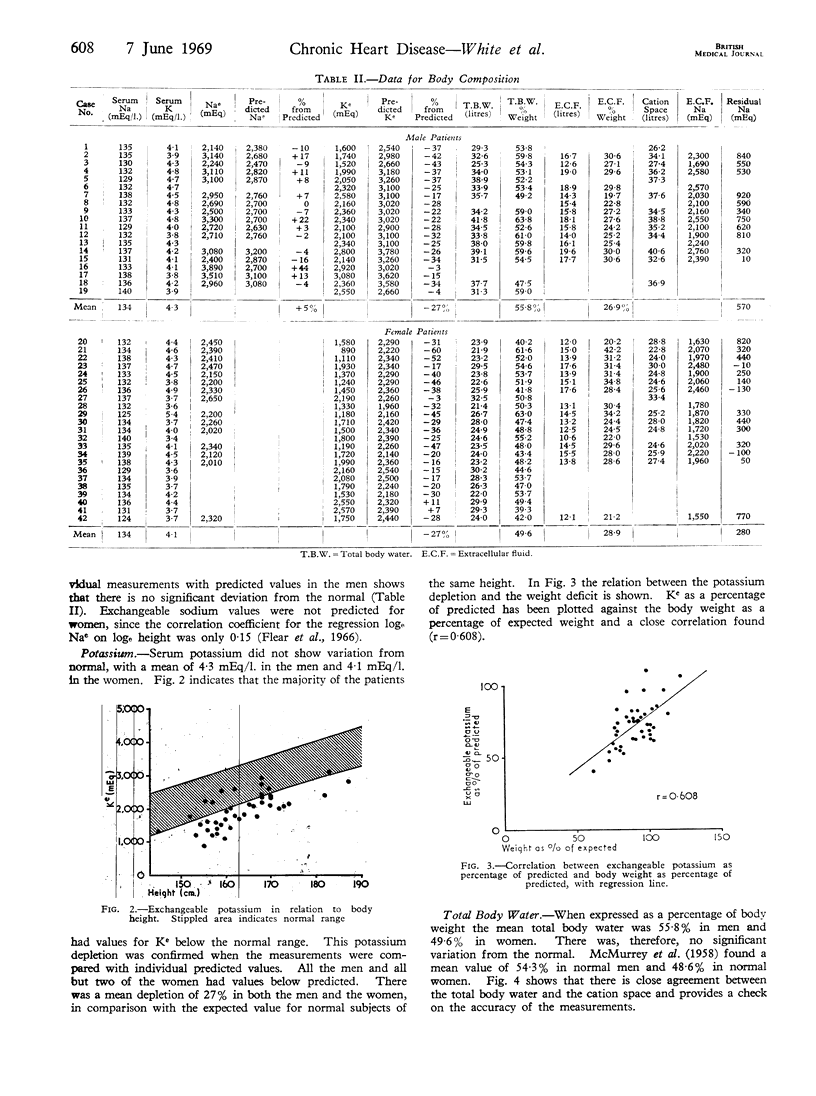
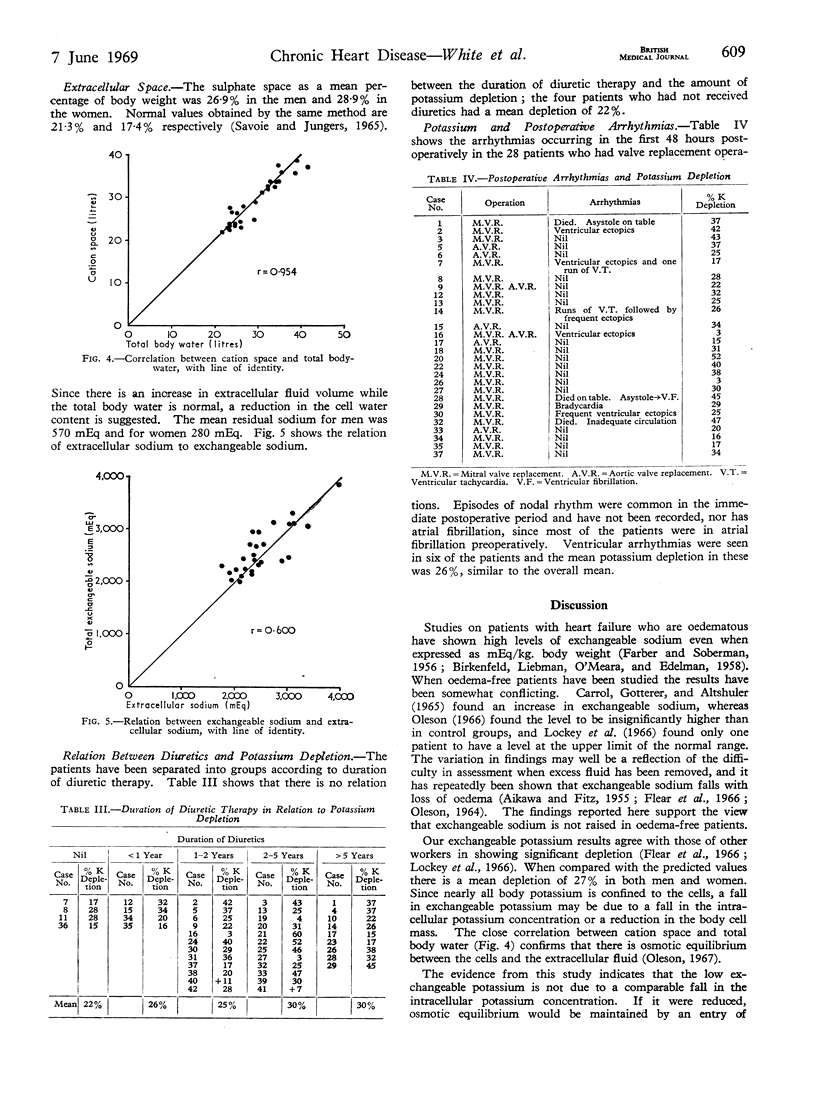
Abstract
Exchangeable sodium and potassium, total body water, and sulphate space were measured in 42 patients with severe valvular heart disease who were free of oedema. Compared with normal subjects of the same height, no increase in exchangeable sodium was found but a mean potassium depletion of 27% was shown. This depletion was not related to diuretic therapy, and no relationship between the degree of depletion and postoperative arrhythmias was found. It is concluded that the major cause of the low exchangeable potassium is the reduction in cell mass that occurs in chronic heart disease, and that there is no significant fall in the intracellular potassium concentration.
Full text
PDF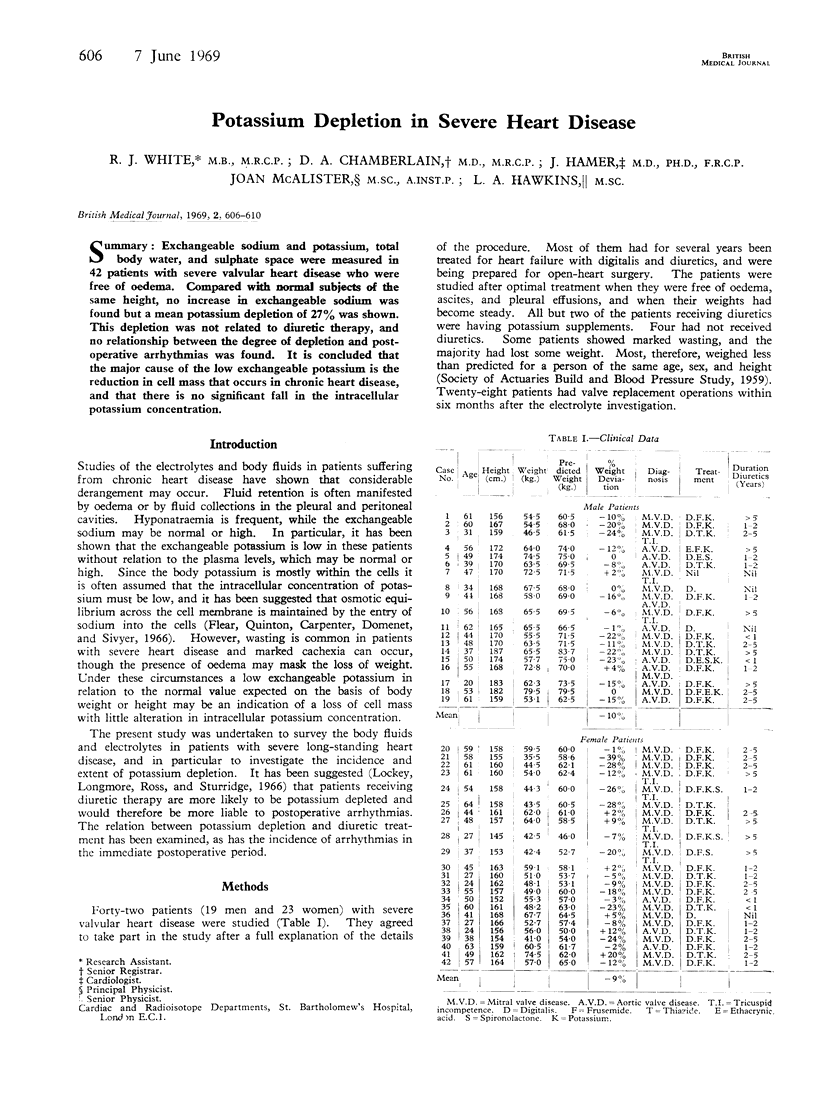


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AIKAWA J. K., FITZ R. H. Alterations in exchangeable sodium content, "sodium 24 space" and body weight during the treatment of congestive failure. Circulation. 1955 Nov;12(5):897–902. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.12.5.897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIRKENFELD L. W., LEIBMAN J., O'MEARA M. P., EDELMAN I. S. Total exchangeable sodium, total exchangeable potassium, and total body water in edematous patients with cirrhosis of the liver and congestive heart failure. J Clin Invest. 1958 May;37(5):687–698. doi: 10.1172/JCI103655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beilin L. J., Knight G. J., Munro-Faure A. D., Anderson J. The sodium, potassium, and water contents of red blood cells of healthy human adults. J Clin Invest. 1966 Nov;45(11):1817–1825. doi: 10.1172/JCI105485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARROLL H. J., GOTTERER R., ALTSHULER B. EXCHANGEABLE SODIUM, BODY POTASSIUM, AND BODY WATER IN PREVIOUSLY EDEMATOUS CARDIAC PATIENTS: EVIDENCE FOR OSMOTIC INACTIVATION OF CATION. Circulation. 