Abstract
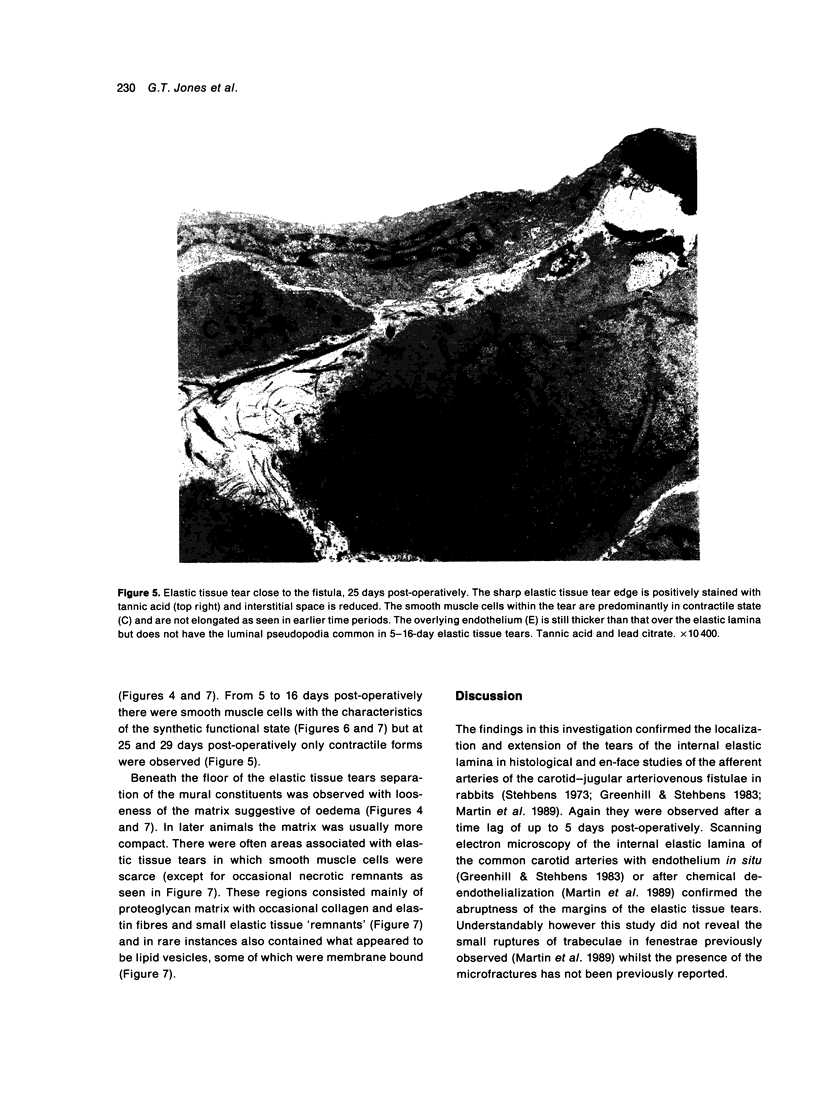
The afferent arteries of 10 carotid-jugular arteriovenous fistulae in rabbits were examined by transmission electron microscopy to determine the early ultrastructural changes in the vicinity of haemodynamically induced tears of the internal elastic lamina. No significant changes appeared to precede the development of the tears but radially orientated partial fractures were observed adjacent to some major tears. The elastic tissue tears became more numerous, extended proximally along the artery and with time involved the innermost medial elastic laminae. Endothelial discontinuities were present over only a few early tears and the small size suggested repair was rapid. Endothelial cells overlying the elastic tissue tears increased in density and thickness. They were adherent to the underlying matrix and eventually to the thickened and multilaminated basal lamina. In the floor of the tears between the edges of the torn internal elastic lamina there were some smooth muscle cells of the synthetic type, degenerative and necrotic muscle cells and areas devoid of matrix with scarce proteoglycan material suggestive of oedema. Sixteen days post-operatively the smooth muscle cells in the floor of the tears were all of the contractile variety with thickened basal laminae overlaid by a relatively normal endothelial layer. There was no suggestion that inflammatory cells were responsible for the elastic tissue tears. The abrupt edges and the adjacent microfractures are consistent with the concept of mechanical failure of the elastic tissue.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Coutard M., Osborne-Pellegrin M. Rupture of the internal elastic lamina and vascular fragility in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats. Stroke. 1991 Apr;22(4):510–515. doi: 10.1161/01.str.22.4.510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenhill N. S., Stehbens W. E. Haemodynamically-induced intimal tears in experimental U-shaped arterial loops as seen by scanning electron microscopy. Br J Exp Pathol. 1985 Oct;66(5):577–584. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenhill N. S., Stehbens W. E. Scanning electron microscopic investigation of the afferent arteries of experimental femoral arteriovenous fistulae in rabbits. Pathology. 1987 Jan;19(1):22–27. doi: 10.3109/00313028709065130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenhill N. S., Stehbens W. E. Scanning electron-microscopic study of experimentally induced intimal tears in rabbit arteries. Atherosclerosis. 1983 Nov;49(2):119–126. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(83)90189-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. T., Martin B. J., Stehbens W. E. Endothelium and elastic tears in the afferent arteries of experimental arteriovenous fistulae in rabbits. Int J Exp Pathol. 1992 Aug;73(4):405–416. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kajikawa K., Yamaguchi T., Katsuda S., Miwa A. An improved electron stain for elastic fibers using tannic acid. J Electron Microsc (Tokyo) 1975;24(4):287–289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin B. J., Stehbens W. E., Davis P. F., Ryan P. A. Scanning electron microscopic study of hemodynamically induced tears in the internal elastic lamina of rabbit arteries. Pathology. 1989 Jul;21(3):207–212. doi: 10.3109/00313028909061060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer W. W., Lind J. Iliac arteries in children with a single umbilical artery. Structure, calcifications, and early atherosclerotic lesions. Arch Dis Child. 1974 Sep;49(9):671–679. doi: 10.1136/adc.49.9.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne-Pellegrin M. J. "Spontaneous" lesions of the intima in the rat caudal artery. Principal morphologic characteristic and occurrence as a function of age and sex. Lab Invest. 1979 Jun;40(6):668–677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne-Pellegrin M. J., Coutard M. Effect of contralateral nephrectomy alone or in association with hypertension on rat renal artery lesions. Atherosclerosis. 1985 Nov;57(2-3):267–280. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(85)90039-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne-Pellegrin M. J. Some ultrastructural characteristics of the renal artery and abdominal aorta in the rat. J Anat. 1978 Mar;125(Pt 3):641–652. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEHBENS W. E. ENDOTHELIAL CELL MITOSIS AND PERMEABILITY. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1965 Jan;50:90–92. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1965.sp001773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stehbens W. E. Cerebral atherosclerosis. Intimal proliferation and atherosclerosis in the cerebral arteries. Arch Pathol. 1975 Nov;99(11):582–591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stehbens W. E. Experimental arterial loops and arterial atrophy. Exp Mol Pathol. 1986 Apr;44(2):177–189. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(86)90068-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stehbens W. E. Experimental arteriovenous fistulae in normal and cholesterol-fed rabbits. Pathology. 1973 Oct;5(4):311–324. doi: 10.3109/00313027309073759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stehbens W. E., Martin B. J., Delahunt B. Light and scanning electron microscopic changes observed in experimental arterial forks of rabbits. Int J Exp Pathol. 1991 Apr;72(2):183–193. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stehbens W. E. The basal attachment of endothelial cells. J Ultrastruct Res. 1966 Jun;15(3):389–399. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(66)80115-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stehbens W. E. The ultrastructure of the anastomosed vein of experimental arteriovenous fistulae in sheep. Am J Pathol. 1974 Aug;76(2):377–400. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]