Abstract
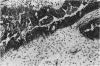
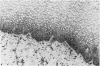
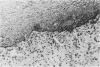
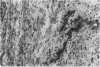
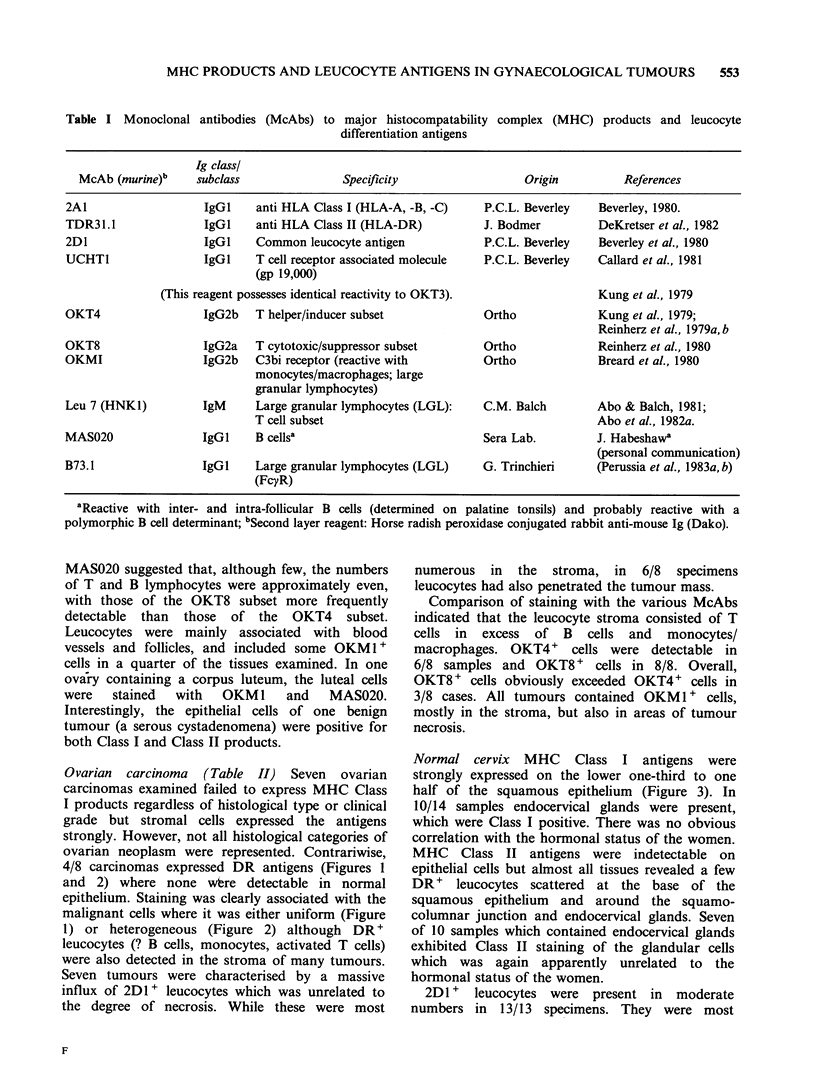
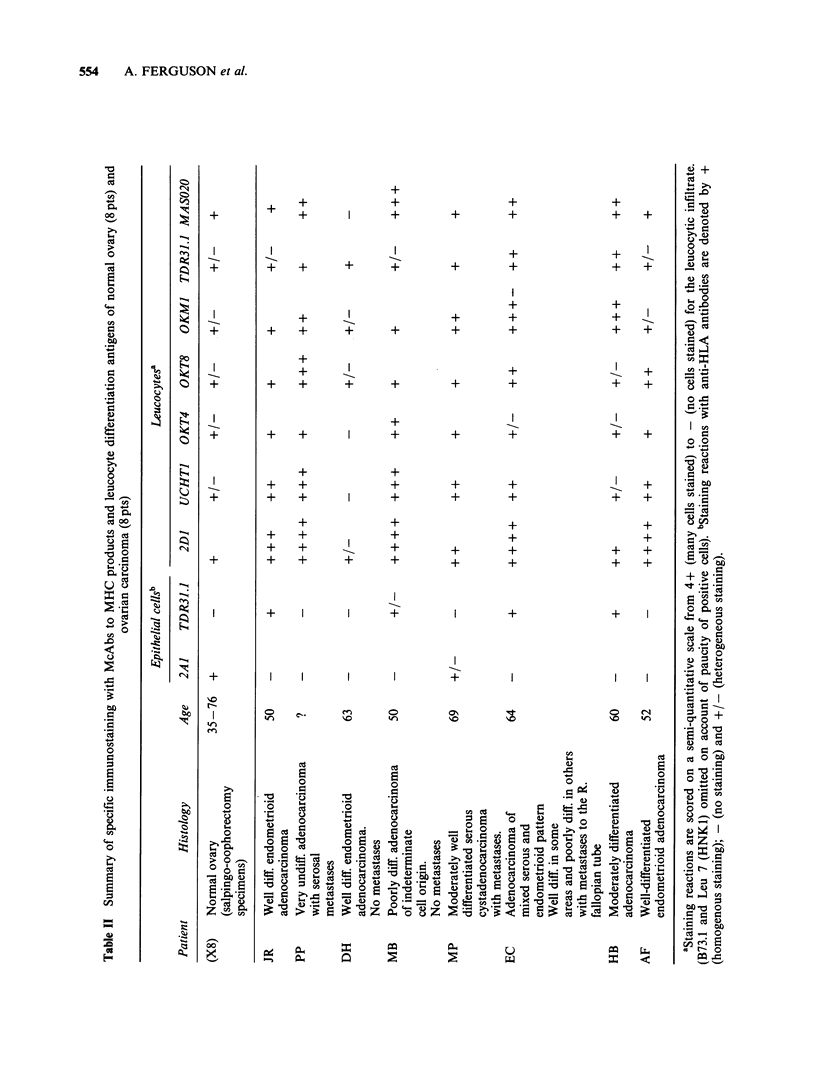
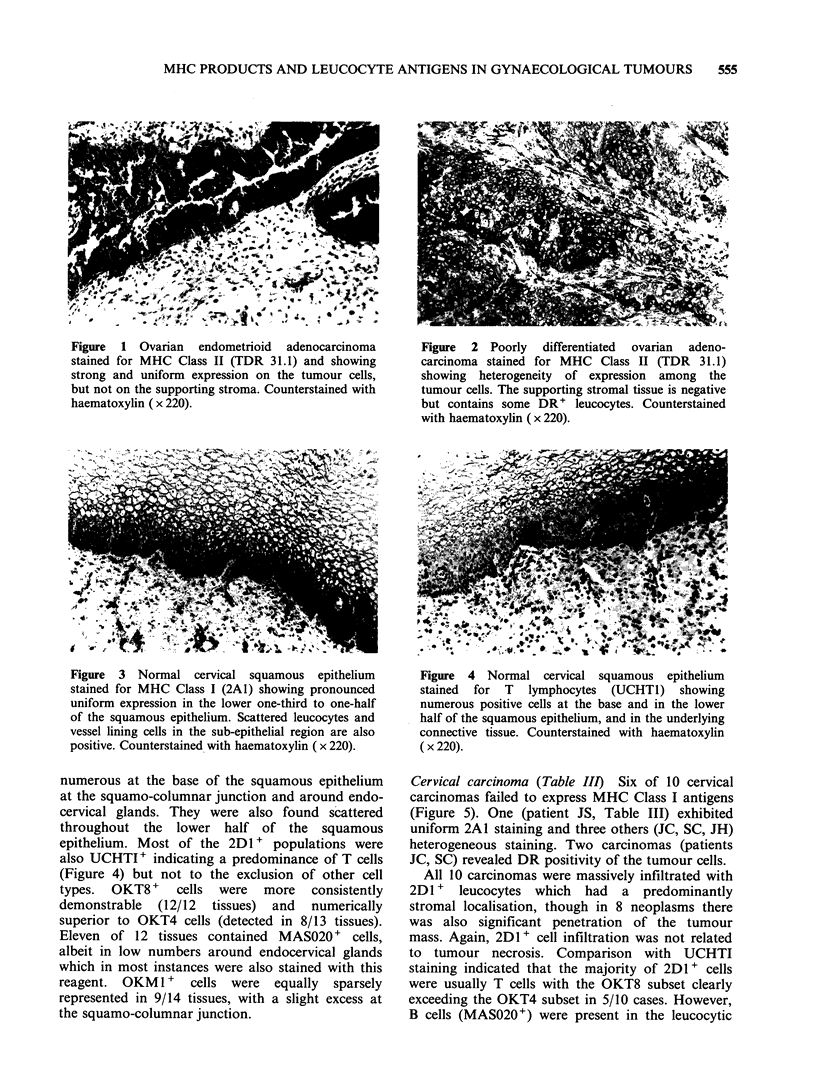
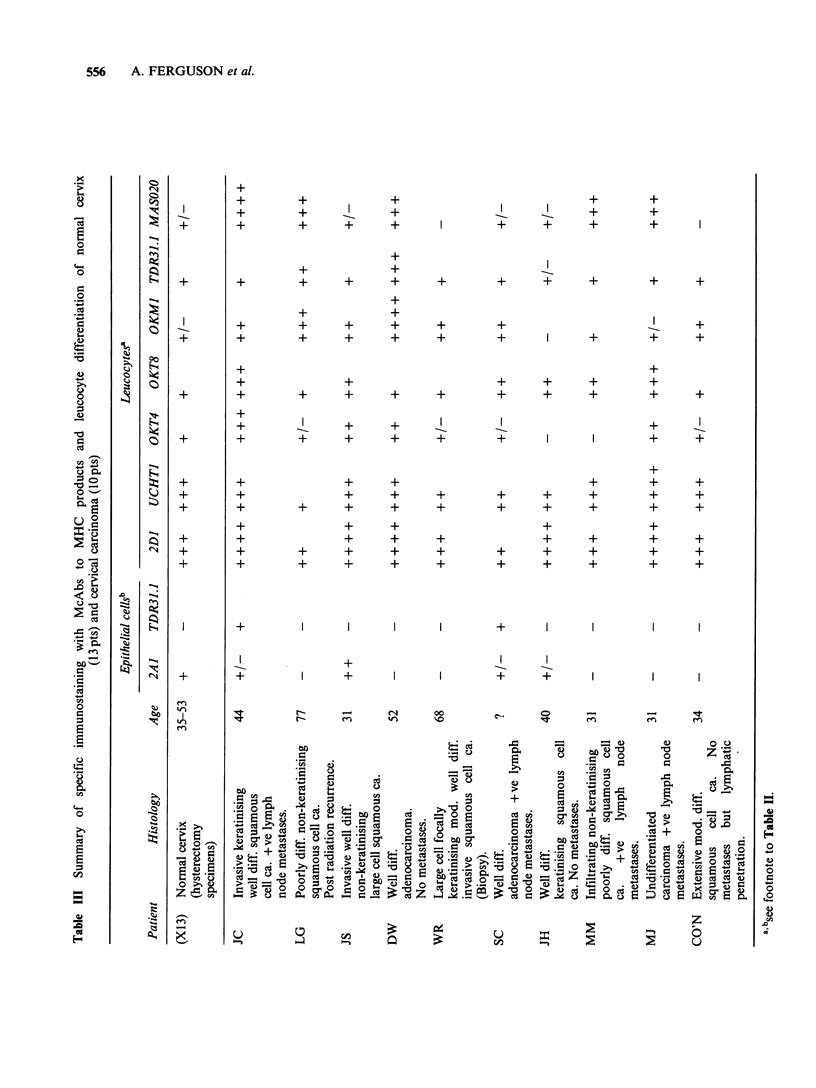
Monoclonal antibodies directed against monomorphic determinants of Class I and Class II products of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) and against leucocyte differentiation antigens were used in an indirect immunoperoxidase technique to compare their expression in normal and malignant disease of the ovary, cervix and endometrium. MHC Class I products, strongly expressed on normal ovarian epithelium, were uniformly absent from 7/8 ovarian carcinomas of varying histology. Lack of Class I expression was also a feature of 6/10 cervical carcinomas and of 4/8 endometrial carcinomas, in comparison with their respective normal tissues. Relative to normal tissue epithelium MHC Class II products, could be either lost or gained, the pattern of expression being either uniform or heterogeneous. Leucocytes were sparse in normal ovary but more numerous in cervix and endometrium. In tumours, with few exceptions, they were abundant, though usually confined to the stroma. T cells, largely of cytotoxic/suppressor (OKT8) phenotype, tended to predominate though in some tumours, particularly cervical carcinoma, large numbers of macrophages and to a lesser extent, B cells were sometimes detected. By contrast, leucocytes of natural killer (NK) phenotype were virtually non-existent in any tumour or normal tissue. The ingress of leucocytes into gynaecological neoplasms does not appear to be a random event and may be evoked by an immune response against tumour-associated antigens. However, the relationship between in situ mononuclear cell infiltration and MHC expression on epithelial tumour cells is complex and remains to be elucidated.
Full text
PDF


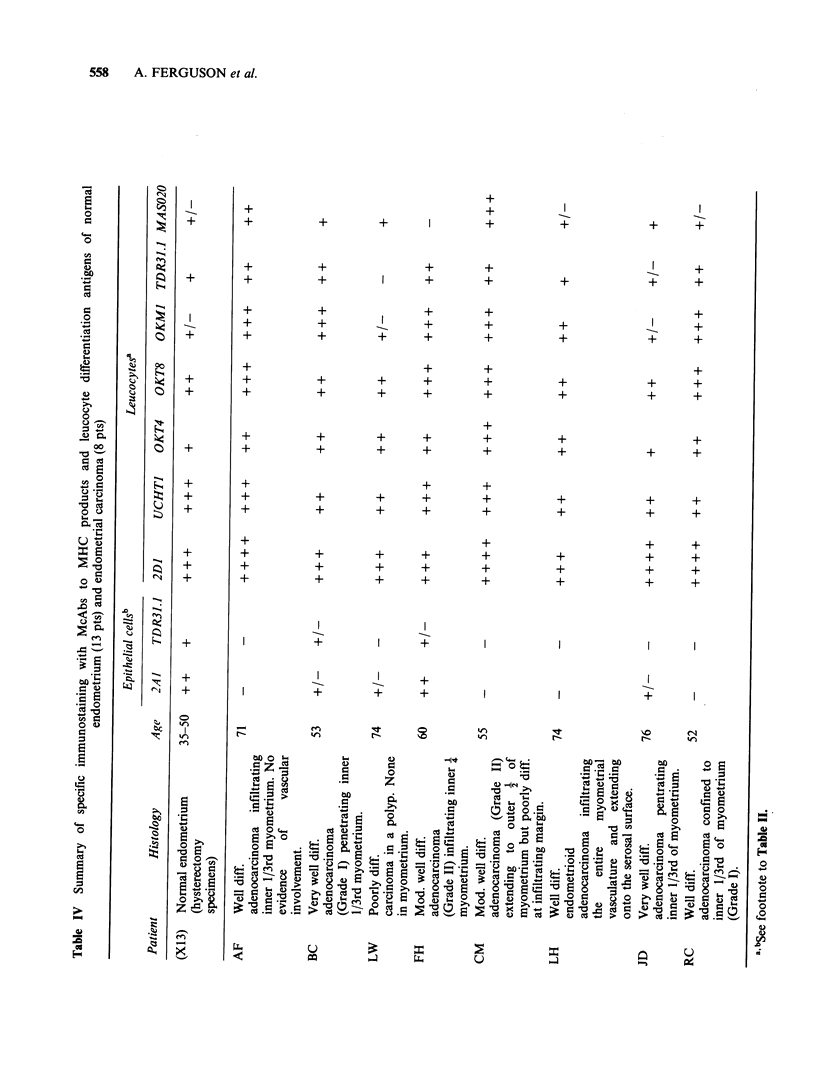
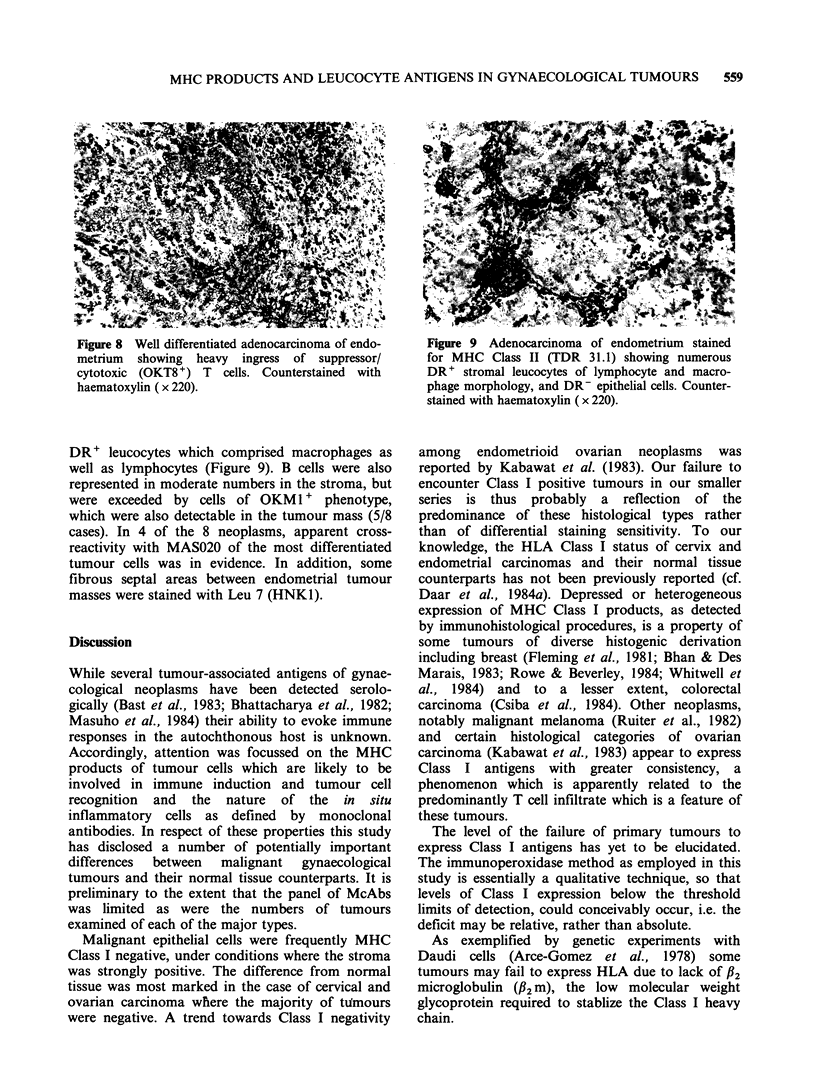




