Abstract
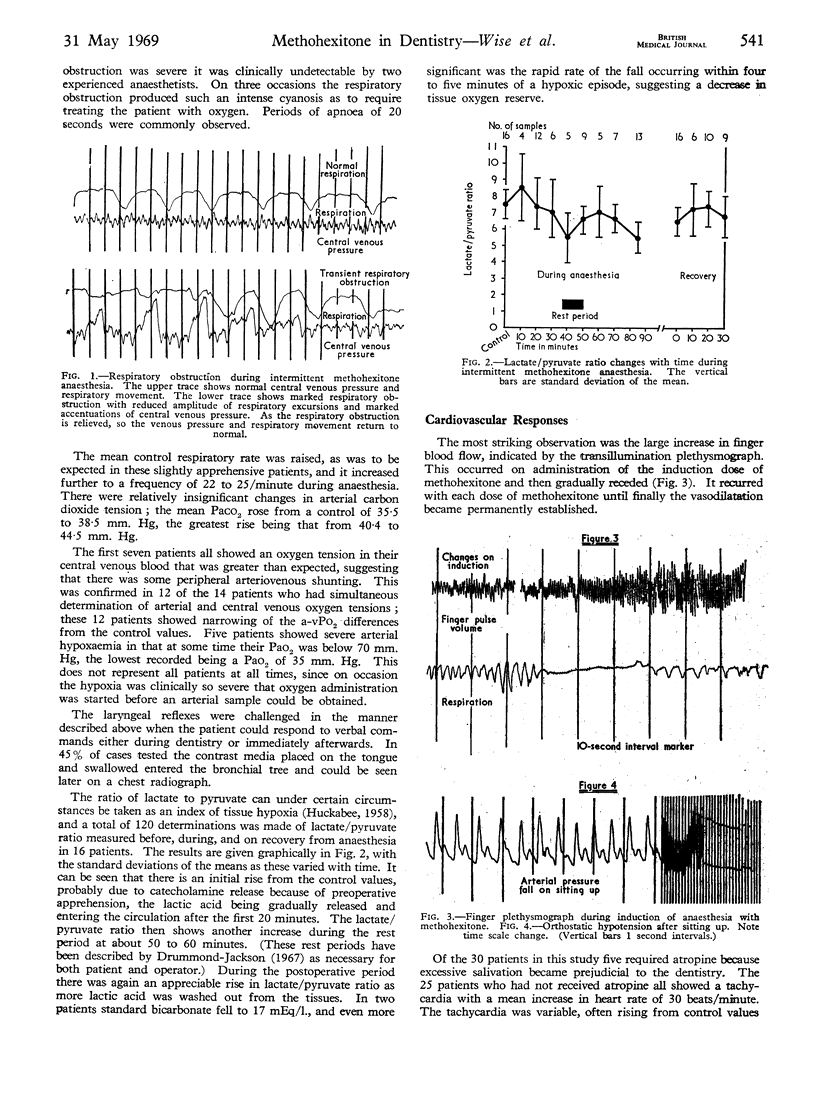
Intermittent methohexitone for conservative dentistry has been shown to cause clinically undetectable respiratory obstruction, depression of the laryngeal reflex, and arterial hypoxaemia. Because of the pronounced decrease in total peripheral resistance, the blood pressure was maintained only by large increases in cardiac output. Furthermore, the output of the heart could not increase when challenged by hypoxia.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- FISHMAN A. P., FRITTS H. W., Jr, COURNAND A. Effects of acute hypoxia and exercise on the pulmonary circulation. Circulation. 1960 Aug;22:204–215. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.22.2.204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLOSTER J. A., HARRIS P. Observations on an enzymic method for the estimation of pyruvate in blood. Clin Chim Acta. 1962 Mar;7:206–211. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(62)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUCKABEE W. E. Relationships of pyruvate and lactate during anaerobic metabolism. I. Effects of infusion of pyruvate or glucose and of hyperventilation. J Clin Invest. 1958 Feb;37(2):244–254. doi: 10.1172/JCI103603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowlands D. J., Howitt G., Logan W. F., Clarke A. D., Jackson P. W. Haemodynamic changes during methohexitone anaesthesia in patients with supraventricular arrhythmias. Br J Anaesth. 1967 Jul;39(7):554–560. doi: 10.1093/bja/39.7.554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlin P. J., Howarth F. H., Robinson J. S. Postoperative atelectasis and laryngeal incompetence. Lancet. 1968 Jun 29;1(7557):1402–1405. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)91978-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


