Abstract
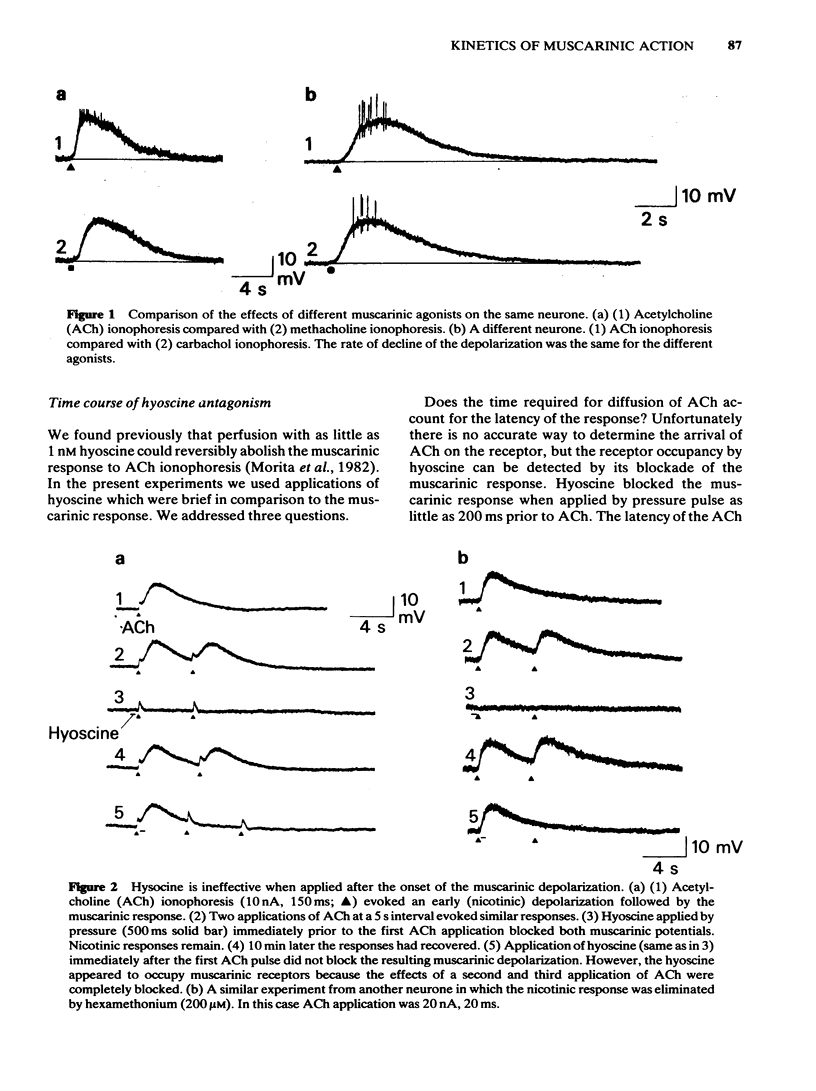
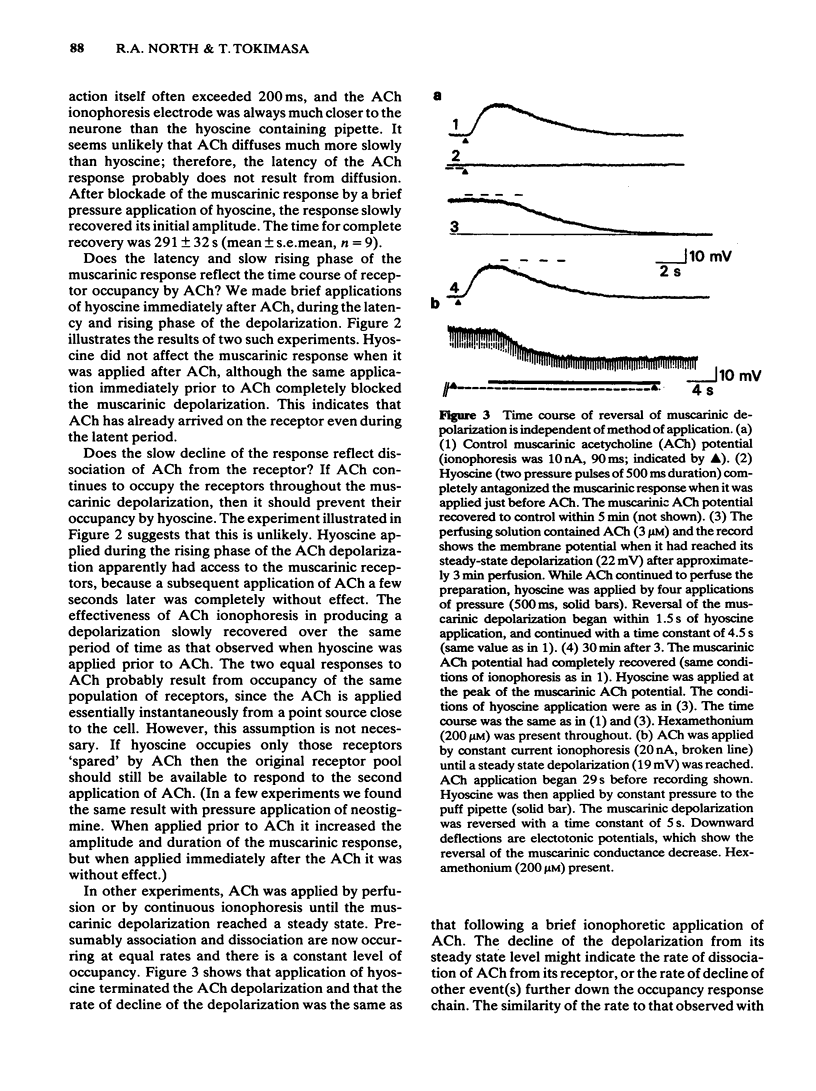
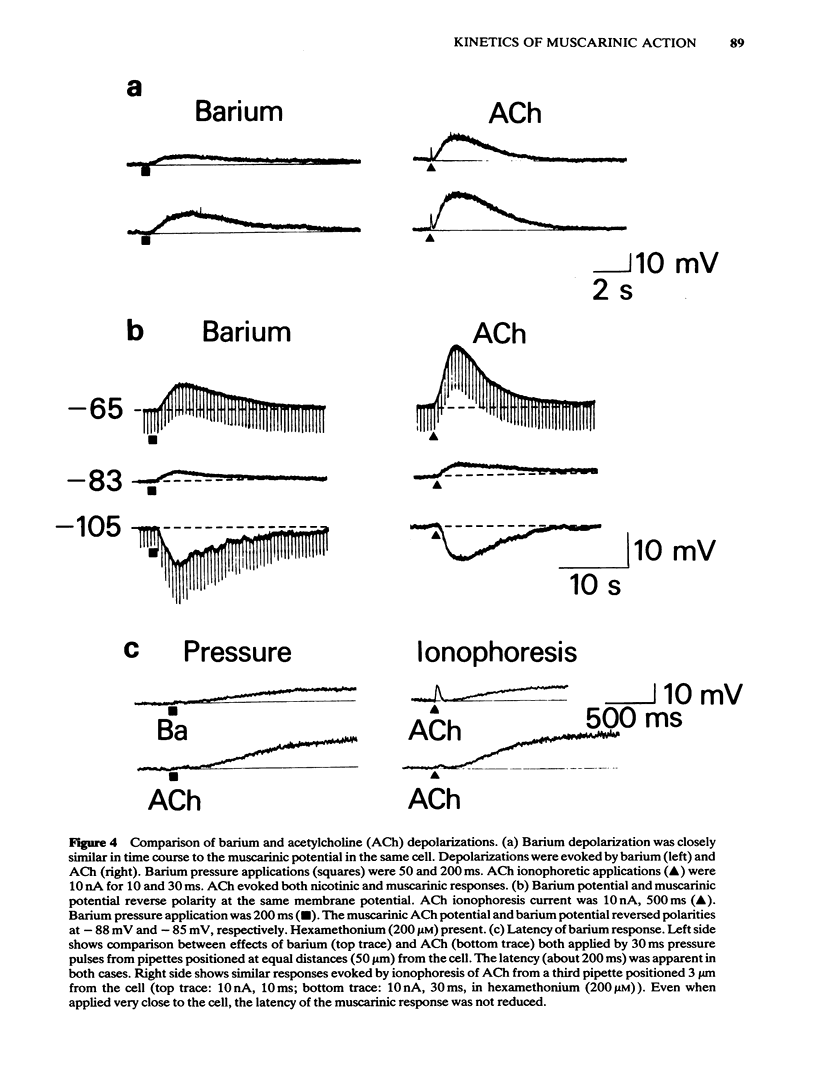
Intracellular recordings were made from neurones in the myenteric plexus of the guinea-pig ileum in vitro. Muscarinic depolarizations were evoked by brief (1-500 ms) ionophoretic applications of acetylcholine (ACh) or other agonists. Nicotinic responses to ACh evoked by the same ionophoretic pulse had short latencies and rapid rise times, indicating close proximity of the ionophoretic pipette to the neurone membrane. The time course (duration several seconds) of the muscarinic depolarization was independent of the identity of the agonists applied (ACh, methacholine, carbachol, oxotremorine). Hyoscine and barium were ejected onto the neurones by brief (30 ms-1 s) pressure pulses applied to micropipettes. Hyoscine applied immediately after ACh, during the latency and rising phase of the muscarinic depolarization, did not antagonize the response to ACh. The same application of hyoscine immediately prior to ACh caused complete antagonism. Muscarinic depolarizations evoked by continuous application of ACh (by repeated ionophoresis or perfusion) were reversed by hyoscine. The time course of this reversal was similar to the decline of the muscarinic response following a single brief application of ACh. Barium caused a