1965 Aug;32:185–192. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.32.2.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROOKS J., BLUHM M. M., MULDOWNEY F. P. The interrelation between total exchangeable sodium, potassium and chloride, and lean body mass in man. Clin Sci. 1959 May;18:175–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman I. S., Olney J. M., James A. H., Brooks L., Moore F. D. Body Composition: Studies in the Human Being by the Dilution Principle. Science. 1952 Apr 25;115(2991):447–454. doi: 10.1126/science.115.2991.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARBER S. J., SOBERMAN R. J. Total body water and total exchangeable sodium in edematous states due to cardiac, renal or hepatic disease. J Clin Invest. 1956 Jul;35(7):779–791. doi: 10.1172/JCI103330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLEAR C. T., CRAMPTON R. F., MATTHEWS D. M. Observations on the electrolyte and water composition of skeletal muscle in patients in congestive cardiac failure, using an in vitro method for determination of inulin space. Clin Sci. 1961 Dec;21:381–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flear C. T., Quinton A., Carpenter R. G., Domenet J. G., Sivyer A. Exchangeable body potassium and sodium in patients in congestive heart failure. Clin Chim Acta. 1966 Jan;13(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(66)90258-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockey E., Ross D. N., Longmore D. B., Sturridge M. F. Potassium and open-heart surgery. Lancet. 1966 Mar 26;1(7439):671–675. