Abstract
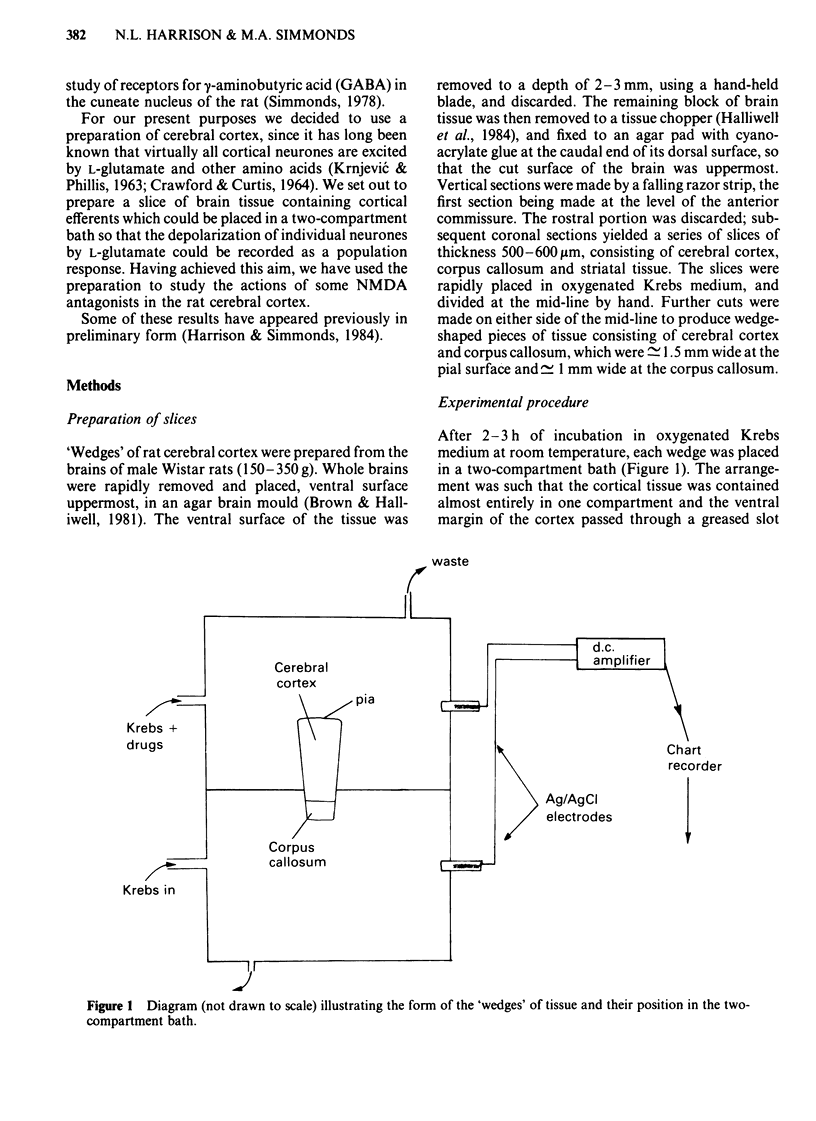
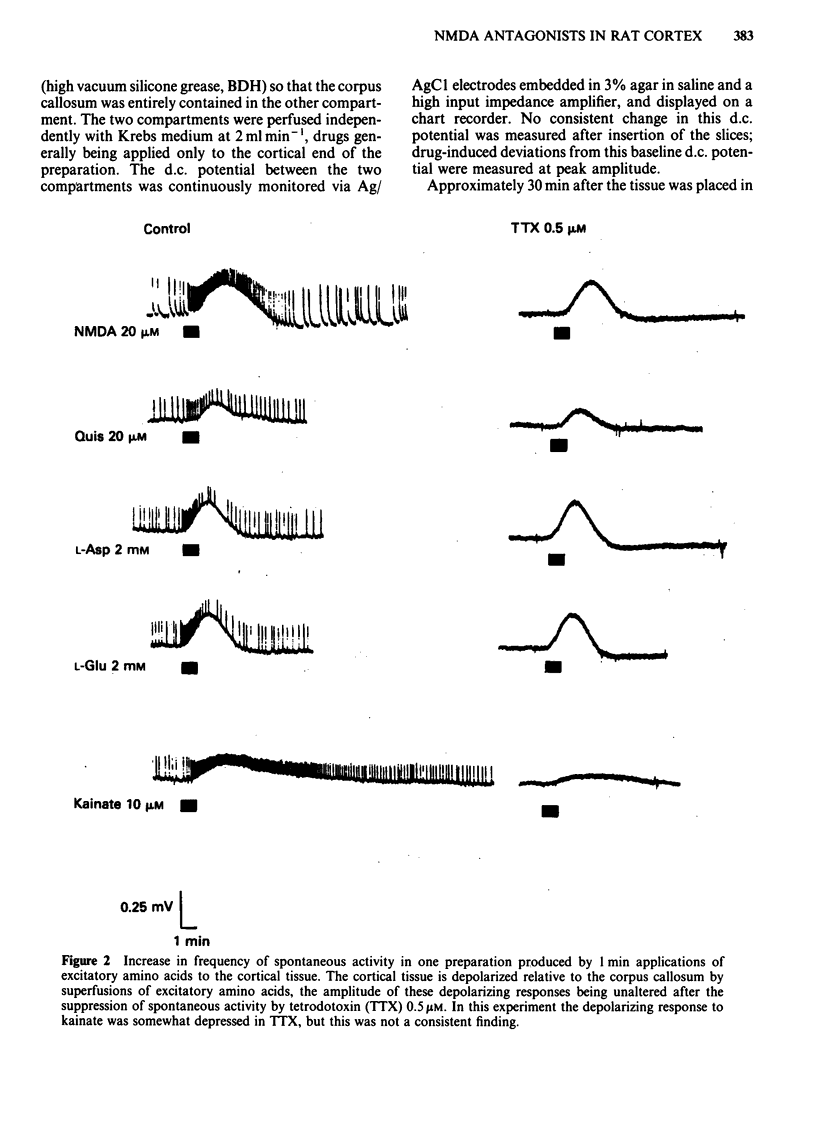
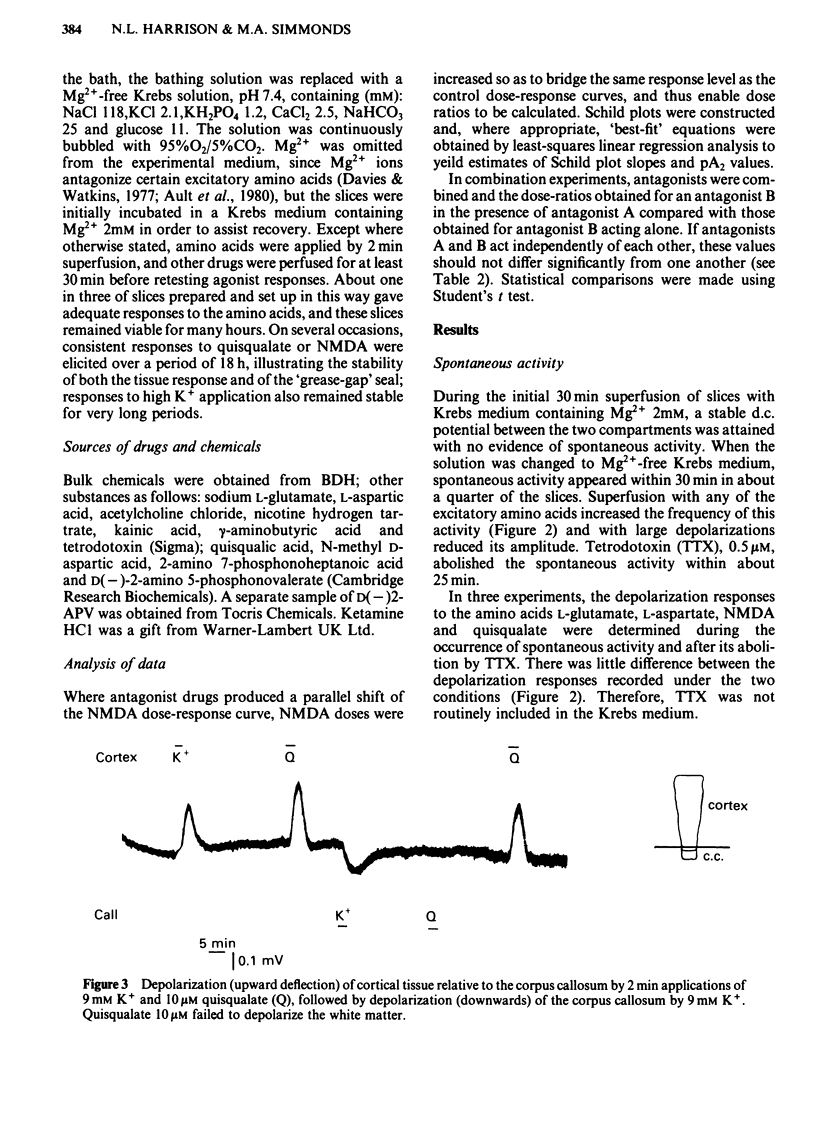
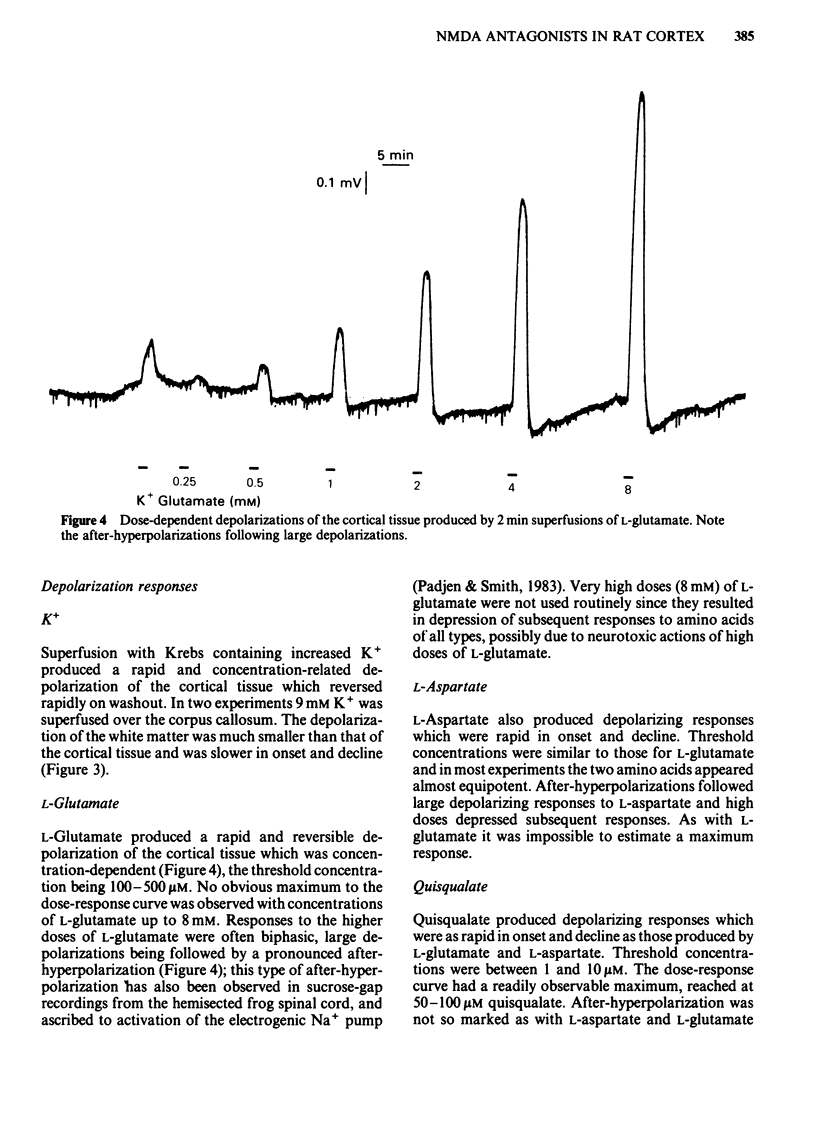
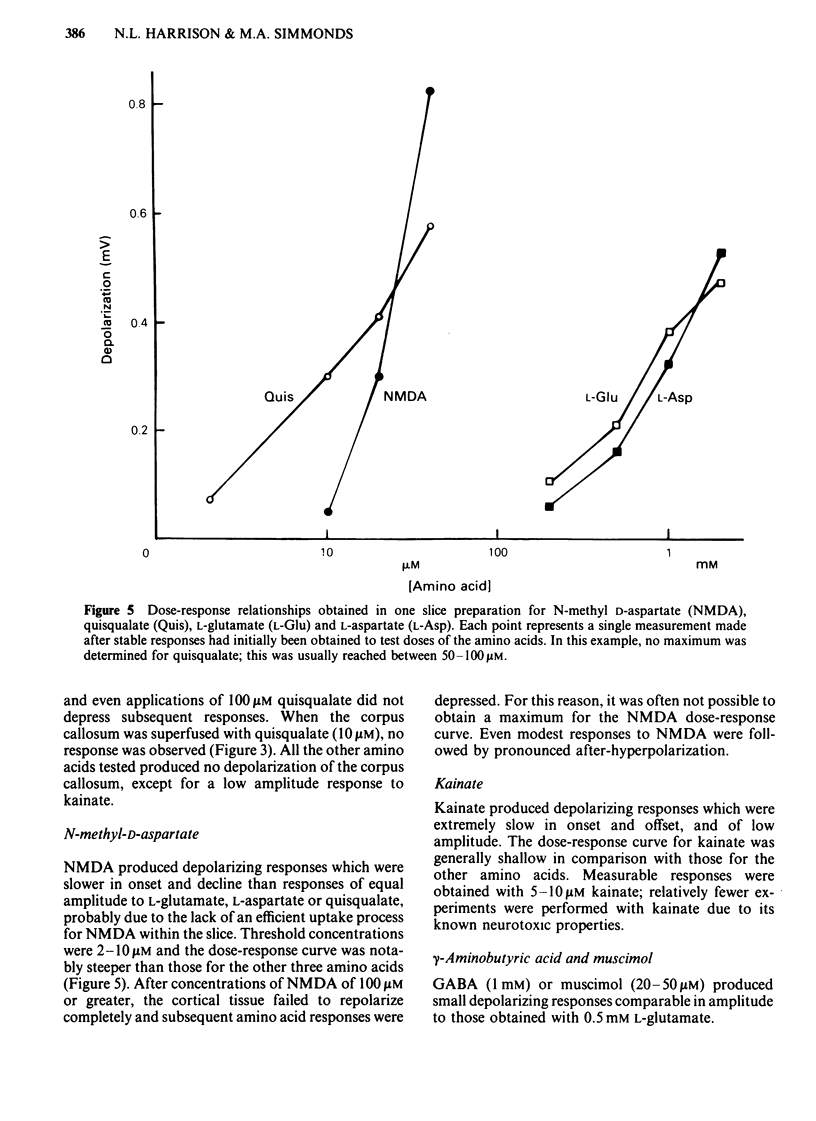
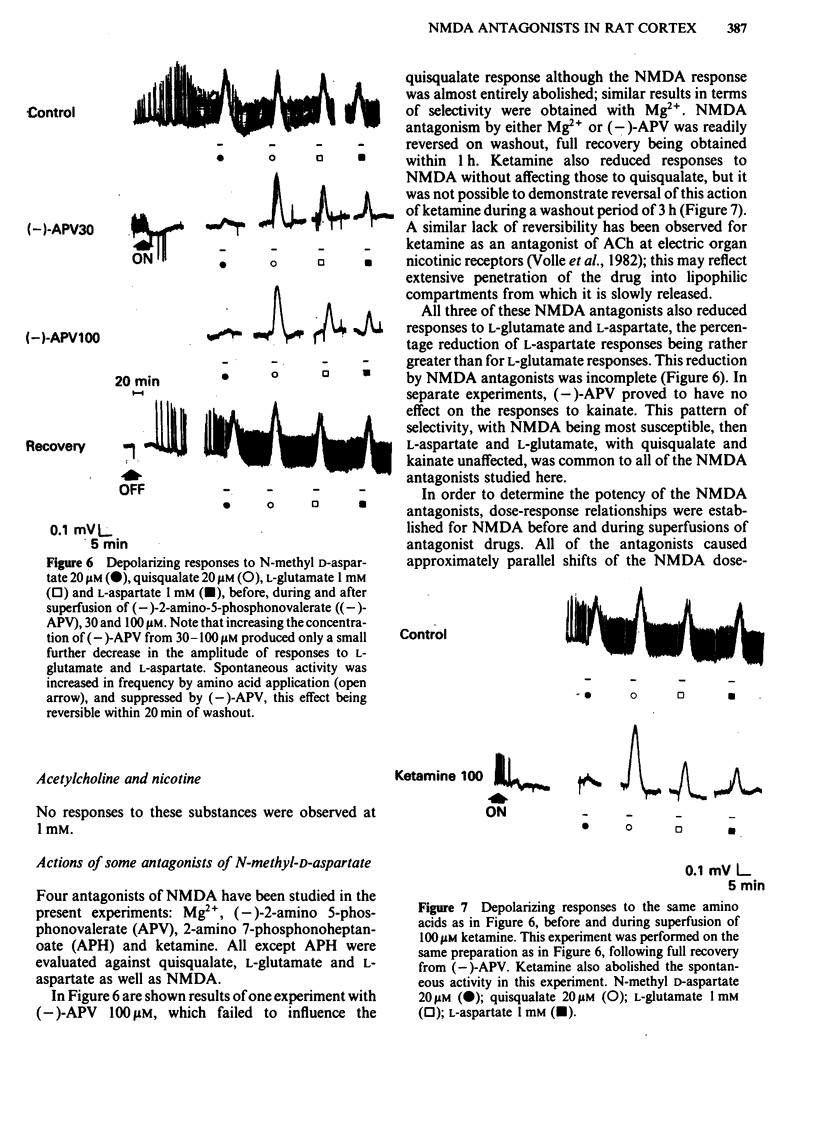
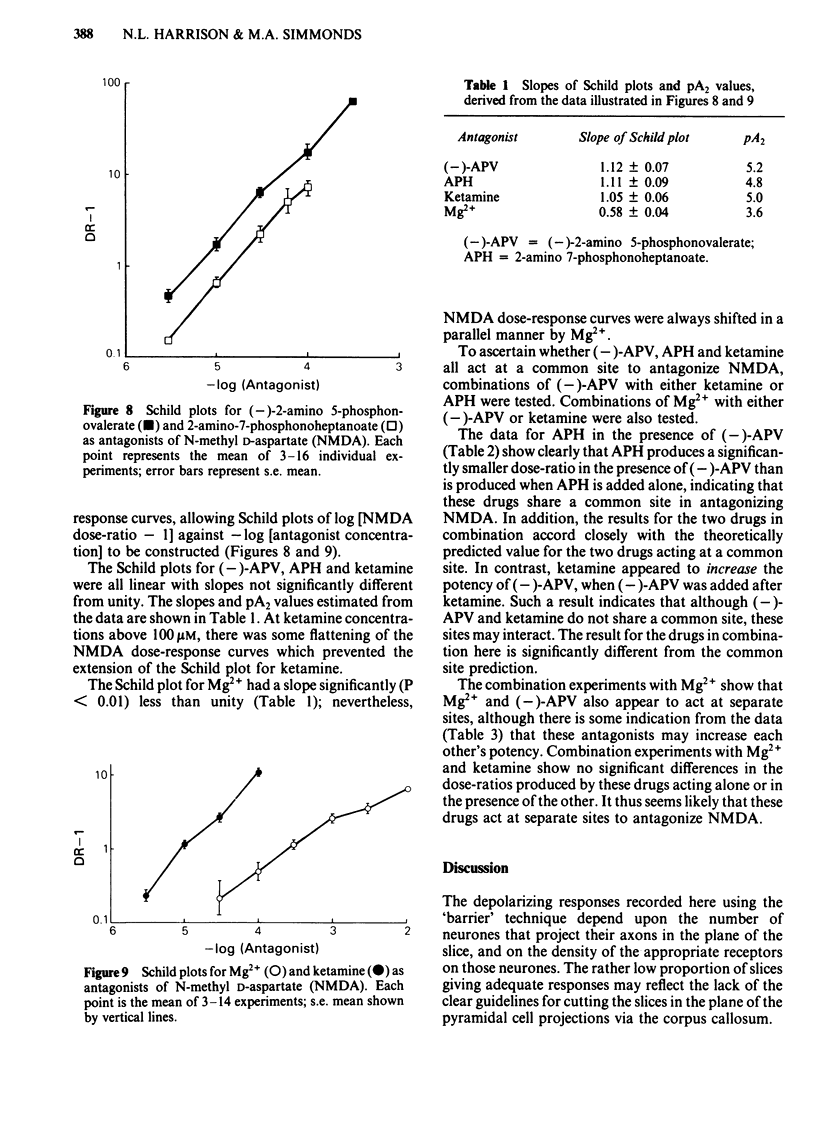
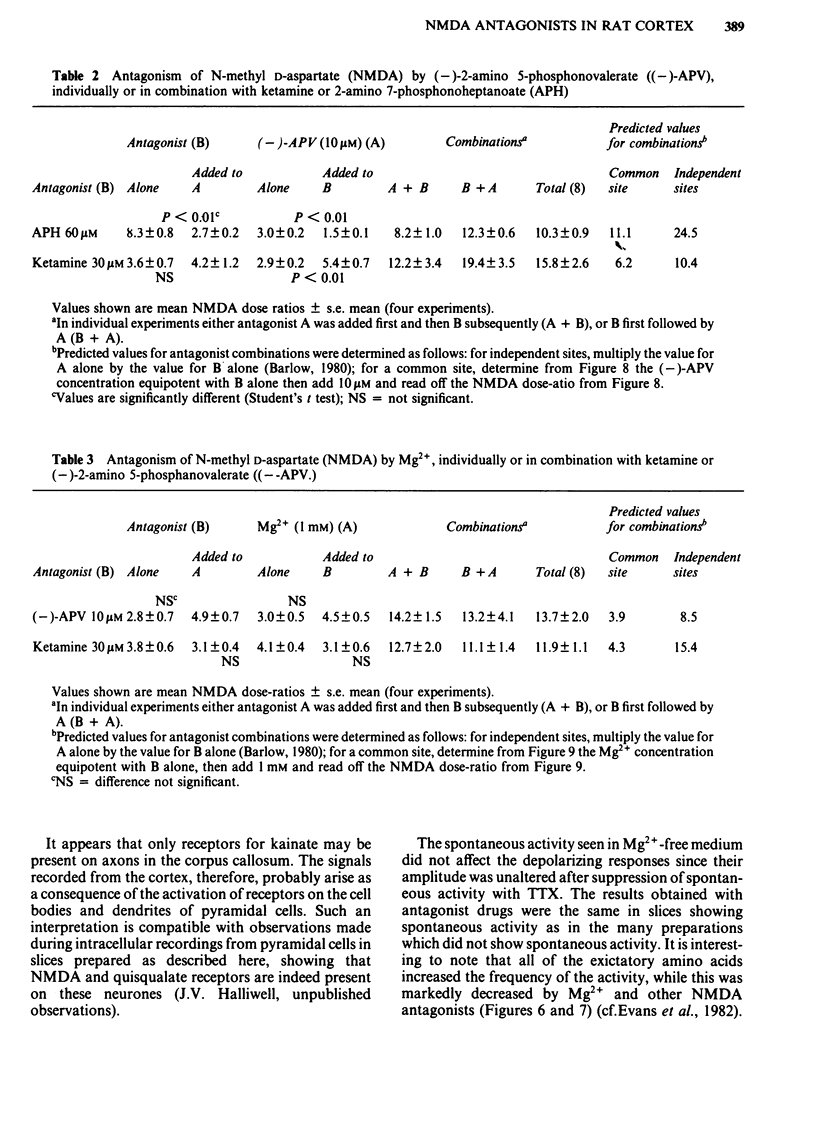
Coronal sections of rat brain (500 micron thick) were trimmed to form 'wedges' of tissue consisting of cerebral cortex and corpus callosum. When these slices were placed in a two-compartment bath, the cortical tissue could be depolarized, relative to the corpus callosum, by superfusions of high K+, or by amino acids such as L-glutamate, L-aspartate, quisqualate, kainate and N-methyl D-aspartate (NMDA). Responses to NMDA were reduced by magnesium ions, by the organic antagonists (-)-2-amino 5-phosphonovalerate (APV) and 2-amino 7-phosphonoheptanoate (APH), and by the dissociative anaesthetic ketamine. In this preparation, all these antagonists shifted