Abstract
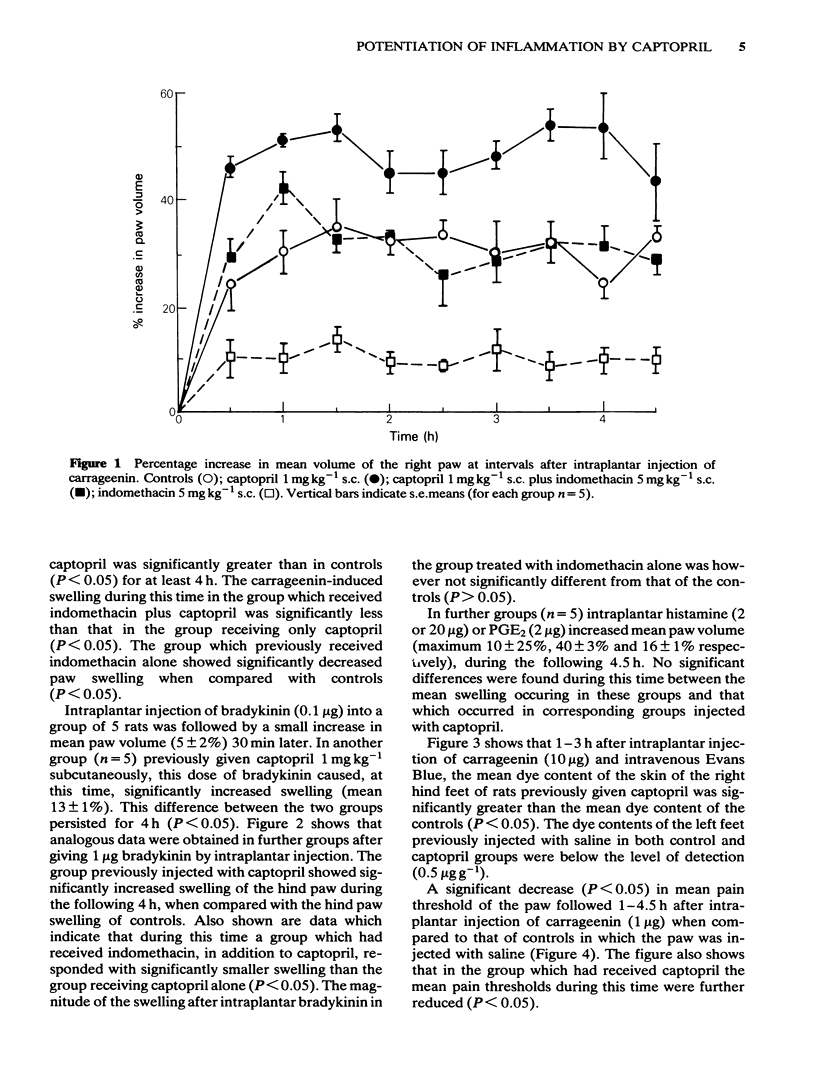
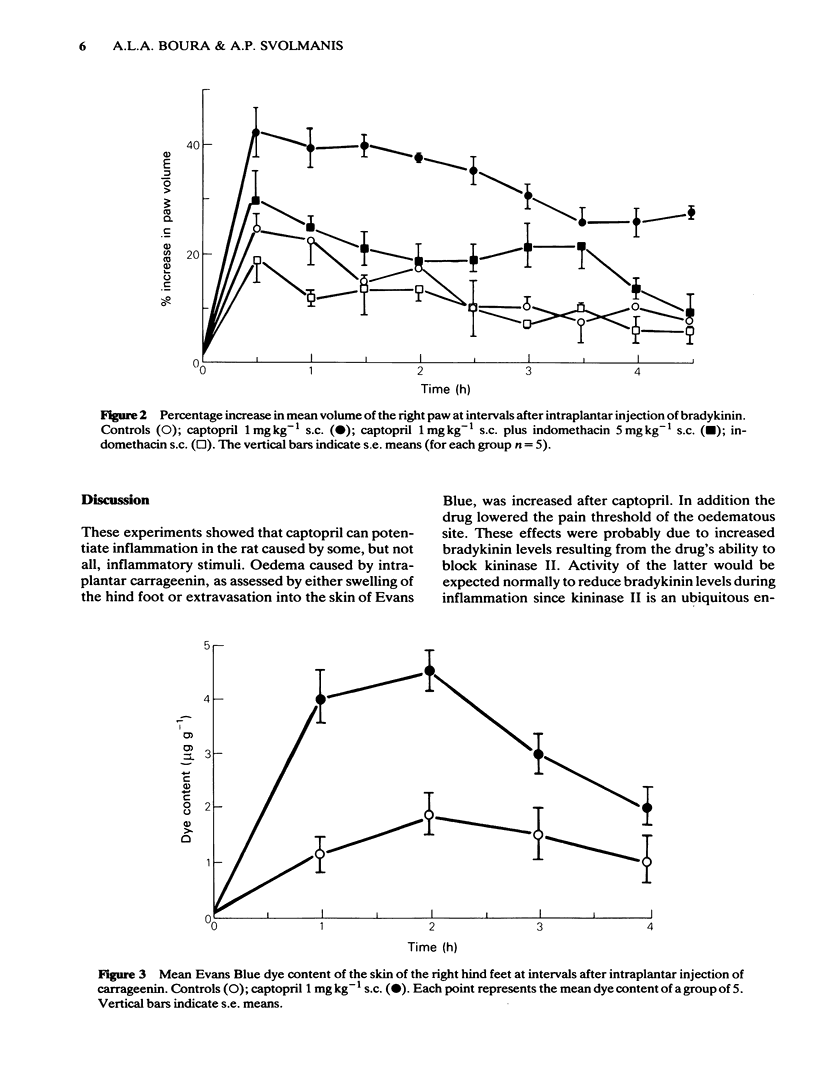
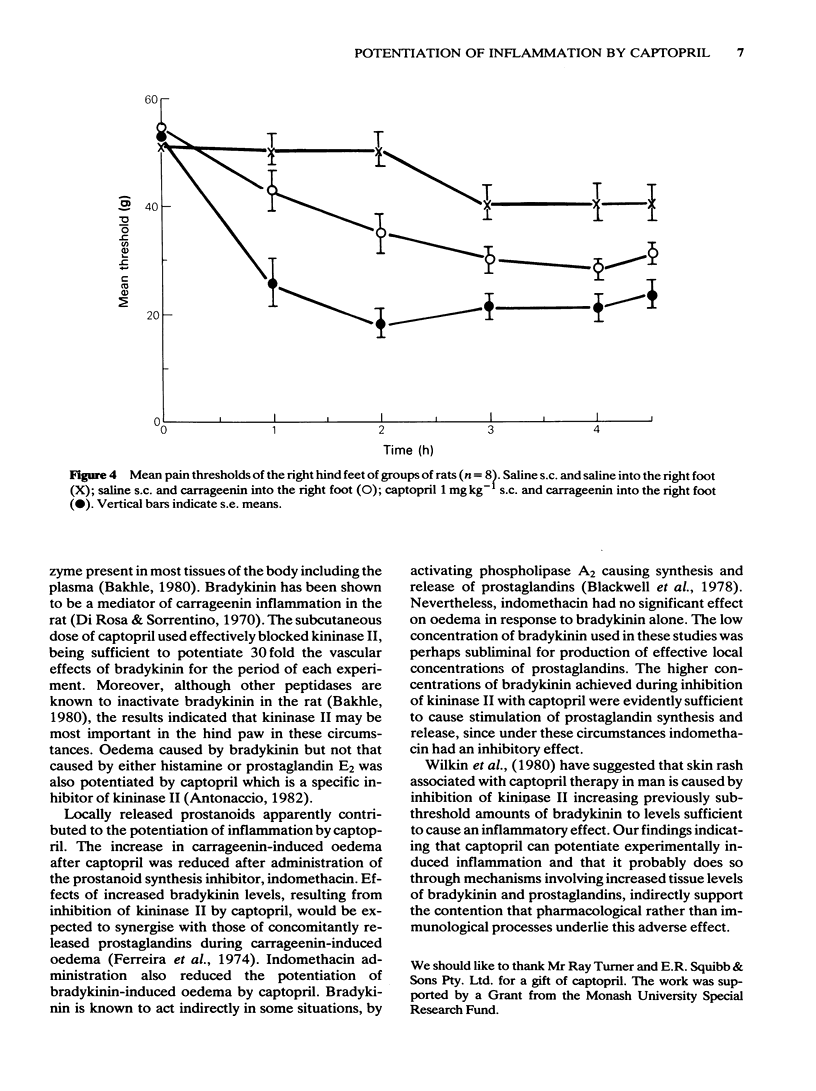
Hind paw oedema in rats, measured by plethysmography or extravasation of Evans Blue dye into the skin, after subplantar injection of submaximal doses of carrageenin (1-100 micrograms) was significantly increased for 4 h during kininase II inhibition with captopril (1 mg kg-1, s.c.). Submaximal oedema, as assessed by paw swelling, after subplantar bradykinin (0.1-1.0 microgram) was also significantly increased after subcutaneous administration of this dose of captopril, whereas that in response to either histamine (2-20 micrograms) or prostaglandin E2 (2 micrograms) was unchanged. The pain threshold of the paw, injected with carrageenin (1 microgram) was lowered significantly after subcutaneous administration of captopril (1 mg kg-1). Potentiation by captopril (1 mg kg-1, s.c.) of paw swelling in response to intraplantar carrageenin (100 micrograms) or bradykinin (1 microgram) was reduced by prior subcutaneous administration of indomethacin (5 mg kg-1). It is suggested that normally, tissue kininase II activity is sufficient to decrease the inflammatory response of the hind paw to carrageenin or bradykinin. After inhibition of kininase II with captopril, bradykinin levels are increased and interact with concomitantly released prostaglandins to potentiate inflammation.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antonaccio M. J. Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1982;22:57–87. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.22.040182.000421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakhle Y. S. Pulmonary angiotensin-converting enzyme and its inhibition: a historical survey. Ciba Found Symp. 1980;78:275–292. doi: 10.1002/9780470720615.ch15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell G. J., Flower R. J., Nijkamp F. P., Vane J. R. Phospholipase A2 activity of guinea-pig isolated perfused lungs: stimulation, and inhibition by anti-inflammatory steroids. Br J Pharmacol. 1978 Jan;62(1):79–89. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1978.tb07009.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Rosa M., Sorrentino L. Some pharmacodynamic properties of carrageenin in the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Jan;38(1):214–220. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb10350.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdös E. G. The angiotensin I converting enzyme. Fed Proc. 1977 Apr;36(5):1760–1765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira S. H., Moncada S., Parsons M., Vane J. R. Proceedings: the concomitant release of bradykinin and prostaglandin in the inflammatory response to carrageenin. Br J Pharmacol. 1974 Sep;52(1):108P–109P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada M., Takeuchi M., Fukao T., Katagiri K. A simple method for the quantitative extraction of dye extravasated into the skin. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1971 Mar;23(3):218–219. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1971.tb08647.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luderer J. R., Lookingbill D. P., Schneck D. W., Demers L. M., Cohen C., Hayes A. H., Jr Captopril-induced skin eruptions. J Clin Pharmacol. 1982 Apr;22(4):151–159. doi: 10.1002/j.1552-4604.1982.tb02156.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel B., Russell T., 2nd, Winkelmann R. K., Gleich G. J. Release of kinins from site of wheal-and-flare allergic skin reactions. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1970;39(5-6):616–624. doi: 10.1159/000230386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ondetti M. A., Rubin B., Cushman D. W. Design of specific inhibitors of angiotensin-converting enzyme: new class of orally active antihypertensive agents. Science. 1977 Apr 22;196(4288):441–444. doi: 10.1126/science.191908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANDALL L. O., SELITTO J. J. A method for measurement of analgesic activity on inflamed tissue. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1957 Sep 1;111(4):409–419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINTER C. A., RISLEY E. A., NUSS G. W. Carrageenin-induced edema in hind paw of the rat as an assay for antiiflammatory drugs. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 Dec;111:544–547. doi: 10.3181/00379727-111-27849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkin J. K., Hammond J. J., Kirkendall W. M. The captopril-induced eruption. A possible mechanism: cutaneous kinin potentiation. Arch Dermatol. 1980 Aug;116(8):902–905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


