Abstract
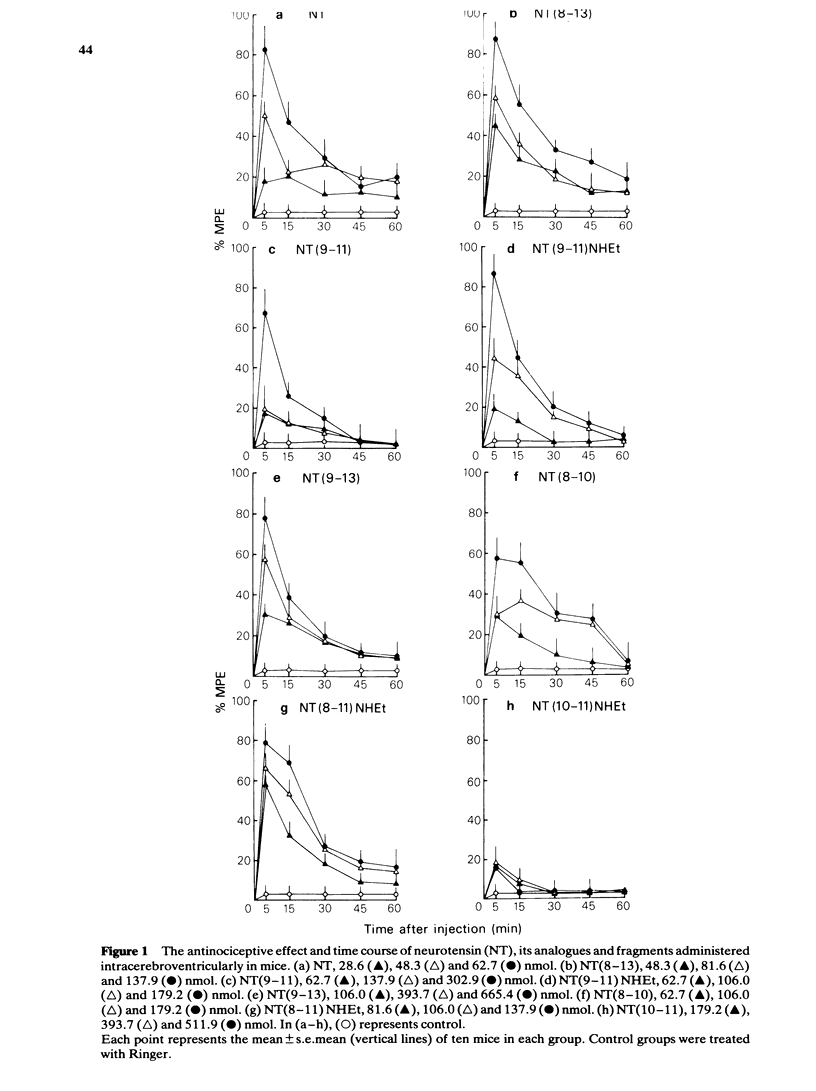
The antinociceptive effects of synthetic neurotensin (NT), its fragments and analogues administered into the lateral cerebroventricle have been compared in the conscious mouse. Intracerebroventricular (i.c.v.) administration of NT produced a dose-dependent antinociceptive effect in the tail pressure test. The NT fragments and analogues, NT(8-13), NT(8-10), NT(9-13), NT(9-11), NT(8-11) NHEt and NT(9-11) NHEt were also effective antinociceptive peptides. The potency of NT(8-13) and the duration of its effects were found to be approximately equal to those of NT. The antinociceptive effects produced by NT, NT(8-13) and NT(9-13) were significantly reversed by the opioid antagonist naloxone but not by thyrotropin releasing hormone. It is concluded that NT(8-13) is required for the full expression of the antinociceptive effects of NT which may be mediated in part through the brain opioid system.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bissette G., Manberg P., Nemeroff C. B., Prange A. J., Jr Neurotensin, a biologically active peptide. Life Sci. 1978 Nov 27;23(22):2173–2182. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90201-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraway R., Leeman S. E. The amino acid sequence of a hypothalamic peptide, neurotensin. J Biol Chem. 1975 Mar 10;250(5):1907–1911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraway R., Leeman S. E. The isolation of a new hypotensive peptide, neurotensin, from bovine hypothalami. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 10;248(19):6854–6861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clineschmidt B. V., McGuffin J. C. Neurotensin administered intracisternally inhibits responsiveness of mice to noxious stimuli. Eur J Pharmacol. 1977 Dec 15;46(4):395–396. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(77)90236-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkers K., Chang D., Humphries J., Carraway R., Leeman S. E., Bowers C. Y. Synthesis and activities of neurotensin, and its acid and amide analogs: possible natural occurrence of [Gln4]-neurotensin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3833–3837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamura S., Sakurada S., Sakurada T., Kisara K., Akutsu Y., Sasaki Y., Suzuki K. Potentiation of cyclo (N-methyl-Tyr-Arg)-induced antinociceptive activity by thyrotropin-releasing hormone in mice. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1984 Feb;36(2):142–144. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1984.tb03018.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitabgi P., Poustis C., Granier C., Van Rietschoten J., Rivier J., Morgat J. L., Freychet P. Neurotensin binding to extraneural and neural receptors: comparison with biological activity and structure--activity relationships. Mol Pharmacol. 1980 Jul;18(1):11–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudo T., Oheda N., Kotani Y., Inoki R. [Effects of endogenous peptides administered intracerebroventricularly on acetic acid-induced writhing syndrome in mice. I. Neurotensin, bradykinin, somatostatin and methionine-enkephalin]. Osaka Daigaku Shigaku Zasshi. 