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)91625-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACGILLIVRAY I., BUCHANAN T. J., BILLEWICZ W. Z. Values of total exchangeable sodium and potassium in normal females based on weight, height and age. Clin Sci. 1960 Feb;19:17–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER H., WILSON G. M. The measurement of exchangeable sodium in man using the isotope 24Na. Clin Sci. 1953 May;12(2):97–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMURREY J. D., BOLING E. A., DAVIS J. M., PARKER H. V., MAGNUS I. C., BALL M. R., MOORE F. D. Body composition: simultaneous determination of several aspects by the dilution principle. Metabolism. 1958 Sep;7(5):651–667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLESEN K. H. BODY COMPOSITION IN HEART DISEASE. TOTAL EXCHANGEABLE POTASSIUM, TOTAL EXCHANGEABLE SODIUM, TOTAL EXCHANGEABLE CHLORIDE AND DERIVED VALUES FOR BODY COMPOSITION IN CARDIAC DISEASE WITH AND WITHOUT EDEMA. Acta Med Scand. 1964 Mar;175:301–324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olesen K. H. Interrelations between total exchangeable sodium, potassium, body water, and serum sodium and potassium concentrations in hyponatremic and normonatremic heart disease. Circulation. 1967 May;35(5):895–903. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.35.5.895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olesen K. H. Total exchangeable sodium in previously edematous cardiac patients. Is there evidence for osmotic inactivation of sodium? Circulation. 1966 Aug;34(2):322–330. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.34.2.322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHMOND J. E., HASTINGS A. B. Distribution of sulfate in blood and between cerebrospinal fluid and plasma in vivo. Am J Physiol. 1960 Nov;199:814–820. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1960.199.5.814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWAN R. C., FEINSTEIN H. M., MADISSO H. Distribution of sulfate ion across semi-permeable membranes. J Clin Invest. 1956 Jun;35(6):607–610. doi: 10.1172/JCI103315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


