Abstract
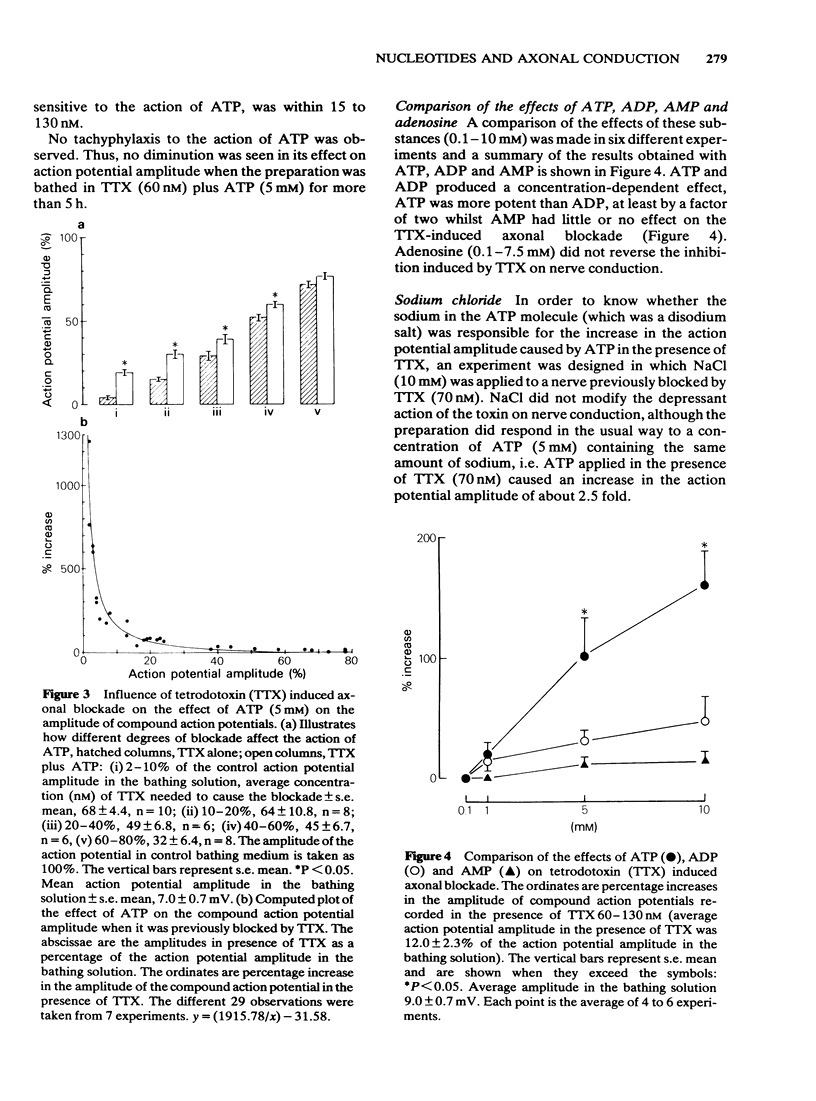
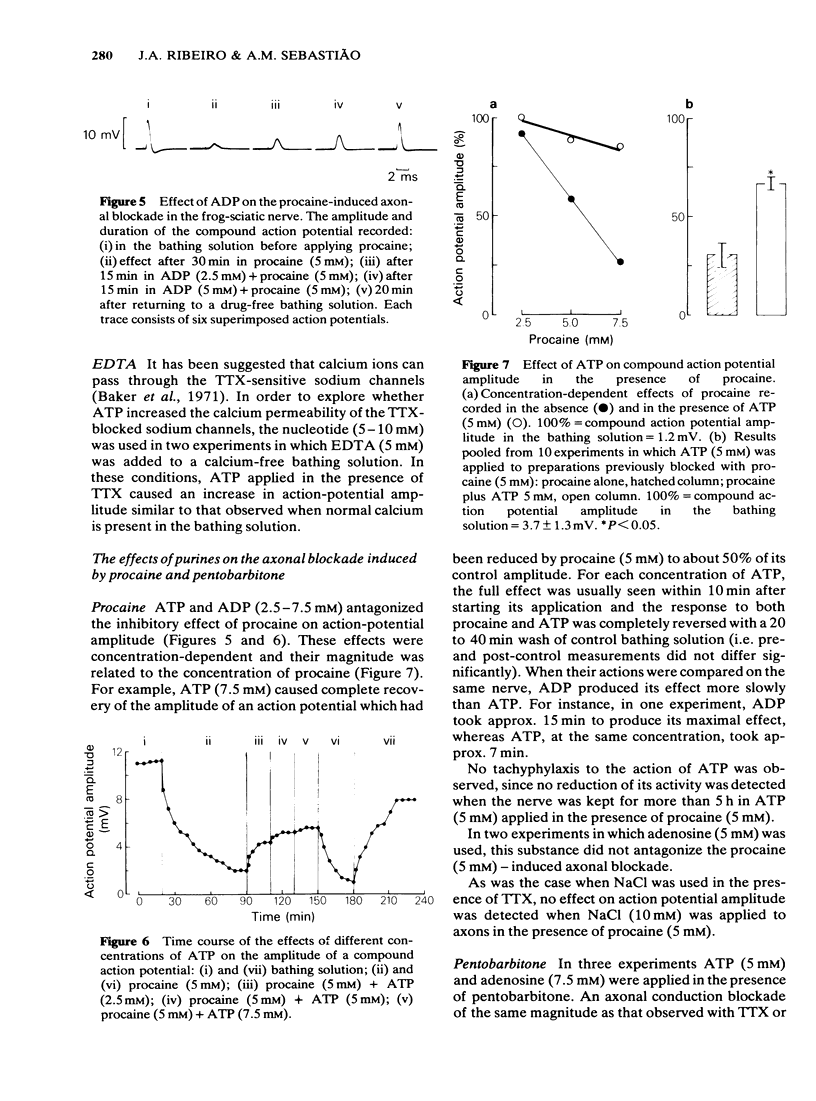
The effects of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), adenosine diphosphate (ADP), adenosine monophosphate (AMP), and adenosine on compound action potentials were investigated in de-sheathed frog-sciatic nerve preparations. ATP and ADP but not adenosine antagonized the inhibitory action of tetrodotoxin (TTX) on nerve conduction. AMP had little or no antagonistic effect on TTX-induced axonal block. ATP was more effective than ADP. The effects of the nucleotides were related to the degree of the TTX-induced inhibition and were more evident where the blockade was more intense. ATP and ADP but not adenosine antagonized the procaine-induced axonal blockade which, in some experiments, was completely reversed by these nucleotides. ATP and ADP were of similar potency. The axonal blockade induced by pentobarbitone was not antagonized by ATP, ADP, AMP or adenosine. The possibility that ATP stimulates a TTX-sensitive sodium channel is discussed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABOOD L. G., KOKETSU K., MIYAMOTO S. Outflux of various phosphates during membrane depolarization of excitable tissues. Am J Physiol. 1962 Mar;202:469–474. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1962.202.3.469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akasu T., Hirai K., Koketsu K. Increase of acetylcholine-receptor sensitivity by adenosine triphosphate: a novel action of ATP on ACh-sensitivity. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Oct;74(2):505–507. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb09997.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BISHOP H., FRAZER A. C., ROBINSON G. B., SCHNEIDER R. THE NATURE OF THE ANTIPERISTALTIC FACTOR FROM WHEAT GLUTEN. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1963 Oct;21:238–243. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1963.tb01522.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Hodgkin A. L., Ridgway E. B. Depolarization and calcium entry in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1971 Nov;218(3):709–755. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P., Goldman D. E. Competitive action of calcium and procaine on lobster axon. A study of the mechanism of action of certain local anesthetics. J Gen Physiol. 