1980 Dec;25(2):264–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDermott J. R., Smith A. I., Edwardson J. A., Griffiths E. C. Mechanism of neurotensin degradation by rat brain peptidases. Regul Pept. 1982 May;3(5-6):397–404. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(82)90062-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemeroff C. B., Osbahr A. J., 3rd, Manberg P. J., Ervin G. N., Prange A. J., Jr Alterations in nociception and body temperature after intracisternal administration of neurotensin, beta-endorphin, other endogenous peptides, and morphine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5368–5371. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orikasa S., Sakurada S., Kisara K. Head-twitch response induced by tyramine. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1980 Jan;67(1):53–59. doi: 10.1007/BF00427595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osbahr A. J., 3rd, Nemeroff C. B., Luttinger D., Mason G. A., Prange A. J., Jr Neurotensin-induced antinociception in mice: antagonism by thyrotropin-releasing hormone. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Jun;217(3):645–651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quirion R., Rioux F., Regoli D., St-Pierre S. Selective blockade of neurotensin-induced coronary vessel constriction in perfused rat hearts by a neurotensin analogue. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980 Feb 8;61(3):309–312. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(80)90133-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurada S., Sakurada T., Jin H., Sato T., Kisara K., Sasaki Y., Suzuki K. Antinociceptive activities of synthetic dipeptides in mice. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1982 Nov;34(11):750–751. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1982.tb06218.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurada T., Sakurada S., Watanabe S., Kawamura S., Sato T., Kisara K., Akutsu Y., Sasaki Y., Suzuki K. Comparison of the antinociceptive effects of intracerebroventricular injection of kyotorphin, cyclo (N-methyl-Tyr-Arg) and Met-enkephalin in mice. Neuropharmacology. 1984 Jan;23(1):7–12. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(84)90209-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhl G. R., Bennett J. P., Jr, Snyder S. H. Neurotensin, a central nervous system peptide: apparent receptor binding in brain membranes. Brain Res. 1977 Jul 15;130(2):299–313. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90277-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Wimersma Greidanus T. B., van Praag M. C., Kalmann R., Rinkel G. J., Croiset G., Hoeke E. C., van Egmond M. A., Fekete M. Behavioral effects of neurotensin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;400:319–329. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb31578.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