depolarization similar to that produced by muscarinic agonists in its latency, time course and temperature sensitivity, and having the same reversal potential (-90 mV). These barium potentials were not affected by hyoscine. It is suggested that neither diffusion of ACh to the receptors nor the kinetics of the agonist-receptor interaction contributes significantly to the latency and prolonged time course of the muscarinic depolarization.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bolton T. B. Cholinergic mechanisms in smooth muscle. Br Med Bull. 1979 Sep;35(3):275–283. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constanti A., Adams P. R., Brown D. A. Who do barium ions imitate acetylcholine? Brain Res. 1981 Feb 9;206(1):244–250. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90125-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartzell H. C., Kuffler S. W., Stickgold R., Yoshikami D. Synaptic excitation and inhibition resulting from direct action of acetylcholine on two types of chemoreceptors on individual amphibian parasympathetic neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Oct;271(3):817–846. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartzell H. C. Mechanisms of slow postsynaptic potentials. Nature. 1981 Jun 18;291(5816):539–544. doi: 10.1038/291539a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill-Smith I., Purves R. D. Synaptic delay in the heart: an ionophoretic study. J Physiol. 1978 Jun;279:31–54. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., Holman M. E., Spence I. Two types of neurones in the myenteric plexus of duodenum in the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1974 Jan;236(2):303–326. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krnjević K., Pumain R., Renaud L. The mechanism of excitation by acetylcholine in the cerebral cortex. J Physiol. 1971 May;215(1):247–268. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita K., North R. A., Tokimasa T. Muscarinic agonists inactivate potassium conductance of guinea-pig myenteric neurones. J Physiol. 1982 Dec;333:125–139. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi S., North R. A. Intracellular recording from the myenteric plexus of the guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1973 Jun;231(3):471–491. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Tokimasa T. Depression of calcium-dependent potassium conductance of guinea-pig myenteric neurones by muscarinic agonists. J Physiol. 1983 Sep;342:253–266. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Tokimasa T. Muscarinic synaptic potentials in guinea-pig myenteric plexus neurones. J Physiol. 1982 Dec;333:151–156. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


