Abstract
The formation of new blood vessels, angiogenesis, is an important event in inflammation, wound healing and tumour growth. Mediators produced by various cells when exposed to endotoxin include cytokines (tumour necrosis factor, interleukins 1 and 6, and basic fibroblast growth factor) which, it has been suggested, stimulate angiogenesis. The angiogenic effect of endotoxin (lipopolysaccharide, LPS) was studied in rats using the quantitative mesenteric window assay. Adult rats were injected intraperitoneally with Escherichia coli LPS (5 pg/ml-20,000 ng/ml) twice daily for 4.5 consecutive days and were sacrificed 14 days after the start of this treatment. An angiogenic response was observed at concentrations of > 2 ng/ml in a dose-dependent manner. No inflammatory cellular exudate was seen in the test tissue at the time of angiogenesis analysis. Suppressed body-weight gain, a marker of the systemic effect of LPS in the rat, was significant only at the highest dose tested. The data suggest that endotoxin-mediated neovascularization could be a component of inflammation and wound healing.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Austgulen R., Nissen-Meyer J. A physico-chemical comparison of the monocyte-derived fibroblast growth factor and the tumour necrosis factor. APMIS. 1988 Apr;96(4):352–356. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1988.tb05315.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blood C. H., Zetter B. R. Tumor interactions with the vasculature: angiogenesis and tumor metastasis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jun 1;1032(1):89–118. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(90)90014-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enerbäck L., Wingren U. Histamine content of peritoneal and tissue mast cells of growing rats. Histochemistry. 1980;66(2):113–124. doi: 10.1007/BF00494639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fajardo L. F., Kwan H. H., Kowalski J., Prionas S. D., Allison A. C. Dual role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in angiogenesis. Am J Pathol. 1992 Mar;140(3):539–544. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Klagsbrun M. Angiogenic factors. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):442–447. doi: 10.1126/science.2432664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giulian D., Woodward J., Young D. G., Krebs J. F., Lachman L. B. Interleukin-1 injected into mammalian brain stimulates astrogliosis and neovascularization. J Neurosci. 1988 Jul;8(7):2485–2490. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-07-02485.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li W. W., Grayson G., Folkman J., D'Amore P. A. Sustained-release endotoxin. A model for inducing corneal neovascularization. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1991 Oct;32(11):2906–2911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattsby-Baltzer I., Lindgren K., Lindholm B., Edebo L. Endotoxin shedding by enterobacteria: free and cell-bound endotoxin differ in Limulus activity. Infect Immun. 1991 Feb;59(2):689–695. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.2.689-695.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May L. T., Torcia G., Cozzolino F., Ray A., Tatter S. B., Santhanam U., Sehgal P. B., Stern D. Interleukin-6 gene expression in human endothelial cells: RNA start sites, multiple IL-6 proteins and inhibition of proliferation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Mar 31;159(3):991–998. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92206-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCuskey R. S., McCuskey P. A., Urbaschek R., Urbaschek B. Species differences in Kupffer cells and endotoxin sensitivity. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):278–280. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.278-280.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Ryan J. L. Endotoxins and disease mechanisms. Annu Rev Med. 1987;38:417–432. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.38.020187.002221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motro B., Itin A., Sachs L., Keshet E. Pattern of interleukin 6 gene expression in vivo suggests a role for this cytokine in angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):3092–3096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.3092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mårild S., Jodal U., Orskov I., Orskov F., Svanborg Edén C. Special virulence of the Escherichia coli O1:K1:H7 clone in acute pyelonephritis. J Pediatr. 1989 Jul;115(1):40–45. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(89)80326-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby K., Eneström S. Cellular and extracellular changes following mast-cell secretion in avascular rat mesentery. An electron-microscopic study. Cell Tissue Res. 1984;235(2):339–345. doi: 10.1007/BF00217858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby K., Jakobsson A., Sörbo J. Age-dependent mast-cell-mediated angiogenesis. APMIS Suppl. 1988;2:251–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby K., Jakobsson A., Sörbo J. Mast-cell secretion and angiogenesis, a quantitative study in rats and mice. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1989;57(4):251–256. doi: 10.1007/BF02899089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby K., Jakobsson A., Sörbo J. Mast-cell-mediated angiogenesis: a novel experimental model using the rat mesentery. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1986;52(3):195–206. doi: 10.1007/BF02889963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
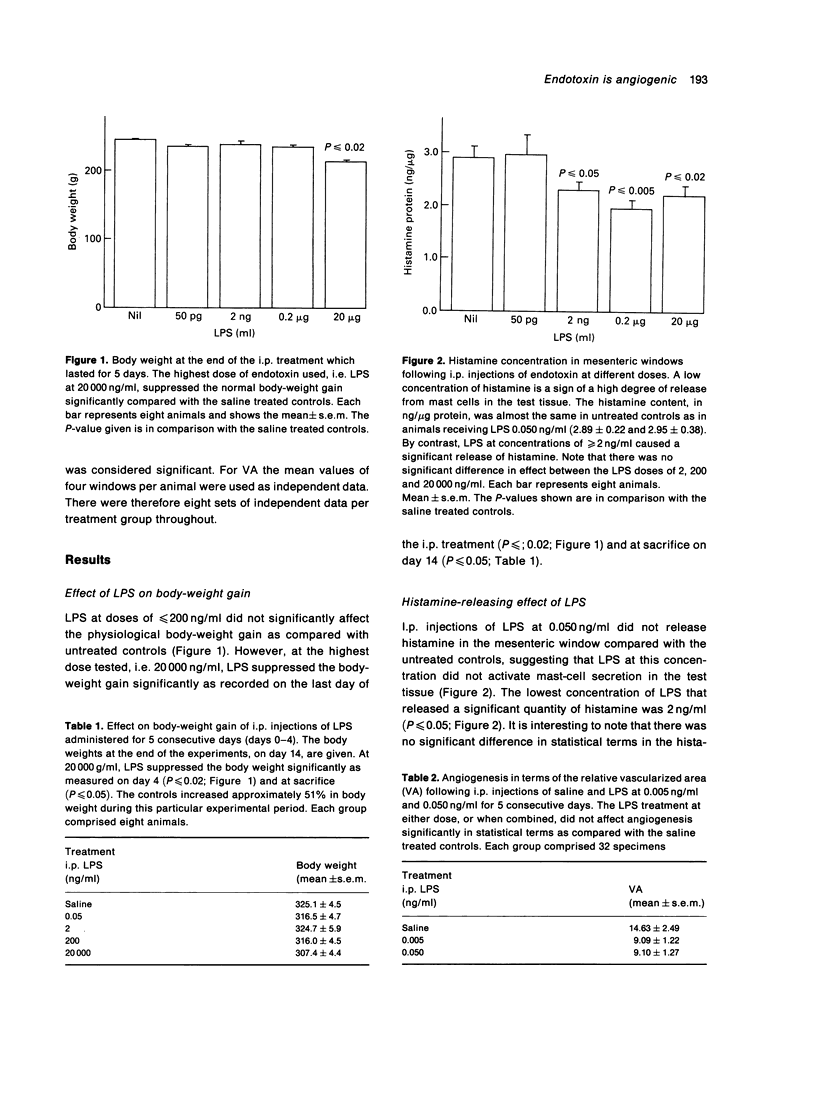
- Norrby K., Jakobsson A., Sörbo J. Quantitative angiogenesis in spreads of intact rat mesenteric windows. Microvasc Res. 1990 May;39(3):341–348. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(90)90047-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partanen J., Vainikka S., Korhonen J., Armstrong E., Alitalo K. Diverse receptors for fibroblast growth factors. Prog Growth Factor Res. 1992;4(1):69–83. doi: 10.1016/0955-2235(92)90005-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
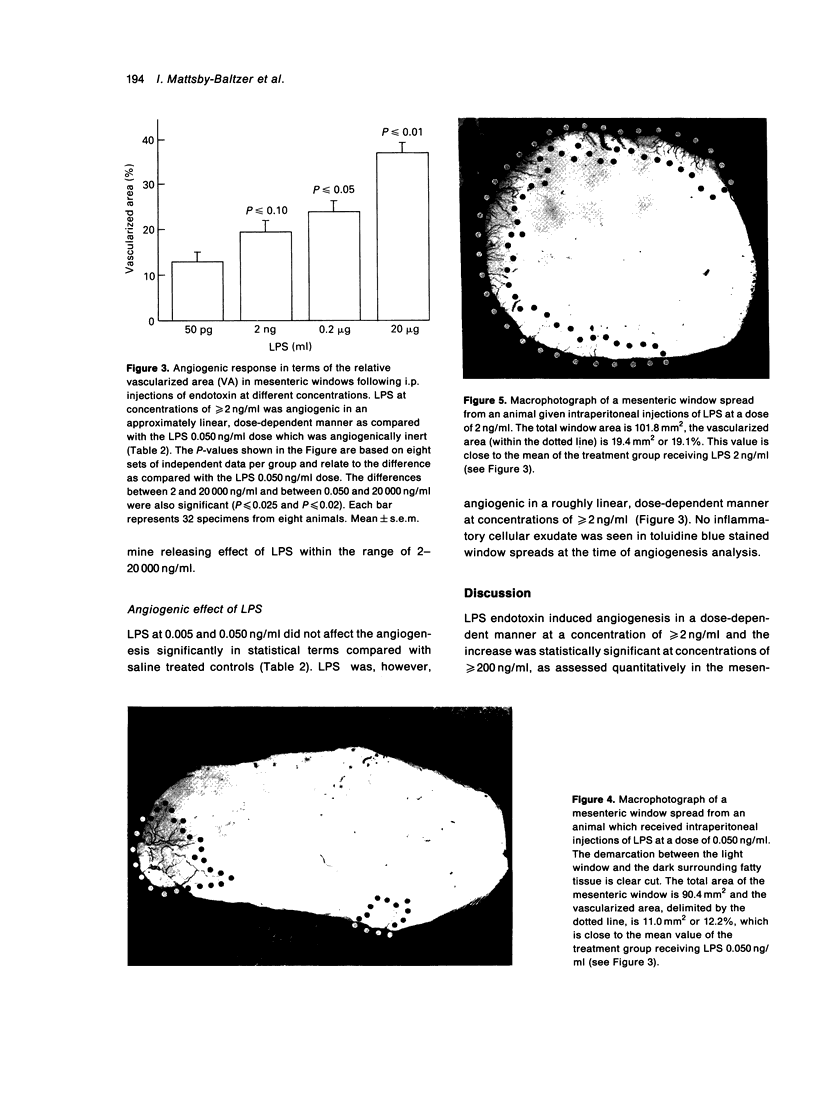
- Piguet P. F., Grau G. E., Vassalli P. Subcutaneous perfusion of tumor necrosis factor induces local proliferation of fibroblasts, capillaries, and epidermal cells, or massive tissue necrosis. Am J Pathol. 1990 Jan;136(1):103–110. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risau W., Drexler H., Mironov V., Smits A., Siegbahn A., Funa K., Heldin C. H. Platelet-derived growth factor is angiogenic in vivo. Growth Factors. 1992;7(4):261–266. doi: 10.3109/08977199209046408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]