Abstract
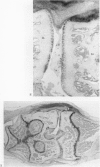
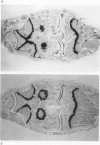
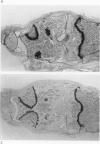
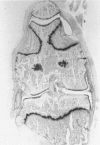
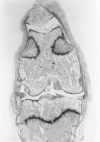
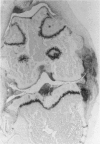
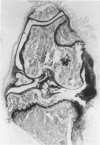
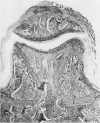
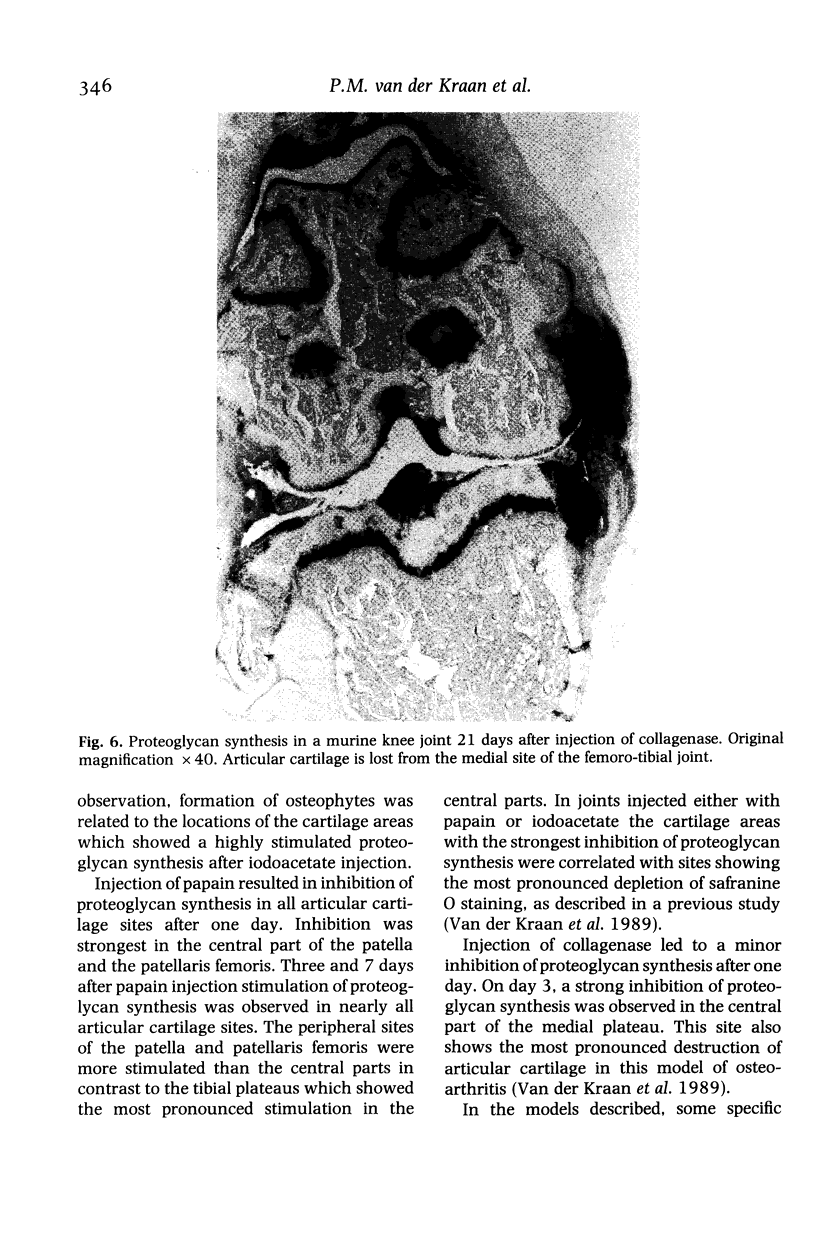
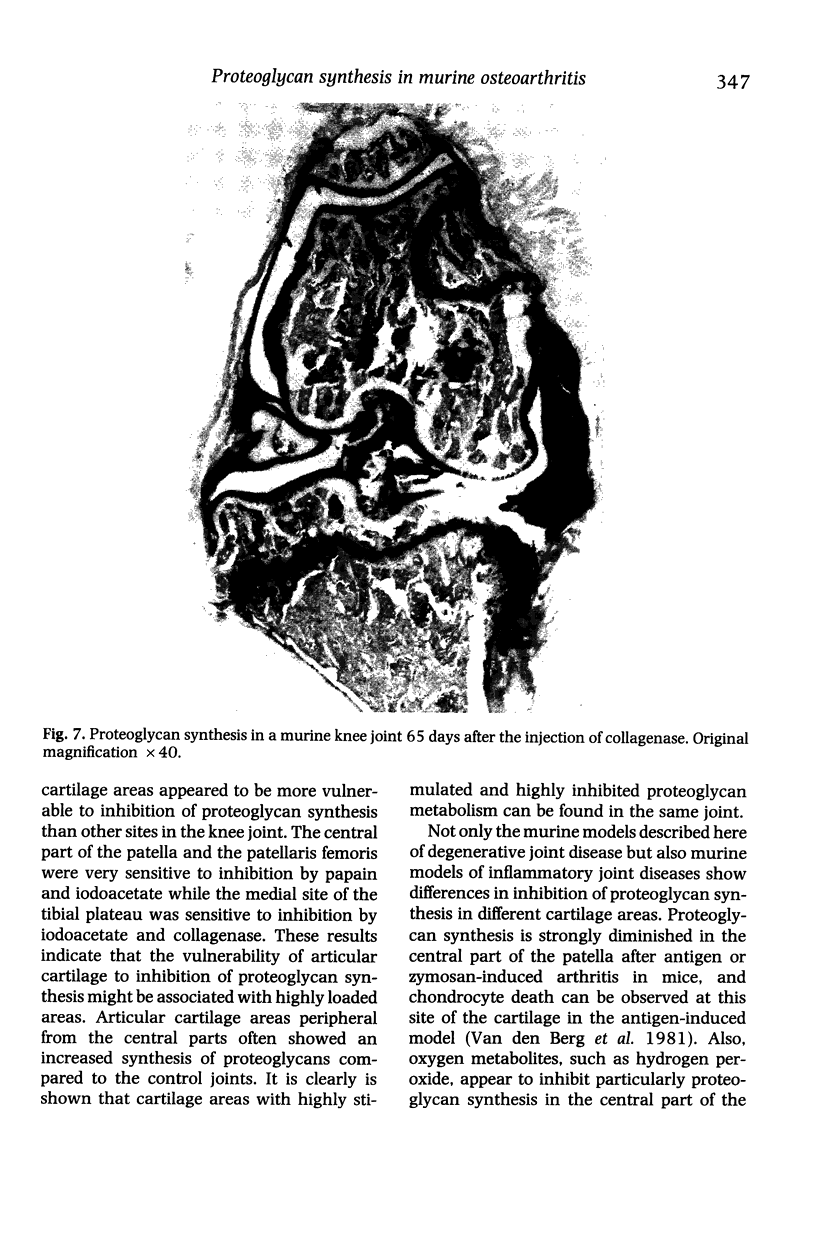
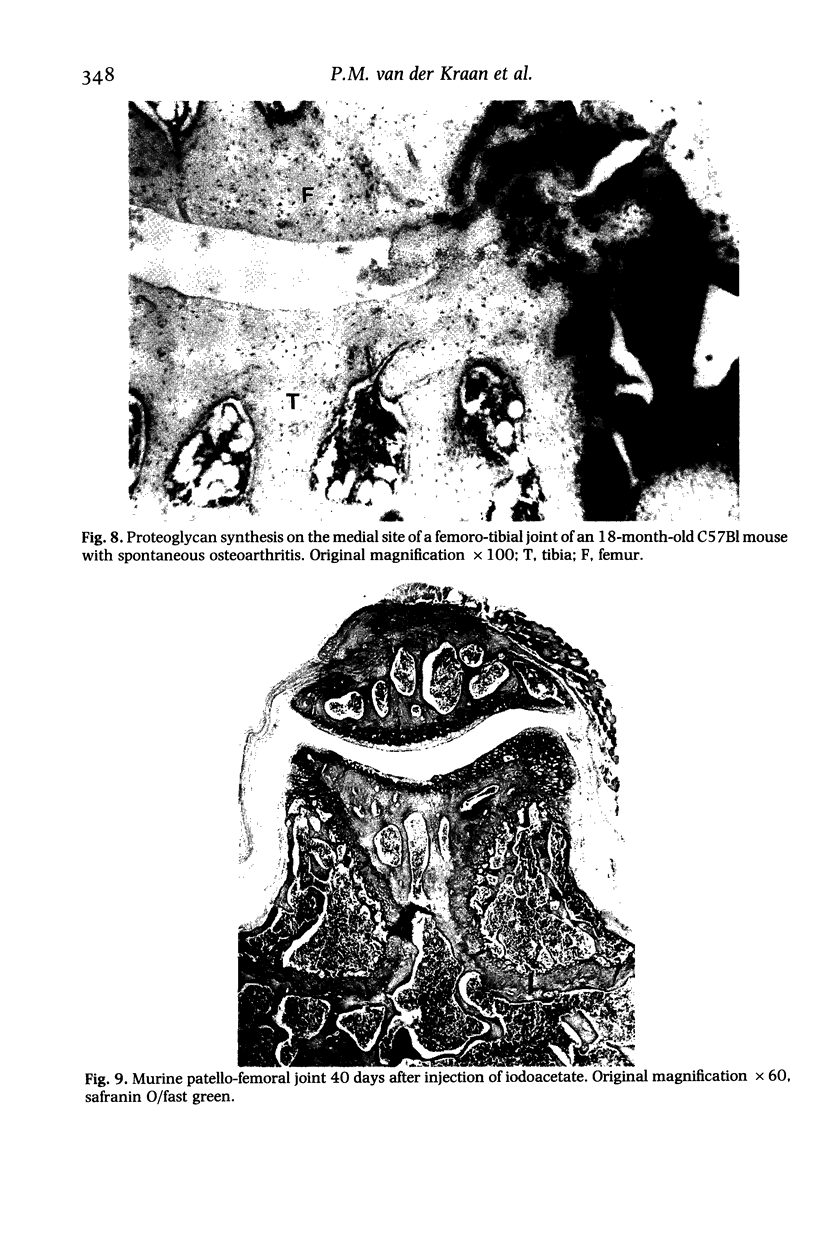
We investigated the in-vivo proteoglycan synthesis in specific areas of murine knee joint articular cartilage after the induction of degenerative joint disease by means of 35S-sulphate autoradiography. Degenerative joint disease was induced either by direct interference with cartilage metabolism (papain and iodoacetate), or by the induction of joint instability (collagenase). Injection of iodoacetate and papain led to inhibition of proteoglycan synthesis mainly in the central parts of the patellae, patellaris femoris and the central part of the medial tibial plateau. Articular cartilage adjacent to the strongly inhibited areas frequently showed a significantly enhanced synthesis of proteoglycans. A strong inhibition of proteoglycan synthesis was observed in the central part of the medial plateau after collagenase injection while other cartilage sites and joint structures such as the capsule and ligaments were stimulated in their proteoglycan synthesis. This study shows that the localization of changes in cartilage metabolism in degenerative joint disease of the knee might be related to differences in the pathogenetic mechanism in different variants of this common joint disorder.
