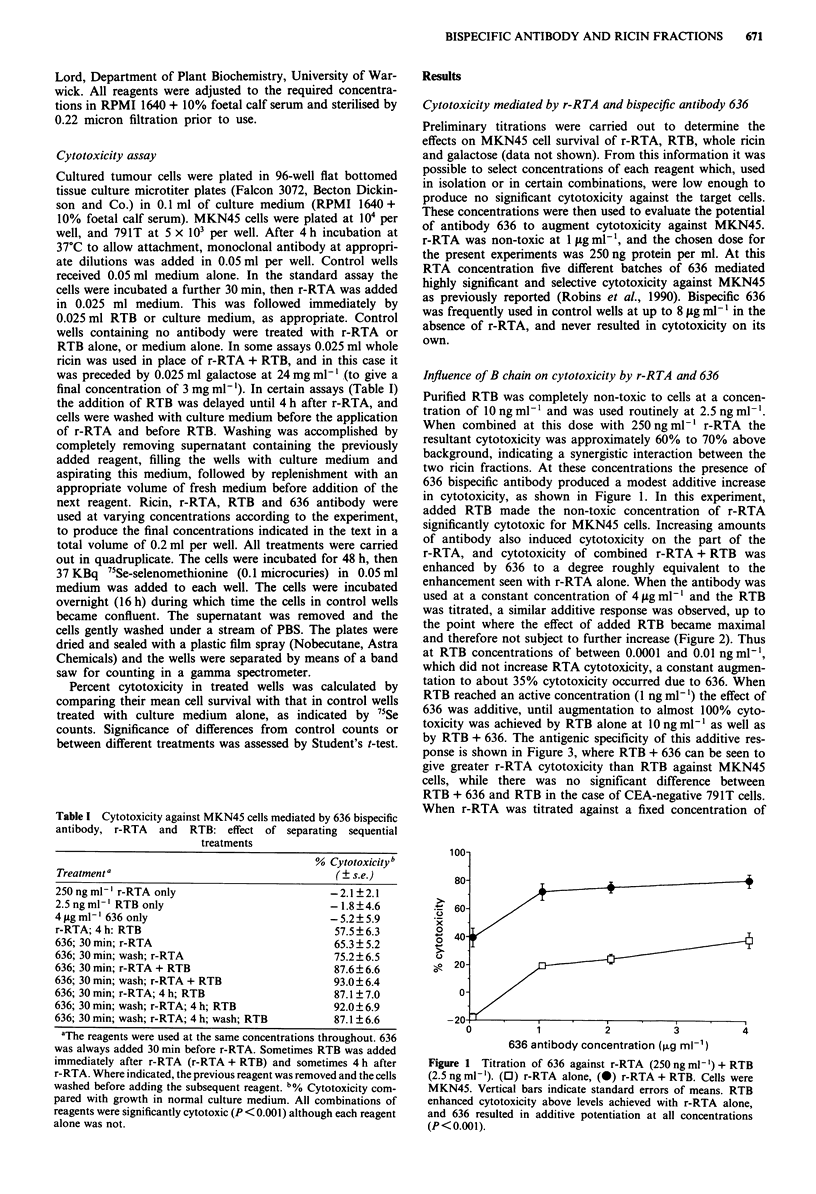
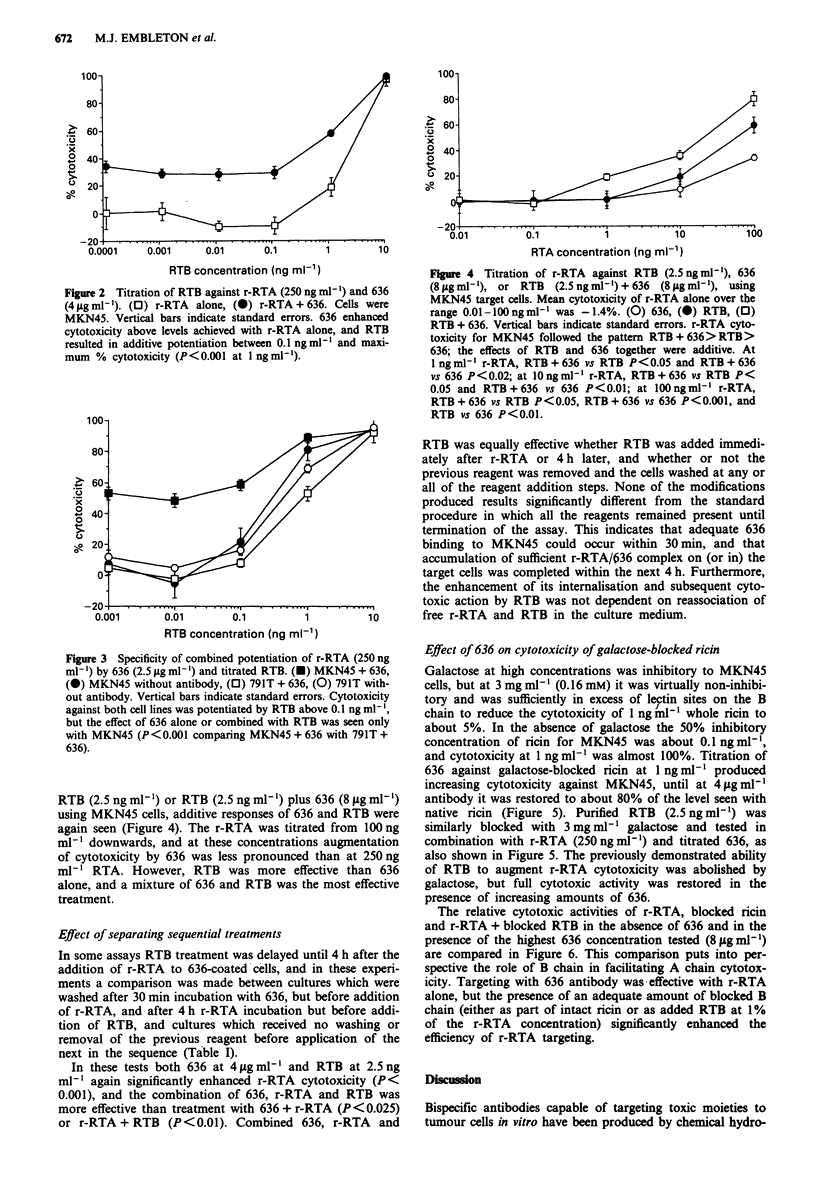
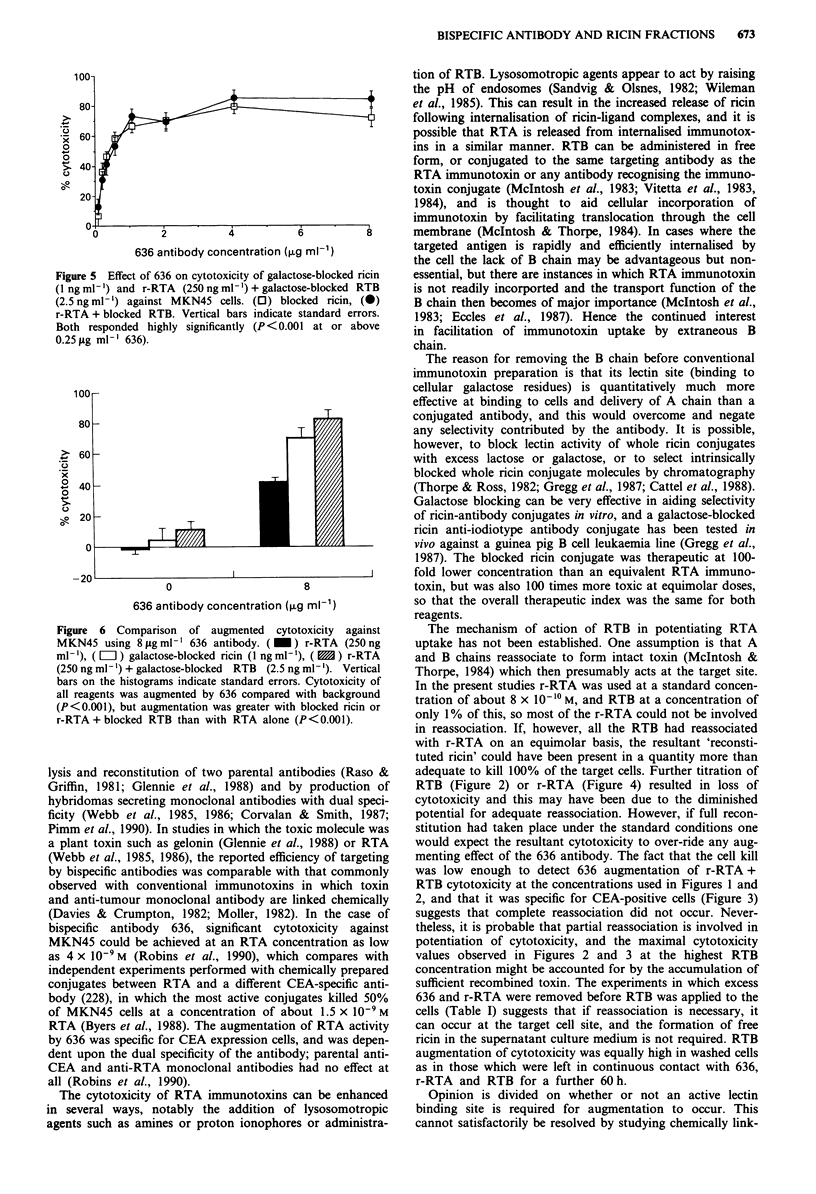
Abstract
A bispecific monoclonal antibody recognising both carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) and ricin toxin A chain (RTA) was tested for its ability to target recombinant RTA (r-RTA) to CEA-expressing tumour cells, alone and in combination with ricin B chain (RTB). The antibody, 636 (Robins et al., 1990), induced significant RTA cytotoxicity against MKN45 gastric carcinoma cells which express high levels of CEA, using the r-RTA at a concentration below that known to be intrinsically cytotoxic. The addition of ricin toxin B chain (RTB) also potentiated cytotoxicity of r-RTA, and there was an additive increase in potentiation against CEA-positive cells when both RTB and 636 were included. The bispecific antibody restored potentiation by RTB after blocking of its binding site with excess galactose, and also the cytotoxic activity of whole ricin which had been blocked with galactose. It was concluded that the 636 bispecific antibody was highly effective in targeting the toxic moiety of the molecule to CEA-expressing cells, and allowed exploitation of the additional ability of the B chain to facilitate cellular incorporation. The facilitating function of the B chain was equally effective whether or not its lectin site was active.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Byers V. S., Pawluczyk I., Pawlucyzk I., Berry N., Durrant L., Robins R. A., Garnett M. C., Price M. R., Baldwin R. W. Potentiation of anti-carcinoembryonic antigen immunotoxin cytotoxicity by monoclonal antibodies reacting with co-expressed carcinoembryonic antigen epitopes. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 1;140(11):4050–4055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers V. S., Pimm M. V., Pawluczyk I. Z., Lee H. M., Scannon P. J., Baldwin R. W. Biodistribution of ricin toxin A chain-monoclonal antibody 791T/36 immunotoxin and influence of hepatic blocking agents. Cancer Res. 1987 Oct 15;47(20):5277–5283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattel L., Delprino L., Brusa P., Dosio F., Comoglio P. M., Prat M. Comparison of blocked and non-blocked ricin-antibody immunotoxins against human gastric carcinoma and colorectal adenocarcinoma cell lines. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1988;27(3):233–240. doi: 10.1007/BF00205445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corvalan J. R., Smith W. Construction and characterisation of a hybrid-hybrid monoclonal antibody recognising both carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) and vinca alkaloids. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1987;24(2):127–132. doi: 10.1007/BF00205589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiklid K., Olsnes S., Pihl A. Entry of lethal doses of abrin, ricin and modeccin into the cytosol of HeLa cells. Exp Cell Res. 1980 Apr;126(2):321–326. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(80)90270-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FitzGerald D., Pastan I. Targeted toxin therapy for the treatment of cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1989 Oct 4;81(19):1455–1463. doi: 10.1093/jnci/81.19.1455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glennie M. J., Brennand D. M., Bryden F., McBride H. M., Stirpe F., Worth A. T., Stevenson G. T. Bispecific F(ab' gamma)2 antibody for the delivery of saporin in the treatment of lymphoma. J Immunol. 1988 Nov 15;141(10):3662–3670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregg E. O., Bridges S. H., Youle R. J., Longo D. L., Houston L. L., Glennie M. J., Stevenson F. K., Green I. Whole ricin and recombinant ricin A chain idiotype-specific immunotoxins for therapy of the guinea pig L2C B cell leukemia. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 15;138(12):4502–4508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pimm M. V., Robins R. A., Embleton M. J., Jacobs E., Markham A. J., Charleston A., Baldwin R. W. A bispecific monoclonal antibody against methotrexate and a human tumour associated antigen augments cytotoxicity of methotrexate-carrier conjugate. Br J Cancer. 1990 Apr;61(4):508–513. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1990.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price M. R., Edwards S., Jacobs E., Pawluczyk I. Z., Byers V. S., Baldwin R. W. Mapping of monoclonal antibody-defined epitopes associated with carcinoembryonic antigen, CEA. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1987;25(1):10–15. doi: 10.1007/BF00199295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raso V., Griffin T. Hybrid antibodies with dual specificity for the delivery of ricin to immunoglobulin-bearing target cells. Cancer Res. 1981 Jun;41(6):2073–2078. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., Olsnes S. Entry of the toxic proteins abrin, modeccin, ricin, and diphtheria toxin into cells. II. Effect of pH, metabolic inhibitors, and ionophores and evidence for toxin penetration from endocytotic vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7504–7513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons B. M., Stahl P. D., Russell J. H. Mannose receptor-mediated uptake of ricin toxin and ricin A chain by macrophages. Multiple intracellular pathways for a chain translocation. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):7912–7920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorpe P. E., Detre S. I., Foxwell B. M., Brown A. N., Skilleter D. N., Wilson G., Forrester J. A., Stirpe F. Modification of the carbohydrate in ricin with metaperiodate-cyanoborohydride mixtures. Effects on toxicity and in vivo distribution. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Feb 15;147(1):197–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08737.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorpe P. E., Ross W. C. The preparation and cytotoxic properties of antibody-toxin conjugates. Immunol Rev. 1982;62:119–158. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00392.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitetta E. S., Cushley W., Uhr J. W. Synergy of ricin A chain-containing immunotoxins and ricin B chain-containing immunotoxins in in vitro killing of neoplastic human B cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6332–6335. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitetta E. S., Fulton R. J., Uhr J. W. Cytotoxicity of a cell-reactive immunotoxin containing ricin A chain is potentiated by an anti-immunotoxin containing ricin B chain. J Exp Med. 1984 Jul 1;160(1):341–346. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.1.341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb K. S., Liberman S. N., Ware J. L., Walther P. J. In vitro synergism between hybrid immunotoxins and chemotherapeutic drugs: relevance to immunotherapy of prostate carcinoma. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1986;21(2):100–106. doi: 10.1007/BF00199856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb K. S., Ware J. L., Parks S. F., Walther P. J., Paulson D. F. Evidence for a novel hybrid immunotoxin recognizing ricin A-chain by one antigen-combining site and a prostate-restricted antigen by the remaining antigen-combining site: potential for immunotherapy. Cancer Treat Rep. 1985 Jun;69(6):663–672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wileman T., Harding C., Stahl P. Receptor-mediated endocytosis. Biochem J. 1985 Nov 15;232(1):1–14. doi: 10.1042/bj2320001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


