Abstract
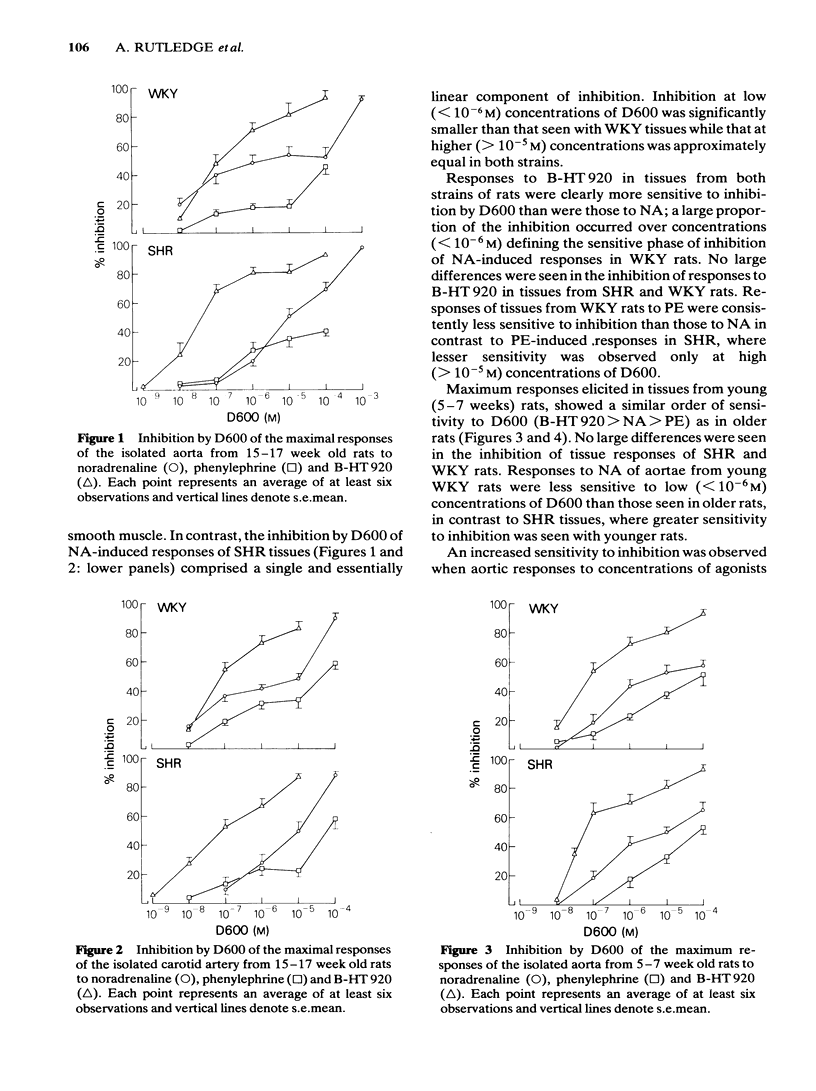
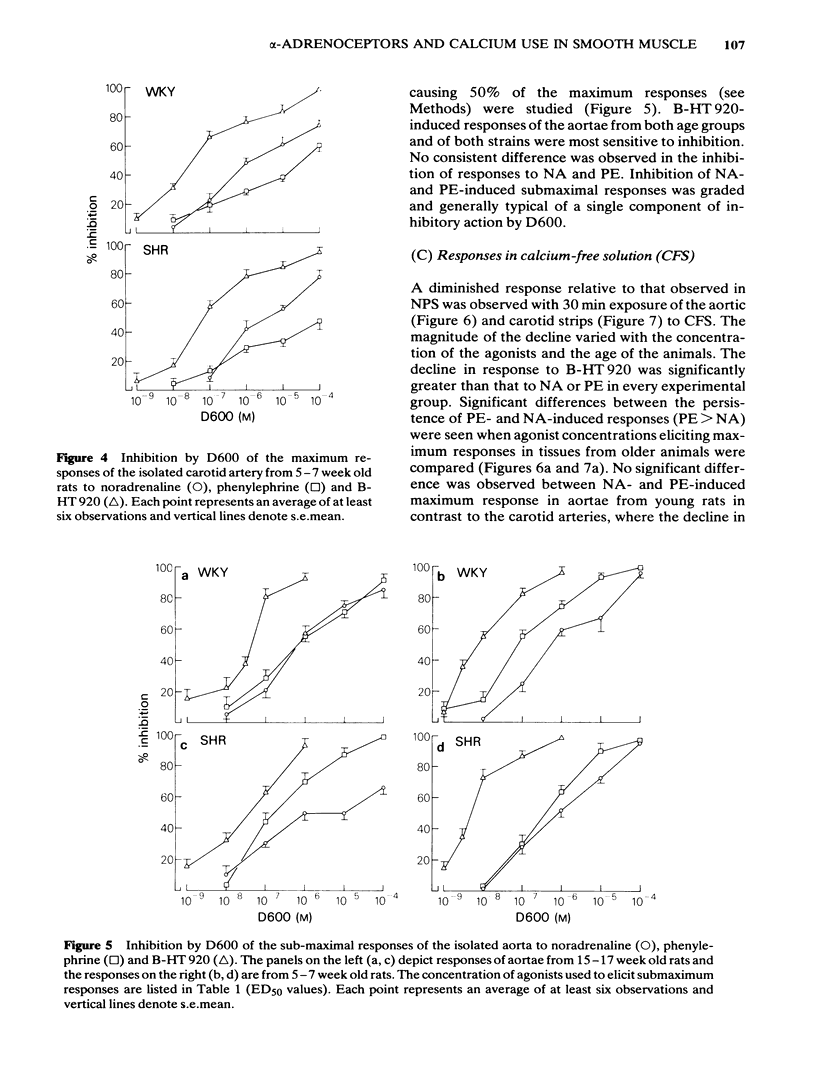
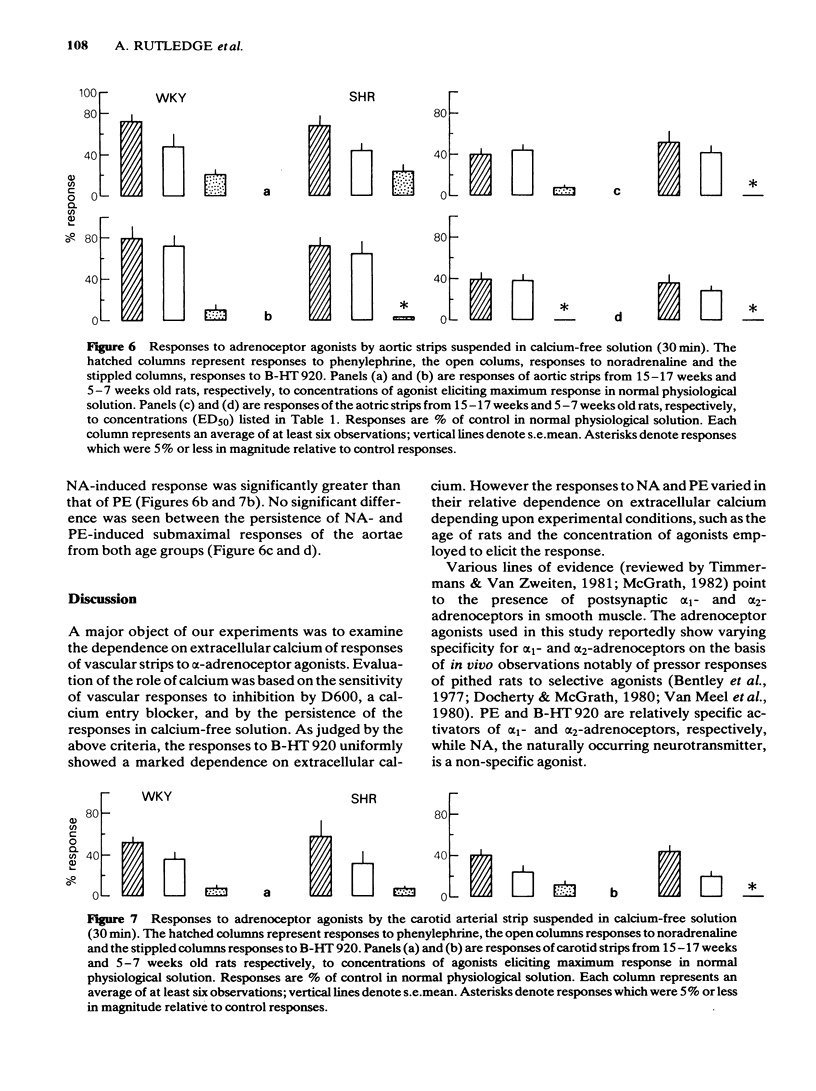
Inhibition by D600 (methoxyverapamil) of responses to an alpha 2-adrenoceptor selective agonist, B-HT 920, (6-allyl-2-amino-5, 6, 7, 8-tetrahydro-4H-thiazolo [4, 5-d] azepin dihydrochloride), an alpha 1-adrenoceptor selective agonist, phenylephrine (PE), and a nonselective agonist, noradrenaline (NA), was studied in isolated preparations of the aortae and carotid arteries obtained from young (5-7 weeks) and old (15-17 weeks) hypertensive (SHR) and normotensive (WKY) rats. Maximum responses of WKY tissues to B-HT 920 were the most sensitive, PE-induced responses the least sensitive and maximum responses to NA were intermediate in their sensitivity to inhibition by D600. Sub-maximal responses to NA and PE were not different in their sensitivity to inhibition by D600, but were less sensitive than the responses to B-HT 20. Sub-maximal responses to PE were significantly more sensitive to D600 inhibition than were the maximal responses to this agonist. NA-induced responses of tissues from older SHR were less sensitive to inhibition by D600 when compared to responses in WKY rats. Responses to B-HT 920, in tissues suspended in calcium-free solutions, showed the largest decline compared to NA- and PE-induced responses. We conclude that responses to B-HT 920 largely utilize extracellular calcium. PE- and NA- induced responses mobilize extracellular calcium to varying degrees depending upon the concentration of the agonist employed to elicit the response.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bentley S. M., Drew G. M., Whiting S. B. Evidence for two distinct types of postsynaptic alpha-adrenoceptor [proceedings]. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Sep;61(1):116P–117P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cauvin C., Loutzenhiser R., Van Breemen C. Mechanisms of calcium antagonist-induced vasodilation. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1983;23:373–396. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.23.040183.002105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Digges K. G., Summers R. J. Characterization of postsynaptic alpha-adrenoceptors in rat aortic strips and portal veins. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Jul;79(3):655–665. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb10002.