Full text
PDF

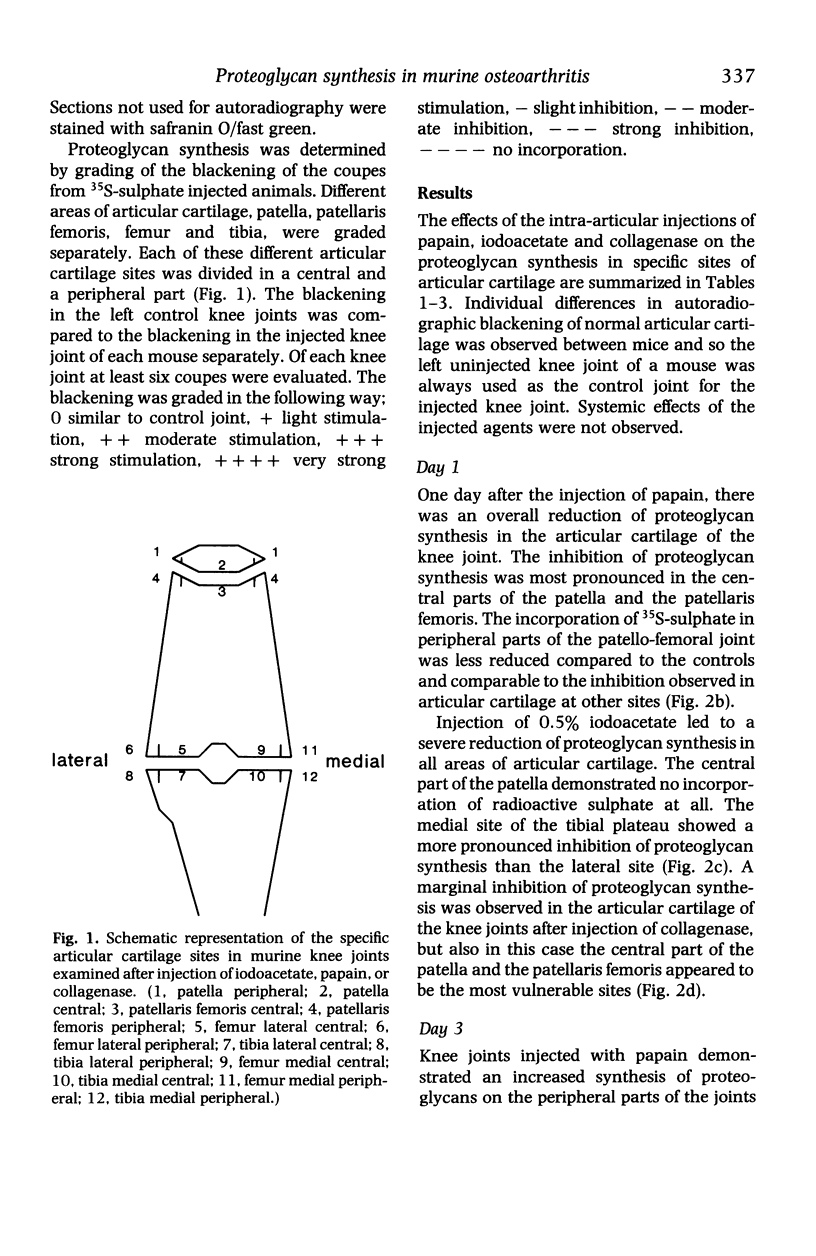
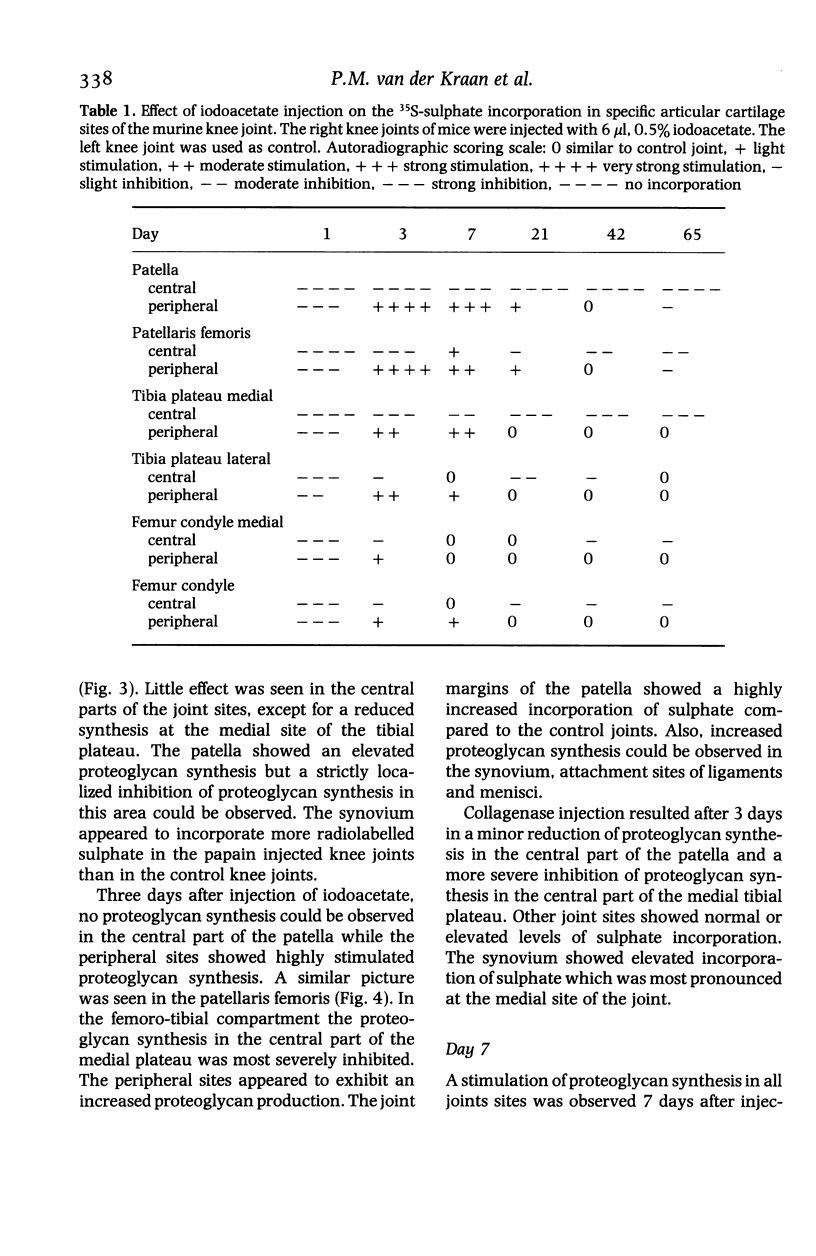
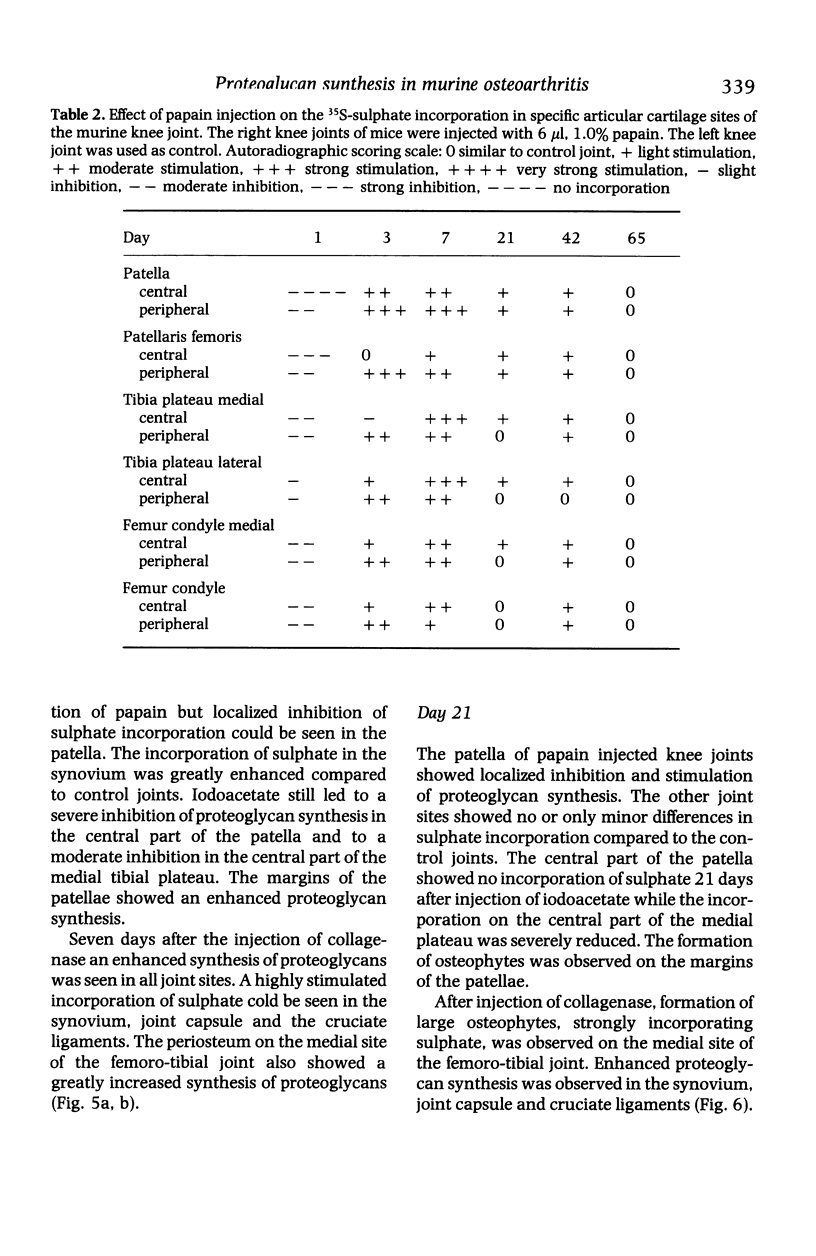
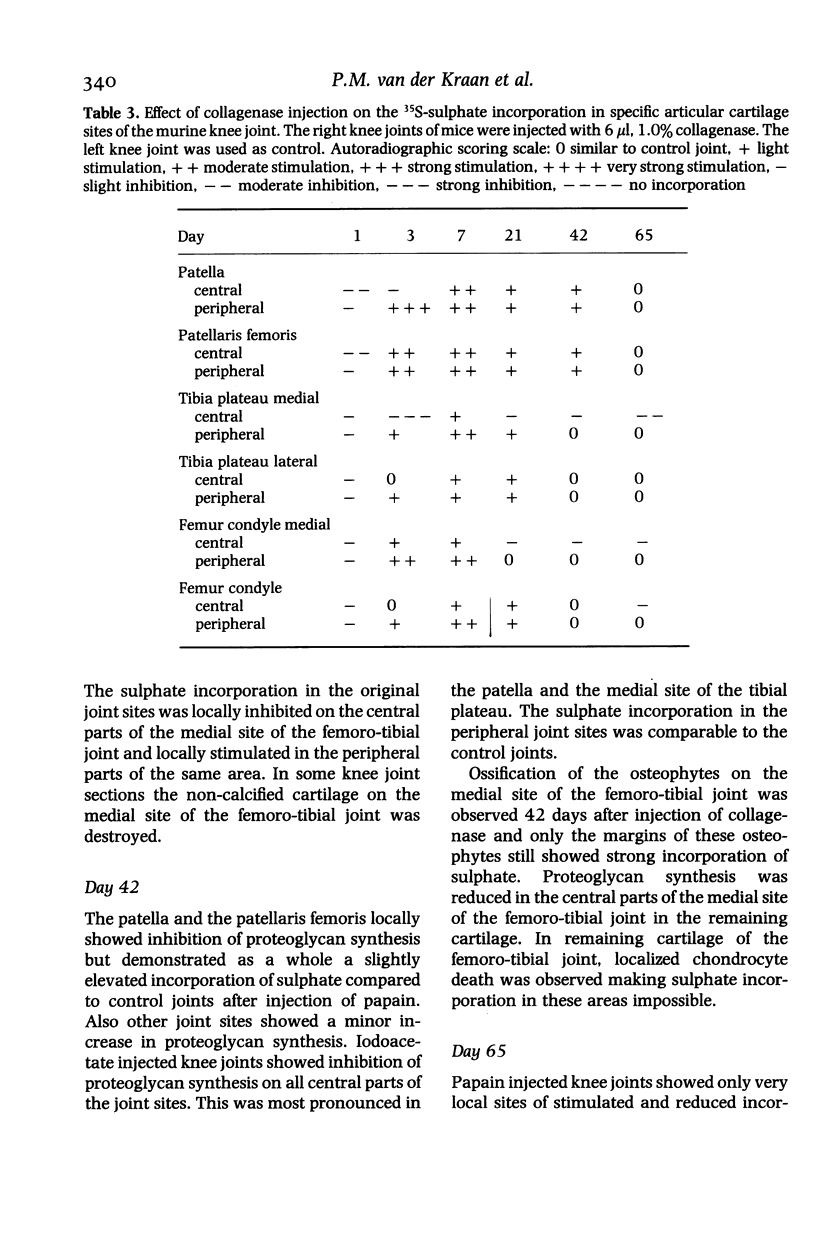
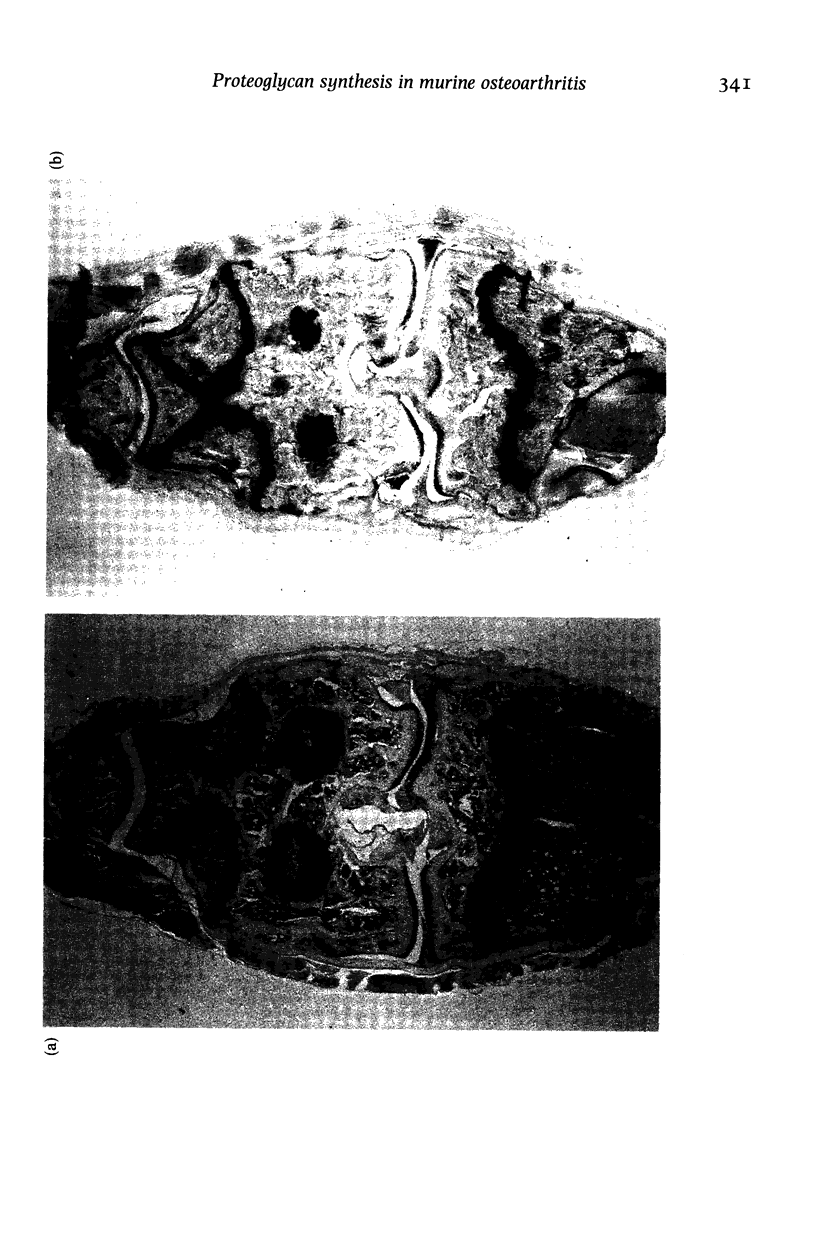
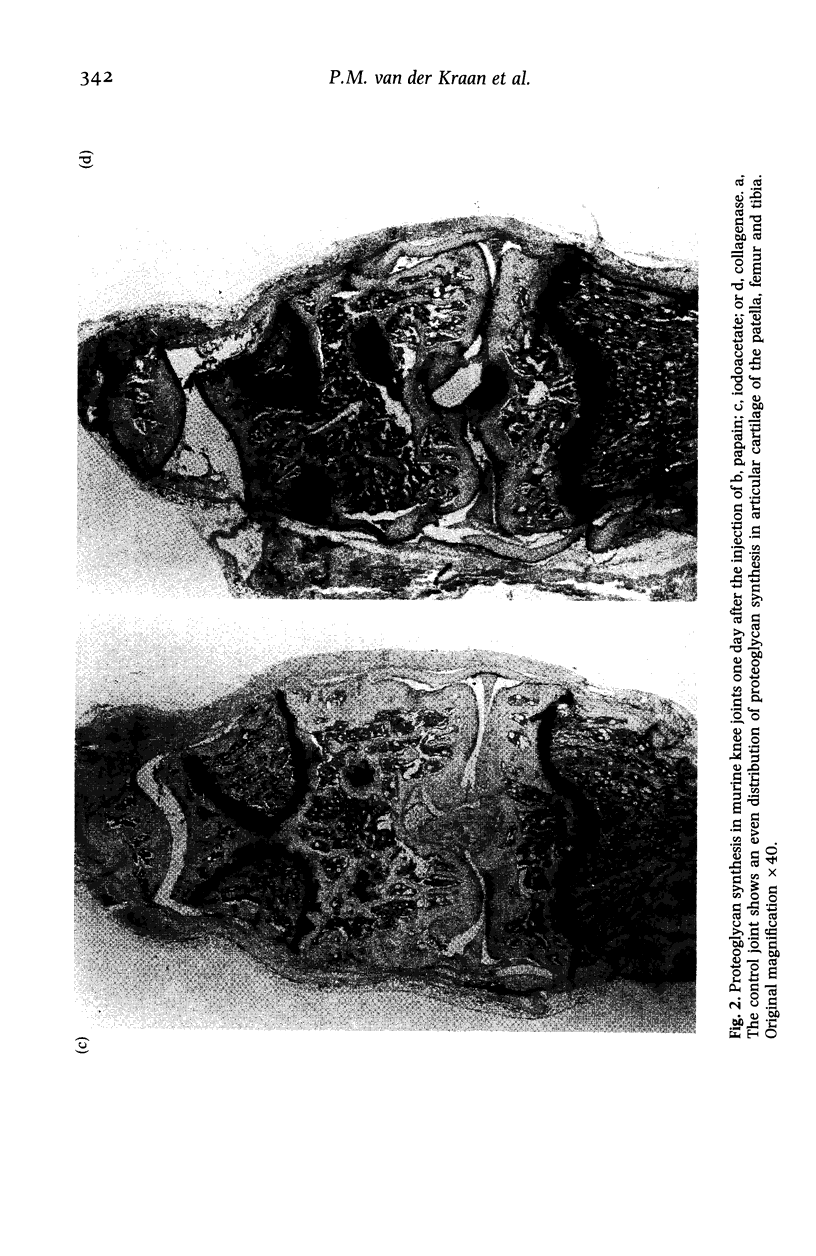
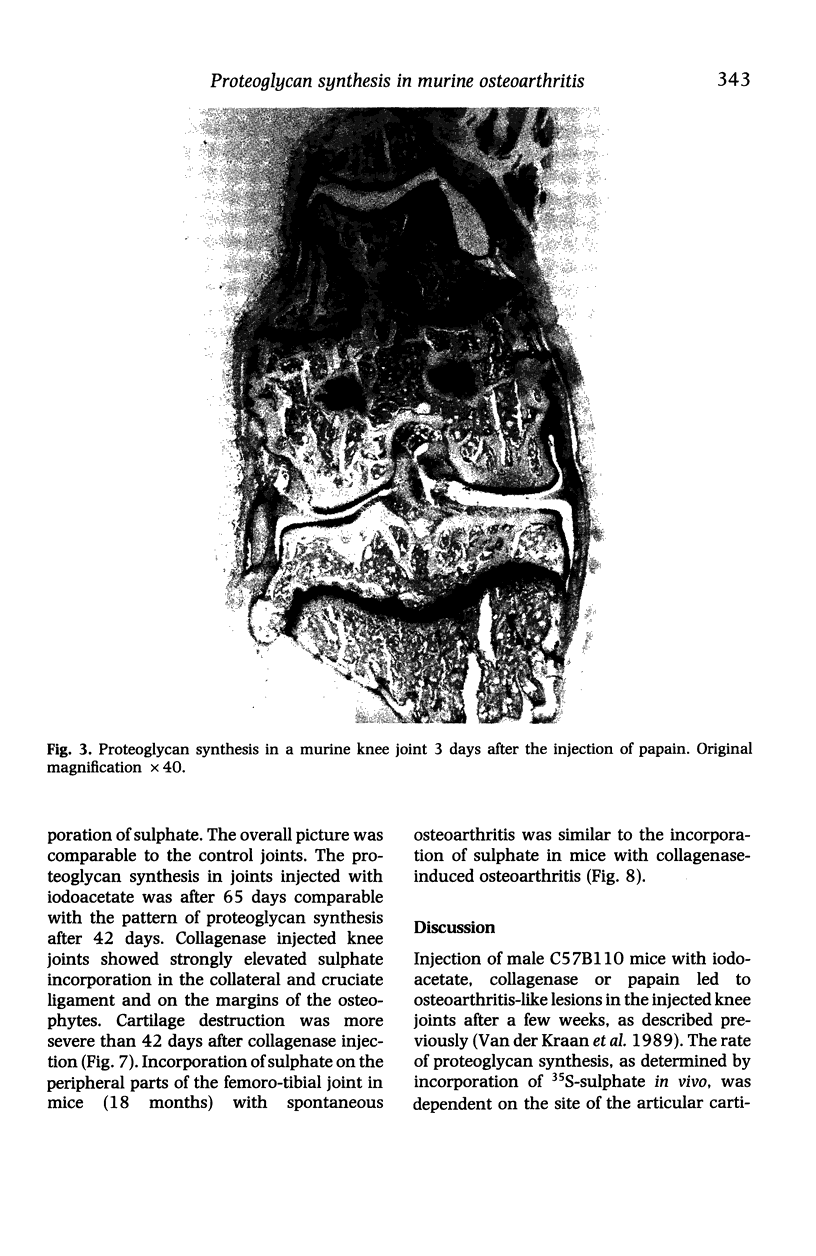
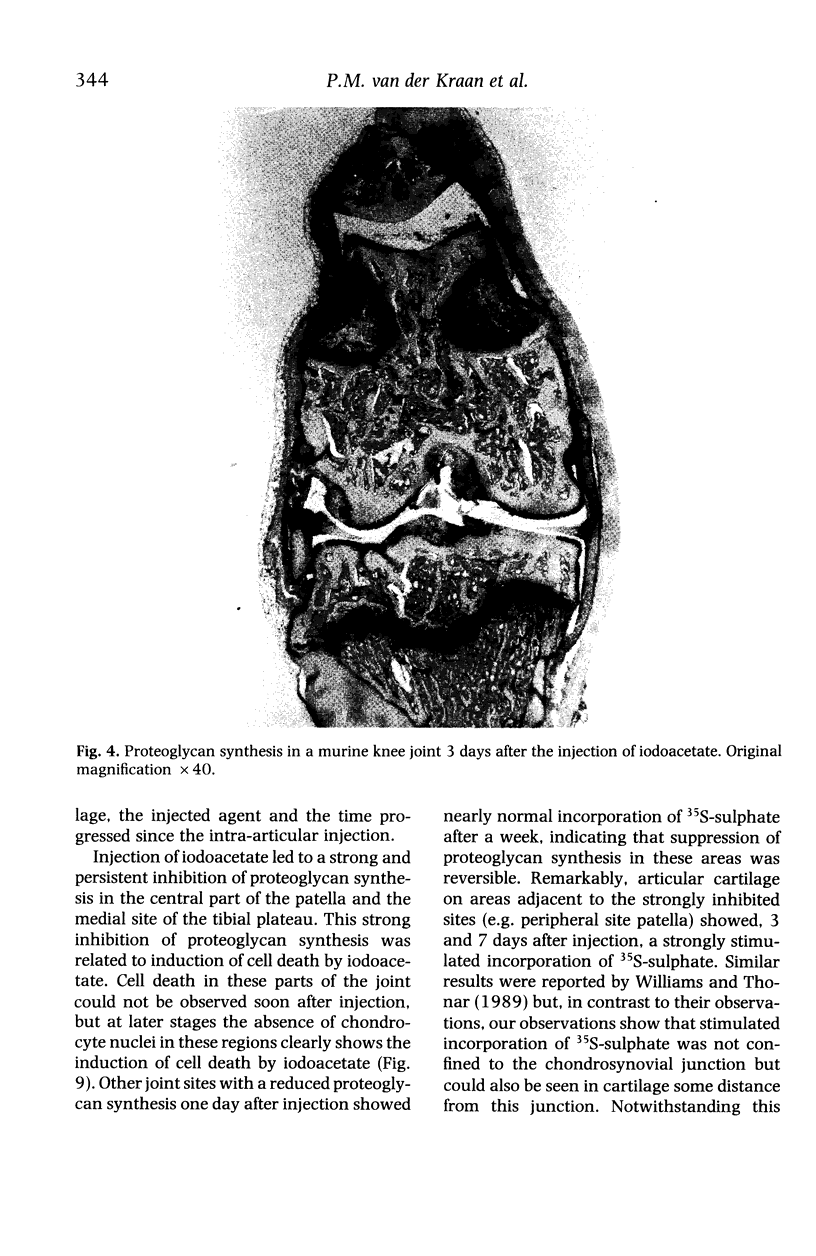



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allard S. A., Bayliss M. T., Maini R. N. The synovium-cartilage junction of the normal human knee. Implications for joint destruction and repair. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Aug;33(8):1170–1179. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altman R. D., Tenenbaum J., Latta L., Riskin W., Blanco L. N., Howell D. S. Biomechanical and biochemical properties of dog cartilage in experimentally induced osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1984 Feb;43(1):83–90. doi: 10.1136/ard.43.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendele A. M. Progressive chronic osteoarthritis in femorotibial joints of partial medial meniscectomized guinea pigs. Vet Pathol. 