Abstract
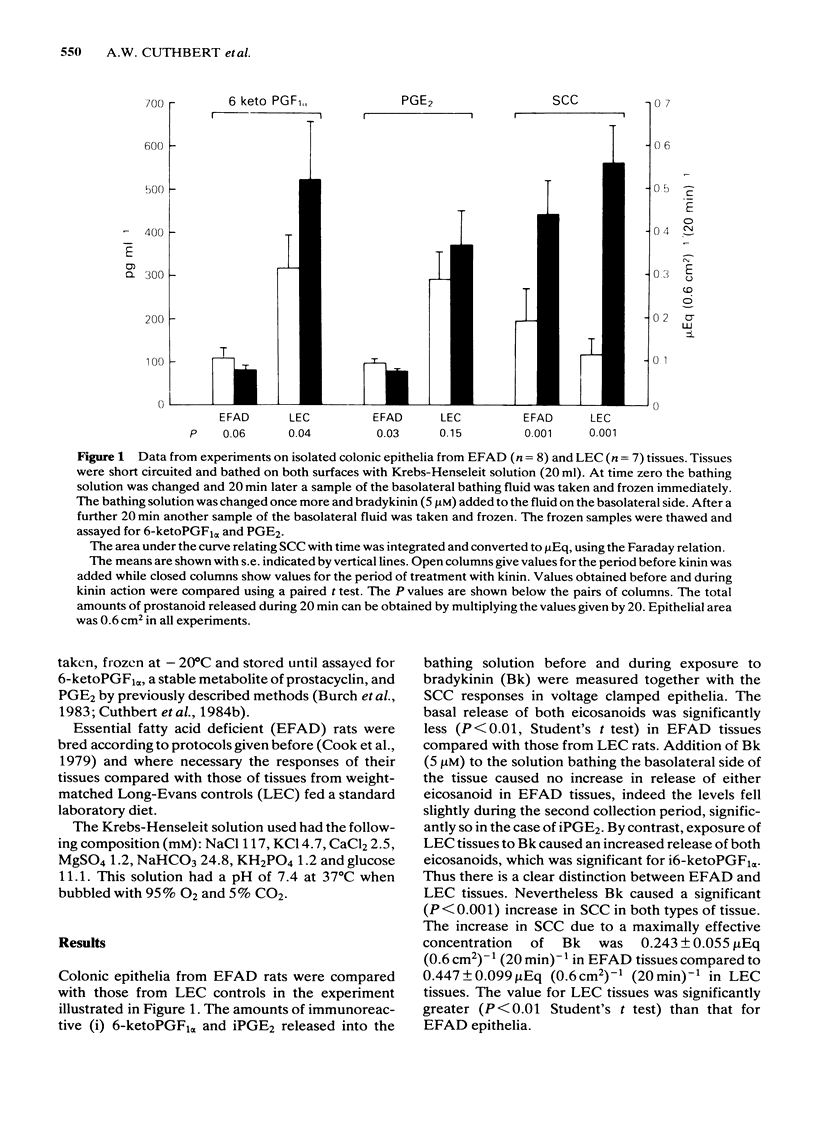
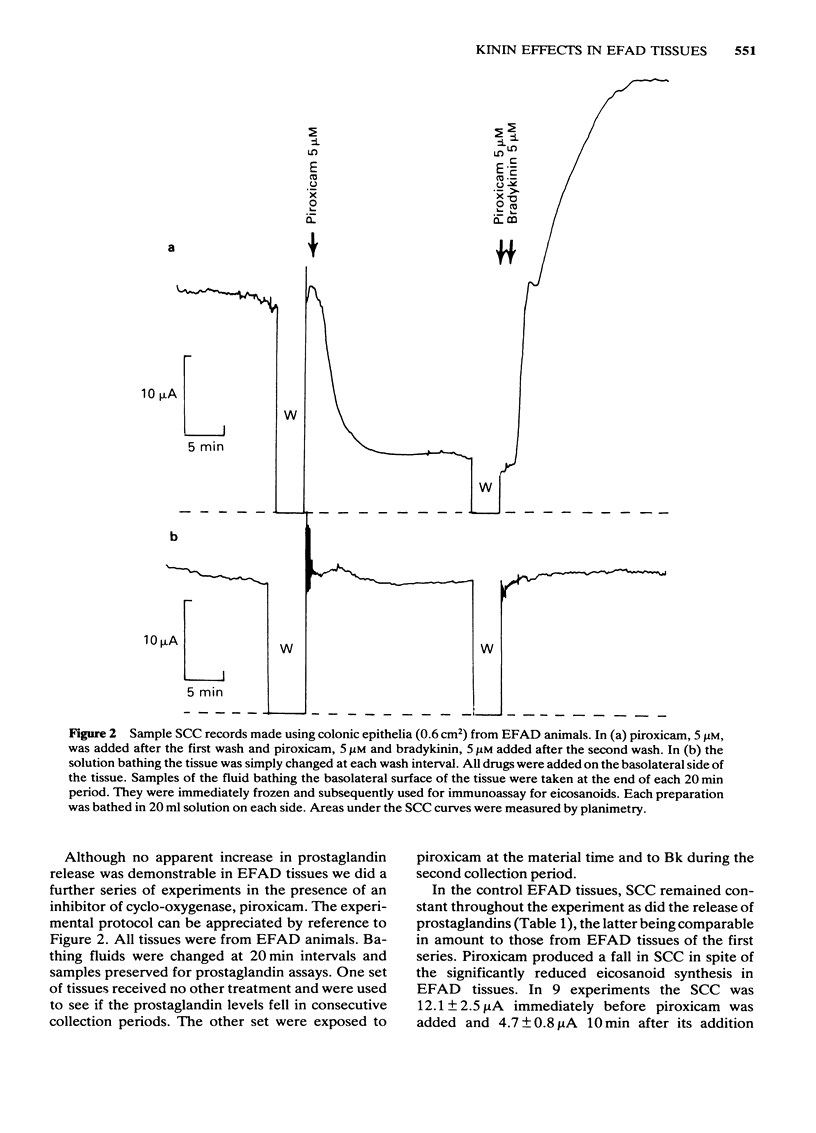
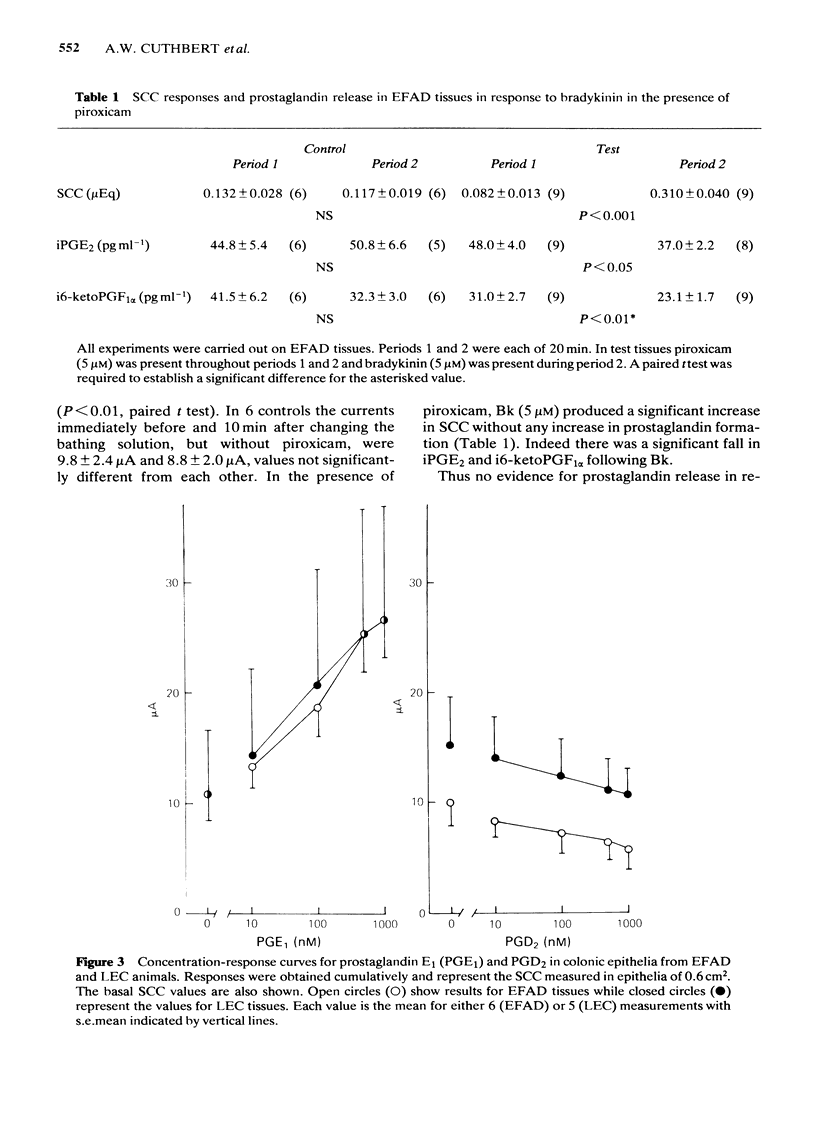
The actions of bradykinin on colonic epithelia from essential fatty acid-deficient (EFAD) rats has been examined. Electrogenic chloride secretion as short circuit current (SCC) and release of immunoreactive prostaglandin E2 (iPGE2) and i 6-keto PGF1 alpha have been measured. Resting release of prostanoids was significantly less in EFAD than in control tissues. Bradykinin, in a maximally effective concentration, produced no increase in prostanoid release in EFAD tissues in contrast to controls, while the SCC response was 55% of that in controls. In EFAD tissues the SCC response to bradykinin was the same whether or not the cyclooxygenase inhibitor piroxicam was present. EFAD tissues were not more sensitive to prostaglandins than control tissues. We conclude that while prostaglandin release contributes to the totality of the response to bradykinin, the latter's effect on electrogenic chloride secretion does not require the obligatory production of arachidonic acid metabolites.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bukhave K., Rask-Madsen J. Saturation kinetics applied to in vitro effects of low prostaglandin E2 and F 2 alpha concentrations on ion transport across human jejunal mucosa. Gastroenterology. 