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty J. R., McGrath J. C. An examination of factors influencing adrenergic transmission in the pithed rat, with special reference to noradrenaline uptake mechanisms and post-junctional alpha-adrenoceptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1980 Aug;313(2):101–111. doi: 10.1007/BF00498564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming W. W., Westfall D. P., De la Lande I. S., Jellett L. B. Log-normal distribution of equiefective doses of norepinephrine and acetylcholine in several tissues. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1972 May;181(2):339–345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gheyouche R., Le Fur G., Colotte O., Burgevin M. C., Uzan A. Evidence of an increase in brain postsynaptic alpha 1-receptors in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1980 May;32(5):366–368. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1980.tb12940.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfraind T., Miller R. C., Lima J. S. Selective alpha 1- and alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonist-induced contractions and 45Ca fluxes in the rat isolated aorta. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Dec;77(4):597–604. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb09337.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederballe Pedersen O., Mikkelsen E., Andersson K. E. Effects of extracellular calcium on potassium and noradrenaline induced contractions in the aorta of spontaneously hypertensive rats--increased sensitivity to nifedipine. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1978 Aug;43(2):137–144. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1978.tb02247.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath J. C. Evidence for more than one type of post-junctional alpha-adrenoceptor. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Feb 15;31(4):467–484. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90147-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nghiem C., Swamy V. C., Triggle D. J. Inhibition by D 600 of norepinephrine- and clonidine-induced responses of the aortae from normotensive (WKY) and spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR). Life Sci. 1982 Jan 4;30(1):45–49. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90634-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nghiem C., Swamy V. C., Triggle D. J. Inhibition by methoxyverapamil of the responses of smooth muscle from spontaneously hypertensive and normotensive rats. Blood Vessels. 