Abstract
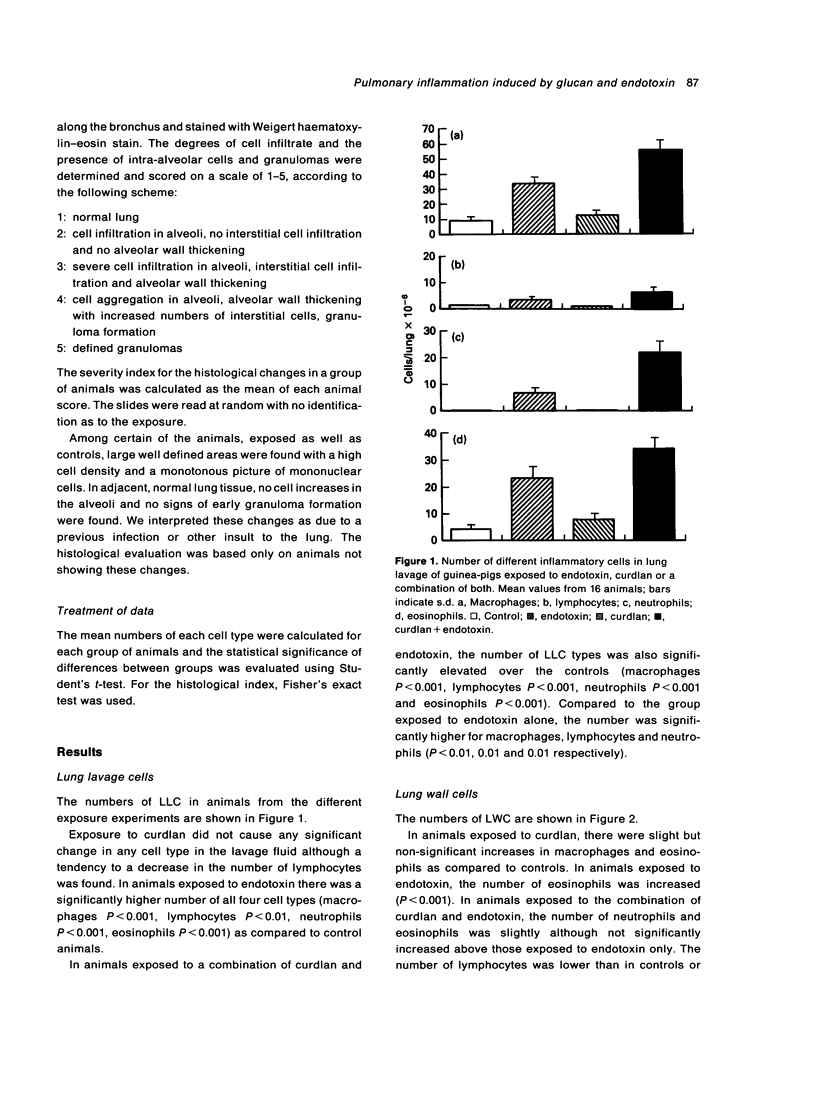
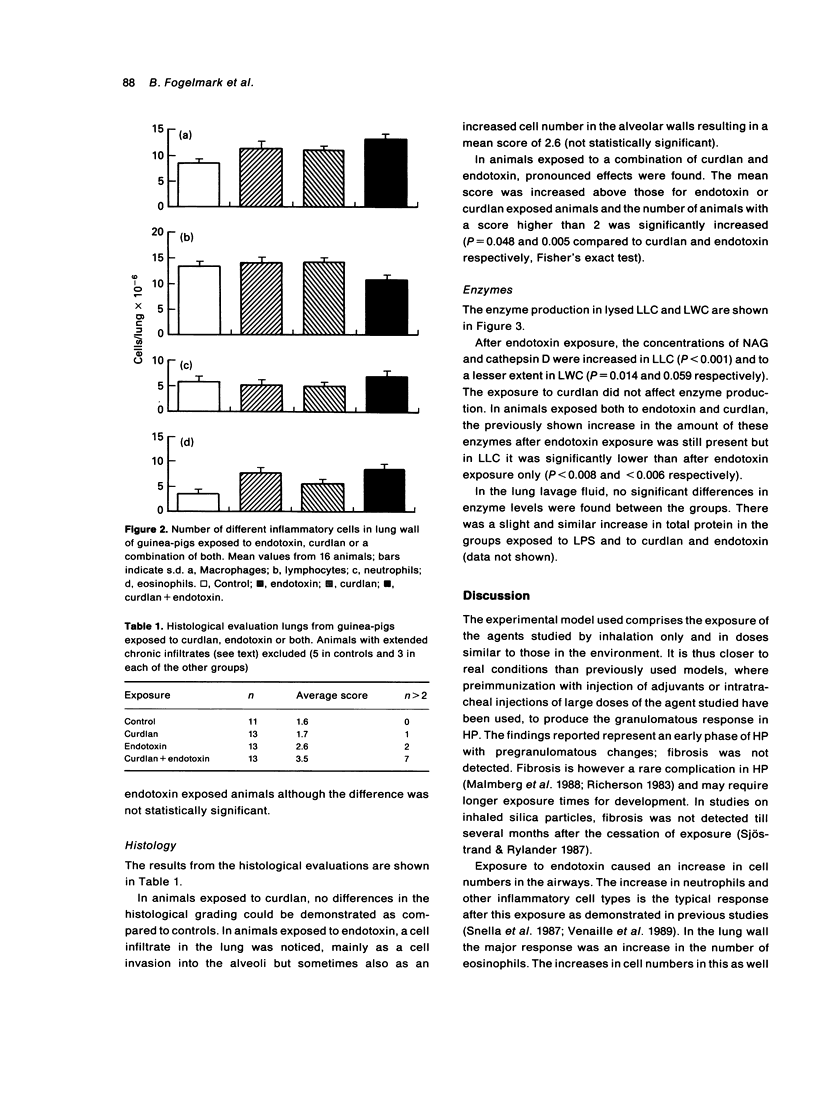
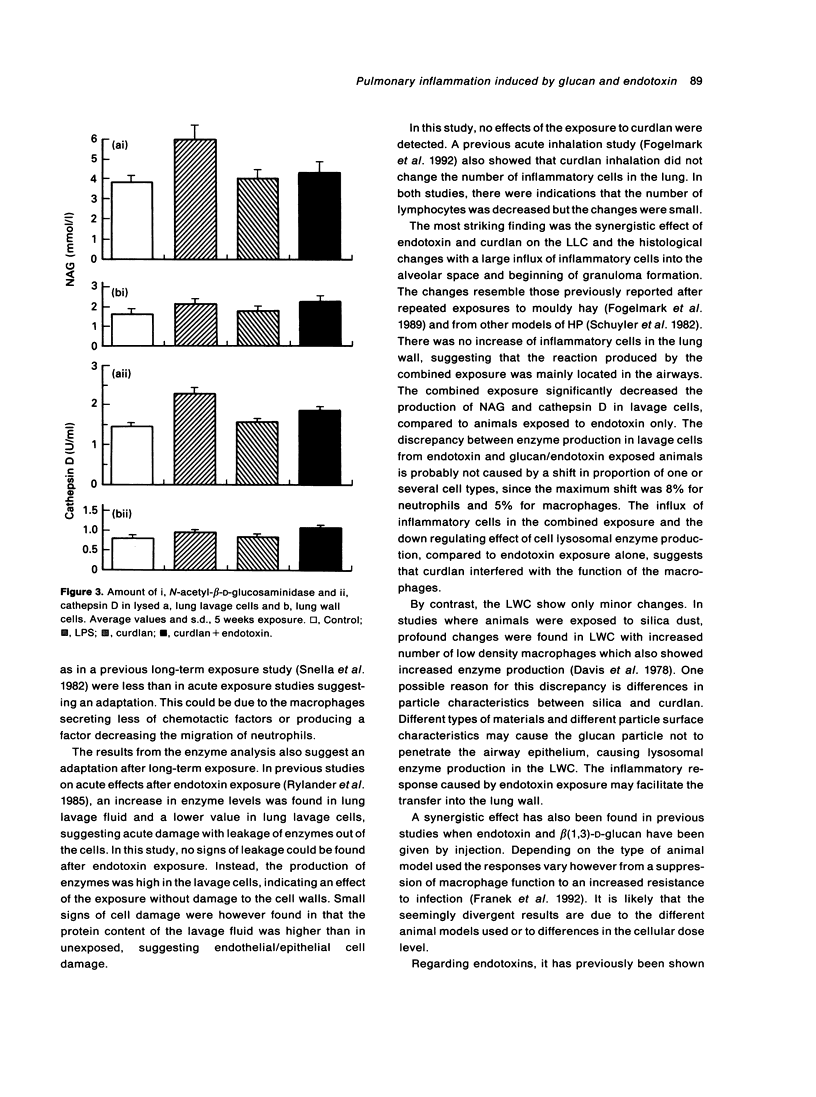
In an animal model of hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP) guinea-pigs were exposed for 5 weeks to an aerosol of bacterial endotoxin, beta(1,3)-D-glucan (curdlan) or a combination. Exposure to endotoxin or curdlan showed only small changes in inflammatory cells in airways or the lung wall, histologically or in terms of enzyme secretion from alveolar macrophages. When the two agents were given together, a histology resembling HP was seen with alveolar infiltrates and early granulomas. Inflammatory cells in airways were increased and enzyme production of macrophages was changed, suggesting an effect of curdlan on the inflammatory regulating capacity of airway macrophages. The results suggest that interference with macrophage function and inflammation are important components in the development of HP.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burrell R. Immunomodulation by bacterial endotoxin. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1990;17(3):189–208. doi: 10.3109/10408419009105725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook J. A., Dougherty W. J., Holt T. M. Enhanced sensitivity to endotoxin induced by the RE stimulant, glucan. Circ Shock. 1980;7(3):225–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis G. S., Brody A. R., Craighead J. E. Analysis of airspace and interstitial mononuclear cell populations in human diffuse interstitial lung disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Jul;118(1):7–15. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.118.1.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Luzio N. R. Update on the immunomodulating activities of glucans. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1985;8(4):387–400. doi: 10.1007/BF01857392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogelmark B., Goto H., Yuasa K., Marchat B., Rylander R. Acute pulmonary toxicity of inhaled beta-1,3-glucan and endotoxin. Agents Actions. 1992 Jan;35(1-2):50–56. doi: 10.1007/BF01990951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogelmark B., Lacey J., Rylander R. Experimental allergic alveolitis after exposure to different microorganisms. Int J Exp Pathol. 