1980 Jan;78(1):32–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch R. M., Wise W. C., Halushka P. V. Prostaglandin-independent inhibition of calcium transport by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: differential effects of carboxylic acids and piroxicam. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Oct;227(1):84–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook J. A., Wise W. C., Callihan C. S. Resistance of essential fatty acid-deficient rats to endotoxic shock. Circ Shock. 1979;6(4):333–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuthbert A. W., Halushka P. V., Margolius H. S., Spayne J. A. Mediators of the secretory response to kinins. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Jul;82(3):597–607. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb10798.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuthbert A. W., Halushka P. V., Margolius H. S., Spayne J. A. Role of calcium ions in kinin-induced chloride secretion. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Jul;82(3):587–595. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb10797.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuthbert A. W., Margolius H. S. Kinins stimulate net chloride secretion by the rat colon. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Apr;75(4):587–598. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb09178.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frizzell R. A. Active chloride secretion by rabbit colon: calcium-dependent stimulation by ionophore A23187. J Membr Biol. 1977 Jun 30;35(2):175–187. doi: 10.1007/BF01869948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning D. C., Snyder S. H., Kachur J. F., Miller R. J., Field M. Bradykinin receptor-mediated chloride secretion in intestinal function. Nature. 1982 Sep 16;299(5880):256–259. doi: 10.1038/299256a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musch M. W., Kachur J. F., Miller R. J., Field M., Stoff J. S. Bradykinin-stimulated electrolyte secretion in rabbit and guinea pig intestine. Involvement of arachidonic acid metabolites. J Clin Invest. 1983 May;71(5):1073–1083. doi: 10.1172/JCI110857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musch M. W., Miller R. J., Field M., Siegel M. I. Stimulation of colonic secretion by lipoxygenase metabolites of arachidonic acid. Science. 1982 Sep 24;217(4566):1255–1256. doi: 10.1126/science.6810465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