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abo T., Balch C. M. A differentiation antigen of human NK and K cells identified by a monoclonal antibody (HNK-1). J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):1024–1029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abo T., Cooper M. D., Balch C. M. Characterization of HNK-1+ (Leu-7) human lymphocytes. I. Two distinct phenotypes of human NK cells with different cytotoxic capability. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1752–1757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abo T., Cooper M. D., Balch C. M. Postnatal expansion of the natural killer and keller cell population in humans identified by the monoclonal HNK-1 antibody. J Exp Med. 1982 Jan 1;155(1):321–326. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.1.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arce-Gomez B., Jones E. A., Barnstable C. J., Solomon E., Bodmer W. F. The genetic control of HLA-A and B antigens in somatic cell hybrids: requirement for beta2 microglobulin. Tissue Antigens. 1978 Feb;11(2):96–112. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1978.tb01233.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bast R. C., Jr, Klug T. L., St John E., Jenison E., Niloff J. M., Lazarus H., Berkowitz R. S., Leavitt T., Griffiths C. T., Parker L. A radioimmunoassay using a monoclonal antibody to monitor the course of epithelial ovarian cancer. N Engl J Med. 1983 Oct 13;309(15):883–887. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198310133091503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beverley P. C., Linch D., Delia D. Isolation of human haematopoietic progenitor cells using monoclonal antibodies. Nature. 1980 Sep 25;287(5780):332–333. doi: 10.1038/287332a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhan A. K., DesMarais C. L. Immunohistologic characterization of major histocompatibility antigens and inflammatory cellular infiltrate in human breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1983 Sep;71(3):507–516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya M., Chatterjee S. K., Barlow J. J., Fuji H. Monoclonal antibodies recognizing tumor-associated antigen of human ovarian mucinous cystadenocarcinomas. Cancer Res. 1982 May;42(5):1650–1654. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodmer W. F. HLA structure and function: a contemporary view. Tissue Antigens. 1981 Jan;17(1):9–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1981.tb00661.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breard J., Reinherz E. L., Kung P. C., Goldstein G., Schlossman S. F. A monoclonal antibody reactive with human peripheral blood monocytes. J Immunol. 1980 Apr;124(4):1943–1948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callard R. E., Smith C. M., Worman C., Linch D., Cawley J. C., Beverley P. C. Unusual phenotype and function of an expanded subpopulation of T cells in patients with haemopoietic disorders. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Mar;43(3):497–505. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csiba A., Whitwell H. L., Moore M. Distribution of histocompatibility and leucocyte differentiation antigens in normal human colon and in benign and malignant colonic neoplasms. Br J Cancer. 1984 Nov;50(5):699–709. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1984.239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daar A. S., Fabre J. W. The membrane antigens of human colorectal cancer cells: demonstration with monoclonal antibodies of heterogeneity within and between tumours and of anomalous expression of HLA-DR. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1983 Feb;19(2):209–220. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(83)90419-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daar A. S., Fuggle S. V., Fabre J. W., Ting A., Morris P. J. The detailed distribution of HLA-A, B, C antigens in normal human organs. Transplantation. 1984 Sep;38(3):287–292. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198409000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daar A. S., Fuggle S. V., Fabre J. W., Ting A., Morris P. J. The detailed distribution of MHC Class II antigens in normal human organs. Transplantation. 1984 Sep;38(3):293–298. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198409000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Kretser T. A., Crumpton M. J., Bodmer J. G., Bodmer W. F. Two-dimensional gel analysis of the polypeptides precipitated by a polymorphic HLA-DR1,2,w6 monoclonal antibody: evidence for a third locus. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Jul;12(7):600–606. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830120713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eremin O., Coombs R. R., Ashby J. Lymphocytes infiltrating human breast cancers lack K-cell activity and show low levels of NK-cell activity. Br J Cancer. 1981 Aug;44(2):166–176. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1981.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming K. A., McMichael A., Morton J. A., Woods J., McGee J. O. Distribution of HLA class 1 antigens in normal human tissue and in mammary cancer. J Clin Pathol. 1981 Jul;34(7):779–784. doi: 10.1136/jcp.34.7.779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerry D., 4th, Alexander M. A., Herlyn M. F., Zehngebot L. M., Mitchell K. F., Zmijewski C. M., Lusk E. J. HLA-DR histocompatibility leukocyte antigens permit cultured human melanoma cells from early but not advanced disease to stimulate autologous lymphocytes. J Clin Invest. 1984 Jan;73(1):267–271. doi: 10.1172/JCI111201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haskill S., Koren H., Becker S., Fowler W., Walton L. Mononuclear-cell infiltration in ovarian cancer. II. Immune function of tumour and ascites-derived inflammatory cells. Br J Cancer. 1982 May;45(5):737–746. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1982.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haskill S., Koren H., Becker S., Fowler W., Walton L. Mononuclear-cell infiltration in ovarian cancer. III. Suppressor-cell and ADCC activity of macrophages from ascitic and solid ovarian tumours. Br J Cancer. 1982 May;45(5):747–753. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1982.116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Introna M., Allavena P., Biondi A., Colombo N., Villa A., Mantovani A. Defective natural killer activity within human ovarian tumors: low numbers of morphologically defined effectors present in situ. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1983 Jan;70(1):21–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ioachim H. L. The stromal reaction of tumors: an expression of immune surveillance. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1976 Sep;57(3):465–475. doi: 10.1093/jnci/57.3.465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabawat S. E., Bast R. C., Jr, Welch W. R., Knapp R. C., Bhan A. K. Expression of major histocompatibility antigens and nature of inflammatory cellular infiltrate in ovarian neoplasms. Int J Cancer. 1983 Nov 15;32(5):547–554. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910320505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klareskog L., Forsum U., Peterson P. A. Hormonal regulation of the expression of Ia antigens on mammary gland epithelium. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Dec;10(12):958–963. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830101212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ko H. S., Fu S. M., Winchester R. J., Yu D. T., Kunkel H. G. Ia determinants on stimulated human T lymphocytes. Occurrence on mitogen- and antigen-activated T cells. J Exp Med. 1979 Aug 1;150(2):246–255. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.2.246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kung P., Goldstein G., Reinherz E. L., Schlossman S. F. Monoclonal antibodies defining distinctive human T cell surface antigens. Science. 1979 Oct 19;206(4416):347–349. doi: 10.1126/science.314668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampert I. A., Suitters A. J., Chisholm P. M. Expression of Ia antigen on epidermal keratinocytes in graft-versus-host disease. Nature. 1981 Sep 10;293(5828):149–150. doi: 10.1038/293149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Londei M., Lamb J. R., Bottazzo G. F., Feldmann M. Epithelial cells expressing aberrant MHC class II determinants can present antigen to cloned human T cells. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):639–641. doi: 10.1038/312639a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason D. W., Dallman M., Barclay A. N. Graft-versus-host disease induces expression of Ia antigen in rat epidermal cells and gut epithelium. Nature. 