Abstract
After giving oral frusemide (Lasix) to 14 normal volunteers significant hypercalciuria occurred in all of them. This could not be accounted for by any change in glomerular filtration rate, but was possibly due to decreased tubular reabsorption.
Full text
PDF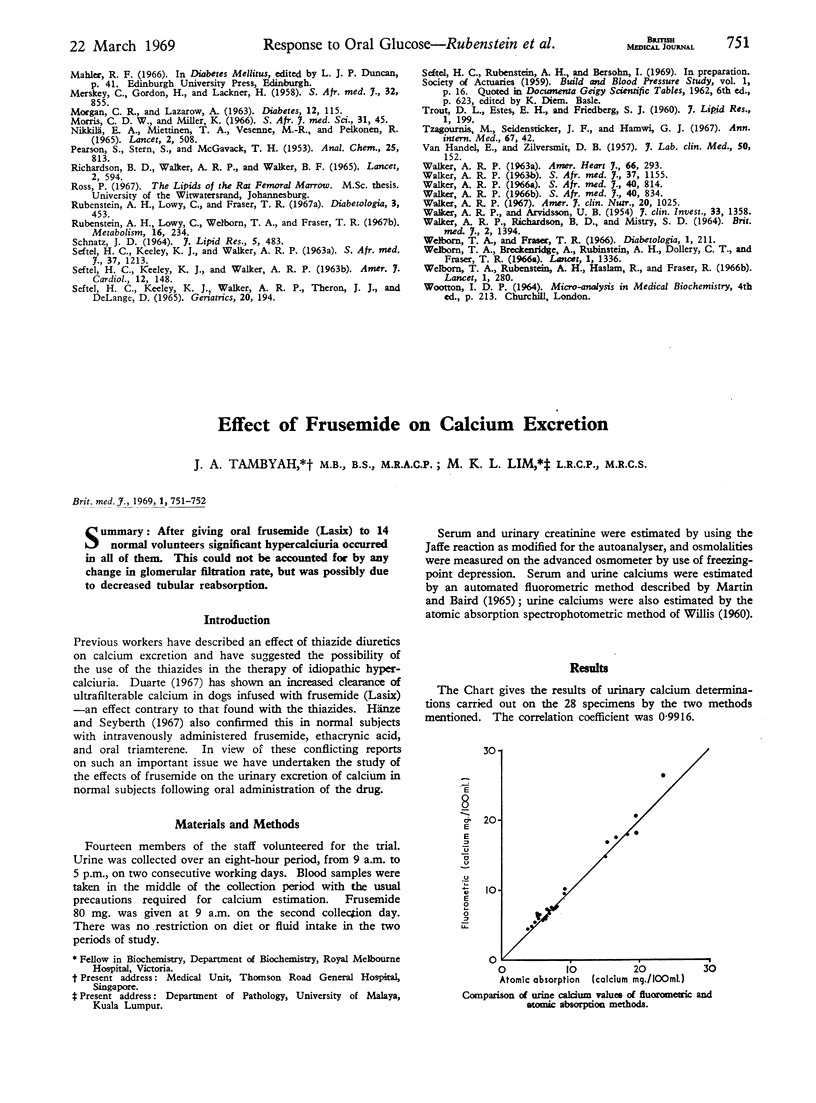

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hänze S., Seyberth H. Untersuchungen zur Wirkung der Diuretica Furosemid, Etacrynsäure und Triamteren auf die renale Magnesium- und Calciumaussecheidung. Klin Wochenschr. 1967 Mar 15;45(6):313–314. doi: 10.1007/BF01747104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAMBERG B. A., KUHLBACK B. Effect of chlorothiazide and hydrochlorothiazide on the excretion of calcium in urine. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1959;11:351–357. doi: 10.3109/00365515909060464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN T. J., BAIRD C. W. SERUM CALCIUM DETERMINATION BY FLUOROMETRY. Med J Aust. 1965 Mar 27;1(13):463–465. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1965.tb71819.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordin B. E., Hodgkinson A., Peacock M. The measurement and the meaning of urinary calcium. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1967 May-Jun;52:293–322. doi: 10.1097/00003086-196700520-00023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLF A. V., BALL S. M. Effect of intravenous sodium sulfate on renal excretion in the dog. Am J Physiol. 1950 Feb;160(2):353–360. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1950.160.2.353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