1982;19(4):177–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randriantsoa A., Heitz C., Stoclet J. C. Functional characterization of postjunctional alpha-adrenoceptors in rat aorta. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Oct 15;75(1):57–60. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90345-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruffolo R. R., Jr, Yaden E. L., Waddell J. E. Receptor interactions of imidazolines. V. clonidine differentiates postsynaptic alpha adrenergic receptor subtypes in tissues from the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 Jun;213(3):557–561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K. Alpha-adrenoceptor subclassification. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1981;88:199–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmermans P. B., van Zwieten P. A. Mini-review. The postsynaptic alpha 2-adrenoreceptor. J Auton Pharmacol. 1981 Mar;1(2):171–183. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1981.tb00509.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Meel J. C., De Jonge A., Kalkman H. O., Wilffert B., Timmermans P. B., Van Zwieten P. A. Vascular smooth muscle contraction initiated by postsynaptic alpha 2-adrenoceptor activation is induced by an influx of extracellular calcium. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Jan 16;69(2):205–208. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90415-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb R. C., Bhalla R. C. Altered calcium sequestration by subcellular fractions of vascular smooth muscle from spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1976 Aug;8(8):651–661. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(76)90050-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. J., Webb R. C., Smith C. B. Alpha-2 adrenoreceptors on arterial smooth muscle: selective labeling by [3H]clonidine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Jun;225(3):599–605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Breemen C., Hwang O., Meisheri K. D. The mechanism of inhibitory action of diltiazem on vascular smooth muscle contractility. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Aug;218(2):459–463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Meel J. C., Timmermans P. B., van Zwieten P. A. alpha 1- and alpha 2-adrenoceptor stimulation in the isolated perfused hindquarters of the rat: an in vitro model. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1983 Jul-Aug;5(4):580–585. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198307000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