1981 Sep 10;293(5828):150–151. doi: 10.1038/293150a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuho Y., Zalutsky M., Knapp R. C., Bast R. C., Jr Interaction of monoclonal antibodies with cell surface antigens of human ovarian carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1984 Jul;44(7):2813–2819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCluskey D. R., Roy A. D., Abram W. P., Martin W. M. T lymphocyte subsets in the peripheral blood of patients with benign and malignant breast disease. Br J Cancer. 1983 Feb;47(2):307–309. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1983.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMichael A. HLA restriction of human cytotoxic T lymphocytes specific for influenza virus. Poor recognition of virus associated with HLA A2. J Exp Med. 1978 Dec 1;148(6):1458–1467. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.6.1458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M., Vose B. M. Extravascular natural cytotoxicity in man: Anti-K562 activity of lymph-node and tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes. Int J Cancer. 1981 Mar 15;27(3):265–272. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910270303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortaldo J. R., Sharrow S. O., Timonen T., Herberman R. B. Determination of surface antigens on highly purified human NK cells by flow cytometry with monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2401–2409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perussia B., Acuto O., Terhorst C., Faust J., Lazarus R., Fanning V., Trinchieri G. Human natural killer cells analyzed by B73.1, a monoclonal antibody blocking Fc receptor functions. II. Studies of B73.1 antibody-antigen interaction on the lymphocyte membrane. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2142–2148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perussia B., Starr S., Abraham S., Fanning V., Trinchieri G. Human natural killer cells analyzed by B73.1, a monoclonal antibody blocking Fc receptor functions. I. Characterization of the lymphocyte subset reactive with B73.1. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2133–2141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizzolo G., Semenzato G., Chilosi M., Morittu L., Ambrosetti A., Warner N., Bofill M., Janossy G. Distribution and heterogeneity of cells detected by HNK-1 monoclonal antibody in blood and tissues in normal, reactive and neoplastic conditions. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Jul;57(1):195–206. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Kung P. C., Goldstein G., Schlossman S. F. A monoclonal antibody reactive with the human cytotoxic/suppressor T cell subset previously defined by a heteroantiserum termed TH2. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1301–1307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Kung P. C., Goldstein G., Schlossman S. F. A monoclonal antibody with selective reactivity with functionally mature human thymocytes and all peripheral human T cells. J Immunol. 1979 Sep;123(3):1312–1317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Kung P. C., Goldstein G., Schlossman S. F. Further characterization of the human inducer T cell subset defined by monoclonal antibody. J Immunol. 1979 Dec;123(6):2894–2896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rognum T. O., Brandtzaeg P., Thorud E. Is heterogeneous expression of HLA-dr antigens and CEA along with DNA-profile variations evidence of phenotypic instability and clonal proliferation in human large bowel carcinomas? Br J Cancer. 1983 Oct;48(4):543–551. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1983.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe D. J., Beverley P. C. Characterisation of breast cancer infiltrates using monoclonal antibodies to human leucocyte antigens. Br J Cancer. 1984 Feb;49(2):149–159. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1984.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiter D. J., Bhan A. K., Harrist T. J., Sober A. J., Mihm M. C., Jr Major histocompatibility antigens and mononuclear inflammatory infiltrate in benign nevomelanocytic proliferations and malignant melanoma. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2808–2815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selby W. S., Janossy G., Mason D. Y., Jewell D. P. Expression of HLA-DR antigens by colonic epithelium in inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Sep;53(3):614–618. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. J., Herlyn M. F., Elder D. E., Clark W. H., Steplewski Z., Koprowski H. Expression of DR antigens in freshly frozen human tumors. Hybridoma. 1982;1(2):161–168. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1.1982.1.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Underwood J. C. Lymphoreticular infiltration in human tumours: prognostic and biological implications: a review. Br J Cancer. 1974 Dec;30(6):538–548. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1974.233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vose B. M., Moore M. Human tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes: a marker of host response. Semin Hematol. 1985 Jan;22(1):27–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vose B. M., Moore M. Suppressor cell activity of lymphocytes infiltrating human lung and breast tumours. Int J Cancer. 1979 Nov 15;24(5):579–585. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910240510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe S., Sato Y., Kodama T., Shimosato Y. Immunohistochemical study with monoclonal antibodies on immune response in human lung cancers. Cancer Res. 1983 Dec;43(12 Pt 1):5883–5889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitwell H. L., Hughes H. P., Moore M., Ahmed A. Expression of major histocompatibility antigens and leucocyte infiltration in benign and malignant human breast disease. Br J Cancer. 1984 Feb;49(2):161–172. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1984.28. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries J. E., Spits H. Cloned human cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) lines reactive with autologous melanoma cells. I. In vitro generation, isolation, and analysis to phenotype and specificity. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):510–519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]