1966 May;49(5):1043–1063. doi: 10.1085/jgp.49.5.1043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn I. M. Membrane adenosine triphosphatase and cation transport. Br Med Bull. 1968 May;24(2):165–169. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUPERMAN A. S., VOLPERT W. A., OKAMOTO M. RELEASE OF ADENINE NUCLEOTIDE FROM NERVE AXONS. Nature. 1964 Dec 5;204:1000–1001. doi: 10.1038/2041000a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmich G. A., Randles J. An ATP- and Ca2+-regulated Na+ channel in isolated intestinal epithelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1982 Sep;243(3):C116–C123. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1982.243.3.C116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraynack B. J., Gintautas J., Racz G. B. Antagonism of procaine conduction block by adenosine 5' triphosphate in vitro. Proc West Pharmacol Soc. 1980;23:429–432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NARAHASHI T., MOORE J. W., SCOTT W. R. TETRODOTOXIN BLOCKAGE OF SODIUM CONDUCTANCE INCREASE IN LOBSTER GIANT AXONS. J Gen Physiol. 1964 May;47:965–974. doi: 10.1085/jgp.47.5.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OKAMOTO M., ASKARI A., KUPERMAN A. S. THE STABILIZING ACTIONS OF ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATE AND RELATED NUCLEOTIDES ON CALCIUM-DEFICIENT NERVE. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1964 May;144:229–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro J. A., Dominguez M. L., Gonçalves M. J. Purine effects at the neuromuscular junction and their modification by theophylline, imidazole and verapamil. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1979 Apr;238(2):206–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro J. A., Dominguez M. L. Mechanisms of depression of neuromuscular transmission by ATP and adenosine. J Physiol (Paris) 1978;74(5):491–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro J. A. The decrease of neuromuscular transmission by adenosine depends on previous neuromuscular depression. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1982 Jan;255(1):59–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone T. W. Physiological roles for adenosine and adenosine 5'-triphosphate in the nervous system. Neuroscience. 1981;6(4):523–555. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90145-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