the NMDA dose-response curve to the right in a parallel manner. A Schild plot for Mg2+ had a slope significantly less than unity, indicative of a non-competitive action, whilst Schild plots for (-)-APV, APH and ketamine appeared linear and had slopes of approximately 1. Analysis of the results of combination experiments suggested that the presumed competitive antagonists, (-)-APV and APH, share a common site of action as NMDA antagonists, and that this site is distinct from that at which ketamine exerts its action. The action of Mg2+ is clearly different from that of either (-)-APV or ketamine. It is concluded that ketamine is a non-competitive antagonist of NMDA and may act at an allosteric site on the NMDA receptor complex to influence its function.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anis N. A., Berry S. C., Burton N. R., Lodge D. The dissociative anaesthetics, ketamine and phencyclidine, selectively reduce excitation of central mammalian neurones by N-methyl-aspartate. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Jun;79(2):565–575. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb11031.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ault B., Evans R. H., Francis A. A., Oakes D. J., Watkins J. C. Selective depression of excitatory amino acid induced depolarizations by magnesium ions in isolated spinal cord preparations. J Physiol. 1980 Oct;307:413–428. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker J. L., McBurney R. N., Mathers D. A. Convulsant-induced depression of amino acid responses in cultured mouse spinal neurones studied under voltage clamp. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Dec;80(4):619–629. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb10051.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRAWFORD J. M., CURTIS D. R. THE EXCITATION AND DEPRESSION OF MAMMALIAN CORTICAL NEURONES BY AMINO ACIDS. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1964 Oct;23:313–329. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1964.tb01589.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collingridge G. L., Kehl S. J., McLennan H. The antagonism of amino acid-induced excitations of rat hippocampal CA1 neurones in vitro. J Physiol. 1983 Jan;334:19–31. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croucher M. J., Collins J. F., Meldrum B. S. Anticonvulsant action of excitatory amino acid antagonists. Science. 1982 May 21;216(4548):899–901. doi: 10.1126/science.7079744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crunelli V., Forda S., Kelly J. S. Blockade of amino acid-induced depolarizations and inhibition of excitatory post-synaptic potentials in rat dentate gyrus. J Physiol. 1983 Aug;341:627–640. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Watkins J. C. Actions of D and L forms of 2-amino-5-phosphonovalerate and 2-amino-4-phosphonobutyrate in the cat spinal cord. Brain Res. 1982 Mar 11;235(2):378–386. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)91017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. H., Francis A. A., Jones A. W., Smith D. A., Watkins J. C. The effects of a series of omega-phosphonic alpha-carboxylic amino acids on electrically evoked and excitant amino acid-induced responses in isolated spinal cord preparations. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Jan;75(1):65–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb08758.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRNJEVIC K., PHILLIS J. W. Iontophoretic studies of neurones in the mammalian cerebral cortex. J Physiol. 1963 Feb;165:274–304. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L., Guthrie P. B. Voltage-dependent block by Mg2+ of NMDA responses in spinal cord neurones. Nature. 1984 May 17;309(5965):261–263. doi: 10.1038/309261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaghan D. T., Holets V. R., Toy D. W., Cotman C. W. Anatomical distributions of four pharmacologically distinct 3H-L-glutamate binding sites. Nature. 