Abstract
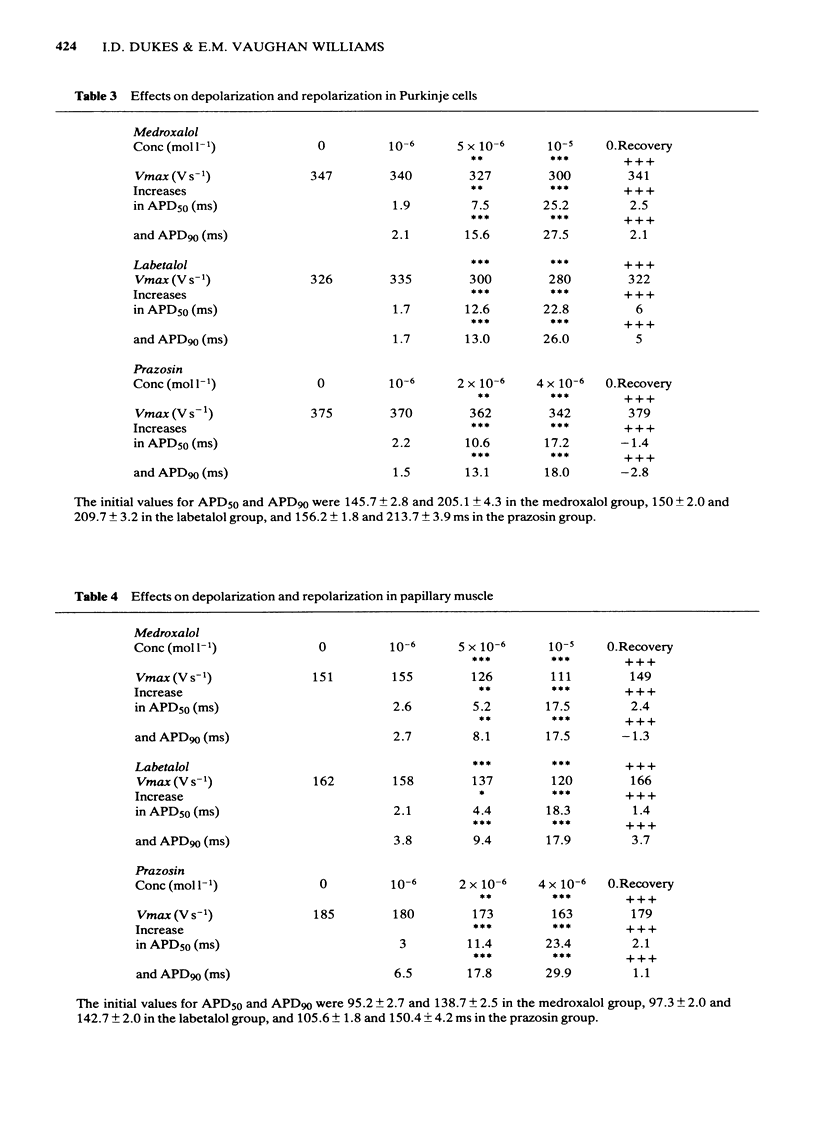
The effects of prazosin, labetalol, and medroxalol were studied in the rabbit sino-atrial node, Purkinje cells and papillary muscles. At concentrations producing similar bradycardia, labetalol and medroxalol reduced the maximum rate of depolarization (Vmax) and overshoot potential in the sinus node. Prazosin had no such effects. These large and highly significant reductions in Vmax and overshoot in sinus node cells were observed at concentrations of medroxalol and labetalol which had no negative inotropic effect. If depolarization in the sinus node was due to the second inward current, this would imply that such currents in the sinus node and contracting cardiac muscle are pharmacologically distinct. All three drugs prolonged action potential duration in the sinus node, Purkinje cells and papillary muscles in a dose-related manner. Recovery after 1 h in drug-free solution from the effects of medroxalol and labetalol was only partial in the sinus node, but almost complete in Purkinje cells and papillary muscle. Recovery from prazosin was complete in all tissues. All three drugs depressed Vmax in Purkinje cells and papillary muscles in a dose-related manner, and recovery was complete. It is concluded that all three drugs had class 1 and class 3 antiarrhythmic actions, which could contribute to their protective effects in ischaemia and reperfusion independently of blockade of myocardial alpha-adrenoceptors.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dage R. C., Cheng H. C., Woodward J. K. Cardiovascular properties of medroxalol, a new antihypertensive drug. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1981 Mar-Apr;3(2):299–315. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198103000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dage R. C., Hsieh C. P., Spedding M. Vasodilation by medroxalol mediated by beta 2-adrenergic receptor stimulation. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1983 Jan-Feb;5(1):143–150. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198301000-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millar J. S., Vaughan Williams E. M. Differential actions on rabbit nodal, atrial, Purkinje cell and ventricular potentials of melperone, a bradycardic agent delaying repolarization: effects of hypoxia. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Jan;75(1):109–121. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb08763.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen M. R., Gelband H., Hoffman B. F. Effects of phentolamine on electrophysiologic properties of isolated canine purkinje fibers. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1971 Dec;179(3):586–593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheridan D. J., Penkoske P. A., Sobel B. E., Corr P. B. Alpha adrenergic contributions to dysrhythmia during myocardial ischemia and reperfusion in cats. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jan;65(1):161–171. doi: 10.1172/JCI109647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart J. R., Burmeister W. E., Burmeister J., Lucchesi B. R. Electrophysiologic and antiarrhythmic effects of phentolamine in experimental coronary artery occlusion and reperfusion in the dog. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1980 Jan-Feb;2(1):77–91. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198001000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughn Williams E. M., Millar J. S., Campbell T. J. Electrophysiological effects of labetolol on rabbit atrial, ventricular and Purkinje cells, in normoxia and hypoxia. Cardiovasc Res. 1982 May;16(5):233–239. doi: 10.1093/cvr/16.5.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