1987 Sep;24(5):444–448. doi: 10.1177/030098588702400512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brocklehurst R., Bayliss M. T., Maroudas A., Coysh H. L., Freeman M. A., Revell P. A., Ali S. Y. The composition of normal and osteoarthritic articular cartilage from human knee joints. With special reference to unicompartmental replacement and osteotomy of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1984 Jan;66(1):95–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carney S. L., Billingham M. E., Muir H., Sandy J. D. Demonstration of increased proteoglycan turnover in cartilage explants from dogs with experimental osteoarthritis. J Orthop Res. 1984;2(3):201–206. doi: 10.1002/jor.1100020301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colombo C., Butler M., O'Byrne E., Hickman L., Swartzendruber D., Selwyn M., Steinetz B. A new model of osteoarthritis in rabbits. I. Development of knee joint pathology following lateral meniscectomy and section of the fibular collateral and sesamoid ligaments. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Jul;26(7):875–886. doi: 10.1002/art.1780260709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean D. D., Martel-Pelletier J., Pelletier J. P., Howell D. S., Woessner J. F., Jr Evidence for metalloproteinase and metalloproteinase inhibitor imbalance in human osteoarthritic cartilage. J Clin Invest. 1989 Aug;84(2):678–685. doi: 10.1172/JCI114215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mankin H. J., Dorfman H., Lippiello L., Zarins A. Biochemical and metabolic abnormalities in articular cartilage from osteo-arthritic human hips. II. Correlation of morphology with biochemical and metabolic data. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1971 Apr;53(3):523–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mankin H. J., Johnson M. E., Lippiello L. Biochemical and metabolic abnormalities in articular cartilage from osteoarthritic human hips. III. Distribution and metabolism of amino sugar-containing macromolecules. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1981 Jan;63(1):131–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskowitz R. W., Davis W., Sammarco J., Martens M., Baker J., Mayor M., Burstein A. H., Frankel V. H. Experimentally induced degenerative joint lesions following partial meniscectomy in the rabbit. Arthritis Rheum. 1973 May-Jun;16(3):397–405. doi: 10.1002/art.1780160317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakahara H., Bruder S. P., Goldberg V. M., Caplan A. I. In vivo osteochondrogenic potential of cultured cells derived from the periosteum. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990 Oct;(259):223–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J. P., Martel-Pelletier J. Cartilage degradation by neutral proteoglycanases in experimental osteoarthritis. Suppression by steroids. Arthritis Rheum. 1985 Dec;28(12):1393–1401. doi: 10.1002/art.1780281212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J. P., Martel-Pelletier J., Cloutier J. M., Woessner J. F., Jr Proteoglycan-degrading acid metalloprotease activity in human osteoarthritic cartilage, and the effect of intraarticular steroid injections. Arthritis Rheum. 1987 May;30(5):541–548. doi: 10.1002/art.1780300508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandy J. D., Adams M. E., Billingham M. E., Plaas A., Muir H. In vivo and in vitro stimulation of chondrocyte biosynthetic activity in early experimental osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1984 Apr;27(4):388–397. doi: 10.1002/art.1780270405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapolsky A. I., Howell D. S., Woessner J. F., Jr Neutral proteases and cathepsin D in human articular cartilage. J Clin Invest. 1974 Apr;53(4):1044–1053. doi: 10.1172/JCI107641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalkwijk J., van den Berg W. B., van de Putte L. B., Joosten L. A. Hydrogen peroxide suppresses the proteoglycan synthesis of intact articular cartilage. J Rheumatol. 1985 Apr;12(2):205–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz E. R., Leveille C. R., Stevens J. W., Oh W. H. Proteoglycan structure and metabolism in normal and osteoarthritic cartilage of guinea pigs. Arthritis Rheum. 1981 Dec;24(12):1528–1539. doi: 10.1002/art.1780241212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vignon E., Arlot M., Hartmann D., Moyen B., Ville G. Hypertrophic repair of articular cartilage in experimental osteoarthrosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1983 Feb;42(1):82–88. doi: 10.1136/ard.42.1.82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vignon E., Gateau O., Martin A., Hartmann D., Bejui J., Biol M. C., Vanier M. T., Louisot P., Richard M. Screening of degradative enzymes from articular cartilage in experimental osteoarthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 1987 Jun;6(2):208–214. doi: 10.1007/BF02201026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. A., Thonar E. J. Early osteophyte formation after chemically induced articular cartilage injury. Am J Sports Med. 1989 Jan-Feb;17(1):7–15. doi: 10.1177/036354658901700102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Beuningen H. M., Arntz O. J., van den Berg W. B. In vivo effects of interleukin-1 on articular cartilage. Prolongation of proteoglycan metabolic disturbances in old mice. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 May;34(5):606–615. doi: 10.1002/art.1780340513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Berg W. B., Kruijsen M. W., van de Putte L. B., van Beusekom H. J., van der Sluis-van der Pol M., Zwarts W. A. Antigen-induced and zymosan-induced arthritis in mice: studies on in vivo cartilage proteoglycan synthesis and chondrocyte death. Br J Exp Pathol. 1981 Jun;62(3):308–316. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Kraan P. M., Vitters E. L., van de Putte L. B., van den Berg W. B. Development of osteoarthritic lesions in mice by "metabolic" and "mechanical" alterations in the knee joints. Am J Pathol. 1989 Dec;135(6):1001–1014. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]