1983 Nov 10;306(5939):176–179. doi: 10.1038/306176a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak L., Bregestovski P., Ascher P., Herbet A., Prochiantz A. Magnesium gates glutamate-activated channels in mouse central neurones. Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):462–465. doi: 10.1038/307462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olverman H. J., Jones A. W., Watkins J. C. L-glutamate has higher affinity than other amino acids for [3H]-D-AP5 binding sites in rat brain membranes. Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):460–462. doi: 10.1038/307460a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padjen A. L., Smith P. A. The role of the electrogenic sodium pump in the glutamate afterhyperpolarization of frog spinal cord. J Physiol. 1983 Mar;336:433–451. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennefather P., Quastel D. M. Modification of dose-response curves by effector blockade and uncompetitive antagonism. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 Sep;22(2):369–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmonds M. A. Classification of some GABA antagonists with regard to site of action and potency in slices of rat cuneate nucleus. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Jun 4;80(4):347–358. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90080-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmonds M. A. Presynaptic actions of gamma-aminobutyric acid and some antagonists in a slice preparation of cuneate nucleus. Br J Pharmacol. 1978 Jul;63(3):495–502. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1978.tb07803.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins J. C., Evans R. H. Excitatory amino acid transmitters. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1981;21:165–204. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.21.040181.001121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


