Abstract
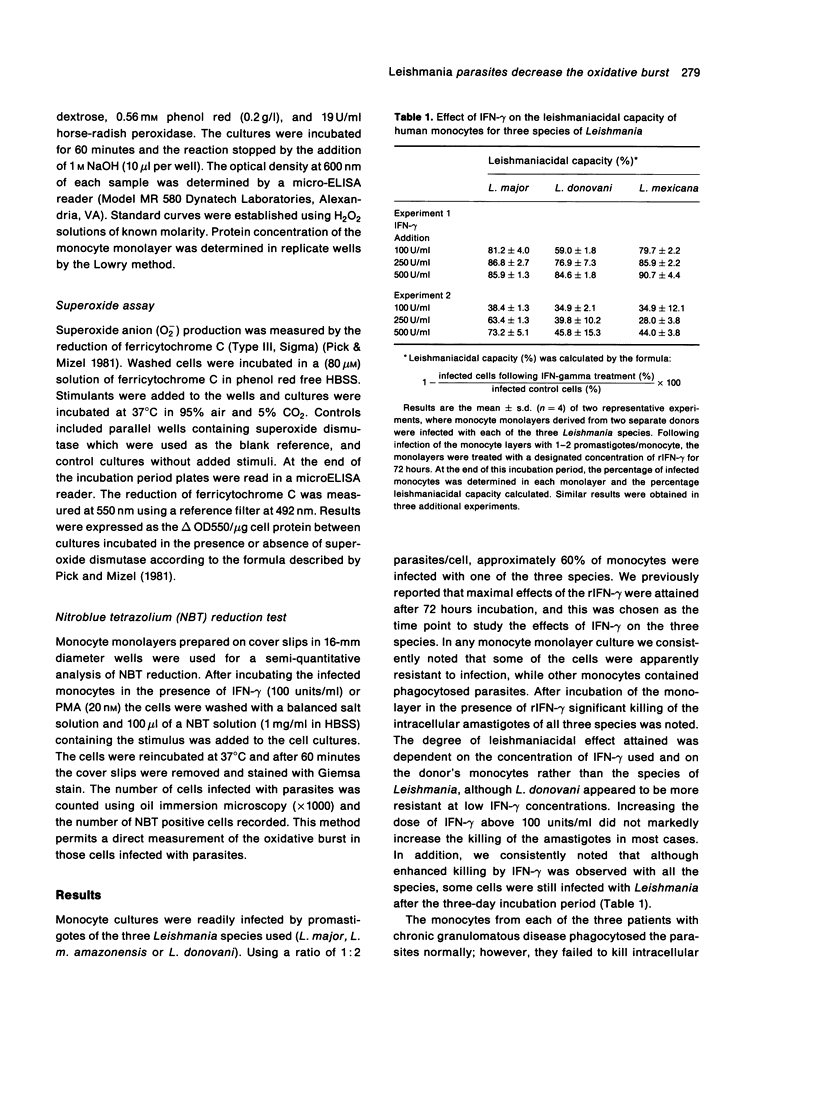
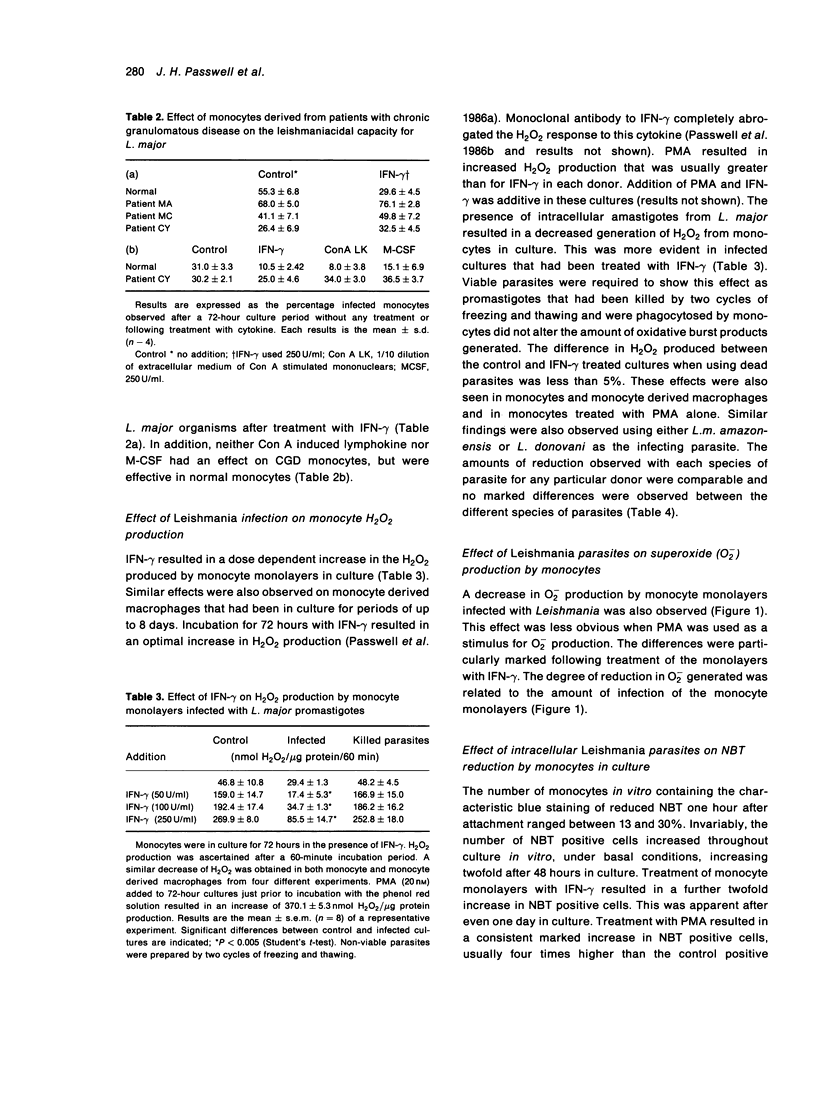
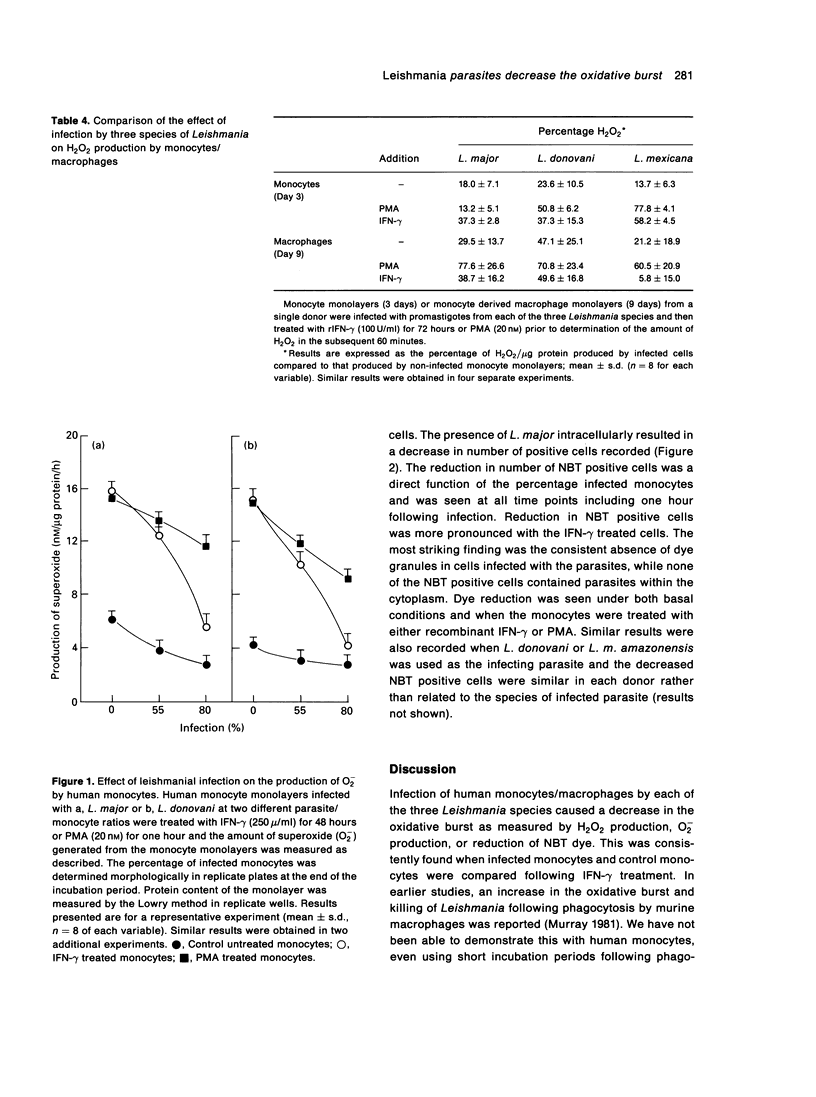
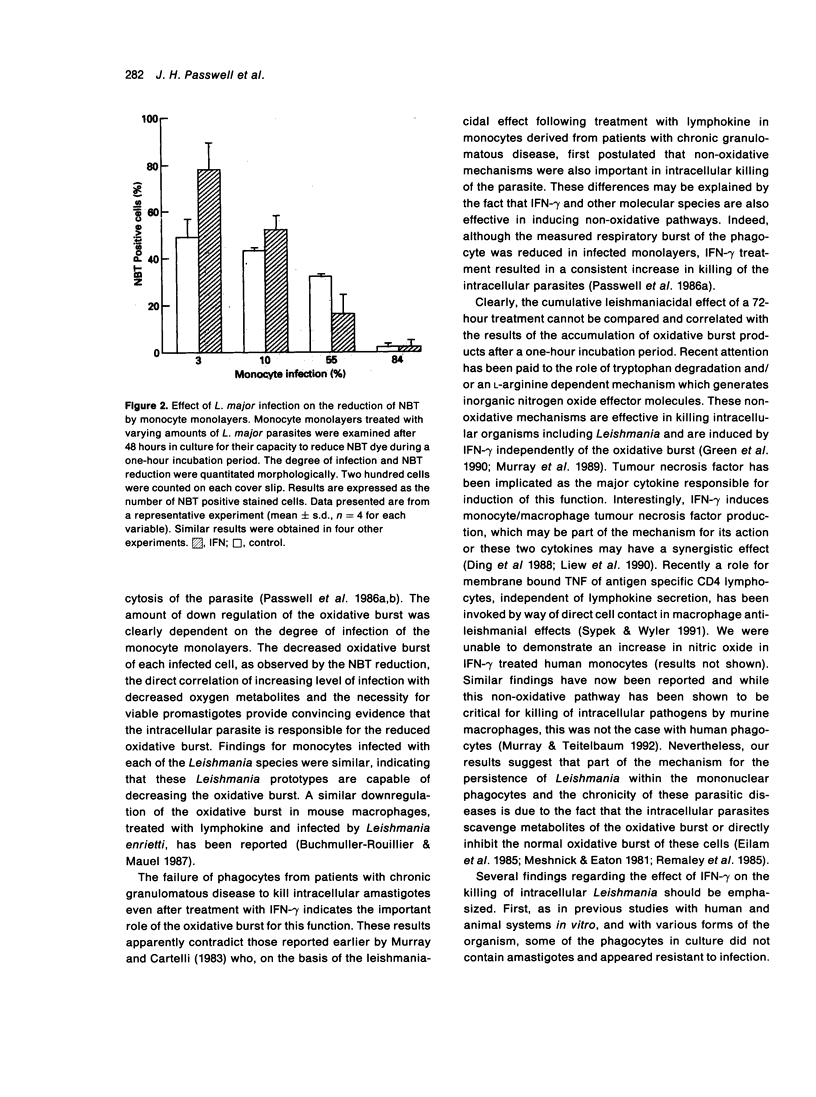
The effect of infection by prototypes from the three major species of Leishmania on the oxidative burst of human mononuclear phagocytes in culture was examined. The presence of intracellular parasites of the three species, L.major, L.donovani and L.mexicana decreased hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and superoxide anion (O2-) production. This was particularly apparent when infected cells were compared to control monocytes following treatment with IFN-gamma. Nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT) reduction by monocytes was also decreased in infected cells. This morphological analysis of infected monolayers clearly showed that infected monocytes were incapable of reducing the dye as compared to uninfected cells. Decrease in NBT positive cells and production of H2O2 and O2- was related to the degree of infection of the monocyte monolayers. These results suggest that the presence of intracellular Leishmania amastigotes in mononuclear phagocytes decreases the oxidative burst and may contribute to parasite survival. Failure of phagocytes from patients with chronic granulomatous disease to kill these intracellular parasites also emphasized the importance of the oxidative burst for this function. Nevertheless, the consistent increase in leishmaniacidal effect attained after IFN-gamma treatment of the monocyte monolayers indicates that other non-oxidative mechanisms induced by this cytokine are also important in the killing of these intracellular parasites.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belosevic M., Davis C. E., Meltzer M. S., Nacy C. A. Regulation of activated macrophage antimicrobial activities. Identification of lymphokines that cooperate with IFN-gamma for induction of resistance to infection. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 1;141(3):890–896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmüller-Rouiller Y., Mauël J. Impairment of the oxidative metabolism of mouse peritoneal macrophages by intracellular Leishmania spp. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):587–593. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.587-593.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmüller Y., Mauel J. Studies on the mechanisms of macrophage activation. II. Parasite destruction in macrophages activated by supernates from concanavalin A-stimulated lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1979 Aug 1;150(2):359–370. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.2.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding A. H., Nathan C. F., Stuehr D. J. Release of reactive nitrogen intermediates and reactive oxygen intermediates from mouse peritoneal macrophages. Comparison of activating cytokines and evidence for independent production. J Immunol. 1988 Oct 1;141(7):2407–2412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilam Y., El-On J., Spira D. T. Leishmania major: excreted factor, calcium ions, and the survival of amastigotes. Exp Parasitol. 1985 Apr;59(2):161–168. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(85)90068-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S. J., Meltzer M. S., Hibbs J. B., Jr, Nacy C. A. Activated macrophages destroy intracellular Leishmania major amastigotes by an L-arginine-dependent killing mechanism. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 1;144(1):278–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haidaris C. G., Bonventre P. F. A role for oxygen-dependent mechanisms in killing of Leishmania donovani tissue forms by activated macrophages. J Immunol. 1982 Aug;129(2):850–855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinzel F. P., Sadick M. D., Holaday B. J., Coffman R. L., Locksley R. M. Reciprocal expression of interferon gamma or interleukin 4 during the resolution or progression of murine leishmaniasis. Evidence for expansion of distinct helper T cell subsets. J Exp Med. 1989 Jan 1;169(1):59–72. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huszar M., Shor R., Trau H., Gazit E., Passwell J. H. The T cell phenotypes in the lesion of patients with cutaneous leishmaniasis. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1987 Mar;12(2):103–107. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2230.1987.tb01874.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liew F. Y., Li Y., Millott S. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha synergizes with IFN-gamma in mediating killing of Leishmania major through the induction of nitric oxide. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 15;145(12):4306–4310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meshnick S. R., Eaton J. W. Leishmanial superoxide dismutase: a possible target for chemotherapy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Oct 15;102(3):970–976. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91633-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modlin R. L., Tapia F. J., Bloom B. R., Gallinoto M. E., Castes M., Rondon A. J., Rea T. H., Convit J. In situ characterization of the cellular immune response in American cutaneous leishmaniasis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 May;60(2):241–248. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Cartelli D. M. Killing of intracellular Leishmania donovani by human mononuclear phagocytes. Evidence for oxygen-dependent and -independent leishmanicidal activity. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):32–44. doi: 10.1172/JCI110972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W. Interaction of Leishmania with a macrophage cell line. Correlation between intracellular killing and the generation of oxygen intermediates. J Exp Med. 1981 Jun 1;153(6):1690–1695. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.6.1690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Masur H., Keithly J. S. Cell-mediated immune response in experimental visceral leishmaniasis. I. Correlation between resistance to Leishmania donovani and lymphokine-generating capacity. J Immunol. 1982 Jul;129(1):344–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Rubin B. Y., Rothermel C. D. Killing of intracellular Leishmania donovani by lymphokine-stimulated human mononuclear phagocytes. Evidence that interferon-gamma is the activating lymphokine. J Clin Invest. 1983 Oct;72(4):1506–1510. doi: 10.1172/JCI111107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W. Susceptibility of Leishmania to oxygen intermediates and killing by normal macrophages. J Exp Med. 1981 May 1;153(5):1302–1315. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.5.1302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Szuro-Sudol A., Wellner D., Oca M. J., Granger A. M., Libby D. M., Rothermel C. D., Rubin B. Y. Role of tryptophan degradation in respiratory burst-independent antimicrobial activity of gamma interferon-stimulated human macrophages. Infect Immun. 1989 Mar;57(3):845–849. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.3.845-849.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Teitelbaum R. F. L-arginine-dependent reactive nitrogen intermediates and the antimicrobial effect of activated human mononuclear phagocytes. J Infect Dis. 1992 Mar;165(3):513–517. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.3.513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nacy C. A., Fortier A. H., Meltzer M. S., Buchmeier N. A., Schreiber R. D. Macrophage activation to kill Leishmania major: activation of macrophages for intracellular destruction of amastigotes can be induced by both recombinant interferon-gamma and non-interferon lymphokines. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3505–3511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nacy C. A., Meltzer M. S., Leonard E. J., Wyler D. J. Intracellular replication and lymphokine-induced destruction of Leishmania tropica in C3H/HeN mouse macrophages. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2381–2386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Murray H. W., Wiebe M. E., Rubin B. Y. Identification of interferon-gamma as the lymphokine that activates human macrophage oxidative metabolism and antimicrobial activity. J Exp Med. 1983 Sep 1;158(3):670–689. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.3.670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passwell J. H., Shor R., Gazit E., Shoham J. The effects of Con A-induced lymphokines from the T-lymphocyte subpopulations on human monocyte leishmanicidal capacity and H2O2 production. Immunology. 1986 Oct;59(2):245–250. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passwell J. H., Shor R., Shoham J. The enhancing effect of interferon-beta and -gamma on the killing of Leishmania tropica major in human mononuclear phagocytes in vitro. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 15;136(8):3062–3066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passwell J., Shor R., Keren G., Messer G., El-On J. Comparison of the effect of various stimuli on the leishmaniacidal capacity of human monocytes in vitro. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Jun;56(3):553–558. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. D., Wheeler D. A., Harrison L. H., Kay H. D. The immunobiology of leishmaniasis. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Sep-Oct;5(5):907–927. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.5.907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pick E., Keisari Y. A simple colorimetric method for the measurement of hydrogen peroxide produced by cells in culture. J Immunol Methods. 1980;38(1-2):161–170. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90340-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pick E., Mizel D. Rapid microassays for the measurement of superoxide and hydrogen peroxide production by macrophages in culture using an automatic enzyme immunoassay reader. J Immunol Methods. 1981;46(2):211–226. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90138-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiner N. E., Ng W., McMaster W. R. Parasite-accessory cell interactions in murine leishmaniasis. II. Leishmania donovani suppresses macrophage expression of class I and class II major histocompatibility complex gene products. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 15;138(6):1926–1932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remaley A. T., Das S., Campbell P. I., LaRocca G. M., Pope M. T., Glew R. H. Characterization of Leishmania donovani acid phosphatases. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):880–886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnur L. F., Zuckerman A., Greenblatt C. L. Leishmanial serotypes as distinguished by the gel diffusion of factors excreted in vitro and in vivo. Isr J Med Sci. 1972 Jul;8(7):932–942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sypek J. P., Wyler D. J. Antileishmanial defense in macrophages triggered by tumor necrosis factor expressed on CD4+ T lymphocyte plasma membrane. J Exp Med. 1991 Oct 1;174(4):755–759. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.4.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