1991 Aug;72(4):387–395. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogelmark B., Rylander R., Lacey J. Experimental allergic alveolitis after inhalation of mouldy hay. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1989 Oct;30(2):81–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogelmark B., Rylander R. Lung inflammatory cells after exposure to mouldy hay. Agents Actions. 1993 May;39(1-2):25–30. doi: 10.1007/BF01975710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournier E., Tonnel A. B., Gosset P., Wallaert B., Ameisen J. C., Voisin C. Early neutrophil alveolitis after antigen inhalation in hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Chest. 1985 Oct;88(4):563–566. doi: 10.1378/chest.88.4.563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franek J., Malina J., Krátká H. Bacterial infection modulated by glucan: a search for the host defense potentiation mechanisms. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1992;37(2):146–152. doi: 10.1007/BF02836620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt P. G., Degebrodt A., Venaille T., O'Leary C., Krska K., Flexman J., Farrell H., Shellam G., Young P., Penhale J. Preparation of interstitial lung cells by enzymatic digestion of tissue slices: preliminary characterization by morphology and performance in functional assays. Immunology. 1985 Jan;54(1):139–147. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. J., Glovsky M., Schrier D. Pulmonary granulomatous vasculitis. Pulmonary granulomatous vasculitis induced in rats by treatment with glucan. Am J Pathol. 1984 Mar;114(3):515–516. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson K., Malmberg P., Eklund A., Belin L., Blaschke E. Exposure to microorganisms, airway inflammatory changes and immune reactions in asymptomatic dairy farmers. Bronchoalveolar lavage evidence of macrophage activation and permeability changes in the airways. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1988;87(2):127–133. doi: 10.1159/000234662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richerson H. B. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis--pathology and pathogenesis. Clin Rev Allergy. 1983 Dec;1(4):469–486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rylander R., Fogelmark B., Sjöstrand M. Free lung cell phagocytosis and lysosomal enzyme activity after inhalation of lipopolysaccharide in guinea-pigs. Agents Actions. 1985 Jul;16(5):353–358. doi: 10.1007/BF01982872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rylander R. Pulmonary defence mechanisms to airborne bacteria. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1968;306:1–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuyler M., Schmitt D., Steinberg D. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis in strain II guinea pigs. I. Histologic features. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1982;68(2):108–111. doi: 10.1159/000233077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöstrand M., Absher P. M., Hemenway D. R., Trombley L., Baldor L. C. Comparison of lung alveolar and tissue cells in silica-induced inflammation. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991 Jan;143(1):47–52. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/143.1.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöstrand M., Rylander R. Lysosomal enzyme activity and fibroblast stimulation of lavage from guinea pigs exposed to silica dust. Br J Exp Pathol. 1987 Jun;68(3):309–318. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snella M. C., Rylander R. Lung cell reactions after inhalation of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Respir Dis. 1982 Nov;63(6):550–557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snella M. C., Venaille T., Holt P., Rylander R. Interstitial and free lung cells in acute inflammation in the guinea-pig. Agents Actions. 1987 Dec;22(3-4):261–269. doi: 10.1007/BF02009055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venaille T., Snella M. C., Holt P. G., Rylander R. Cell recruitment into lung wall and airways of conventional and pathogen-free guinea pigs after inhalation of endotoxin. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Jun;139(6):1356–1360. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/139.6.1356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


