Abstract
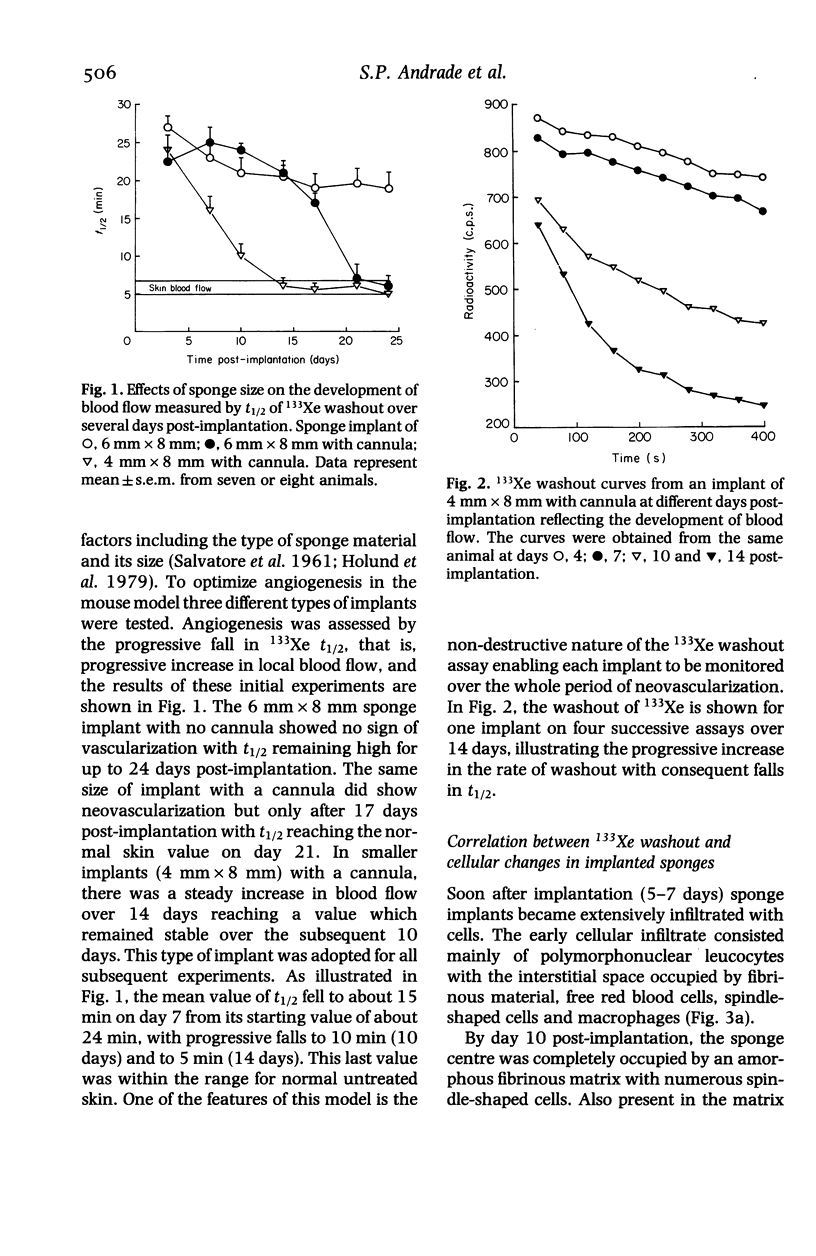
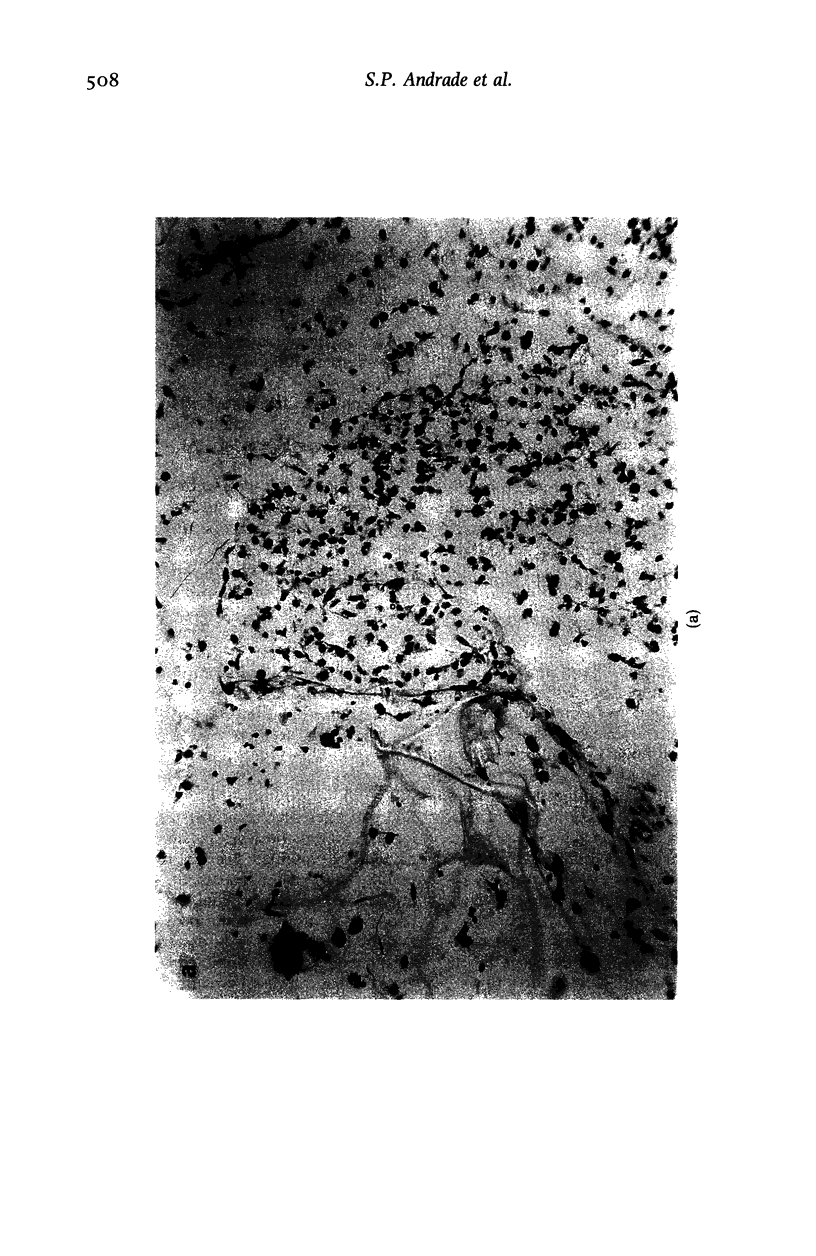
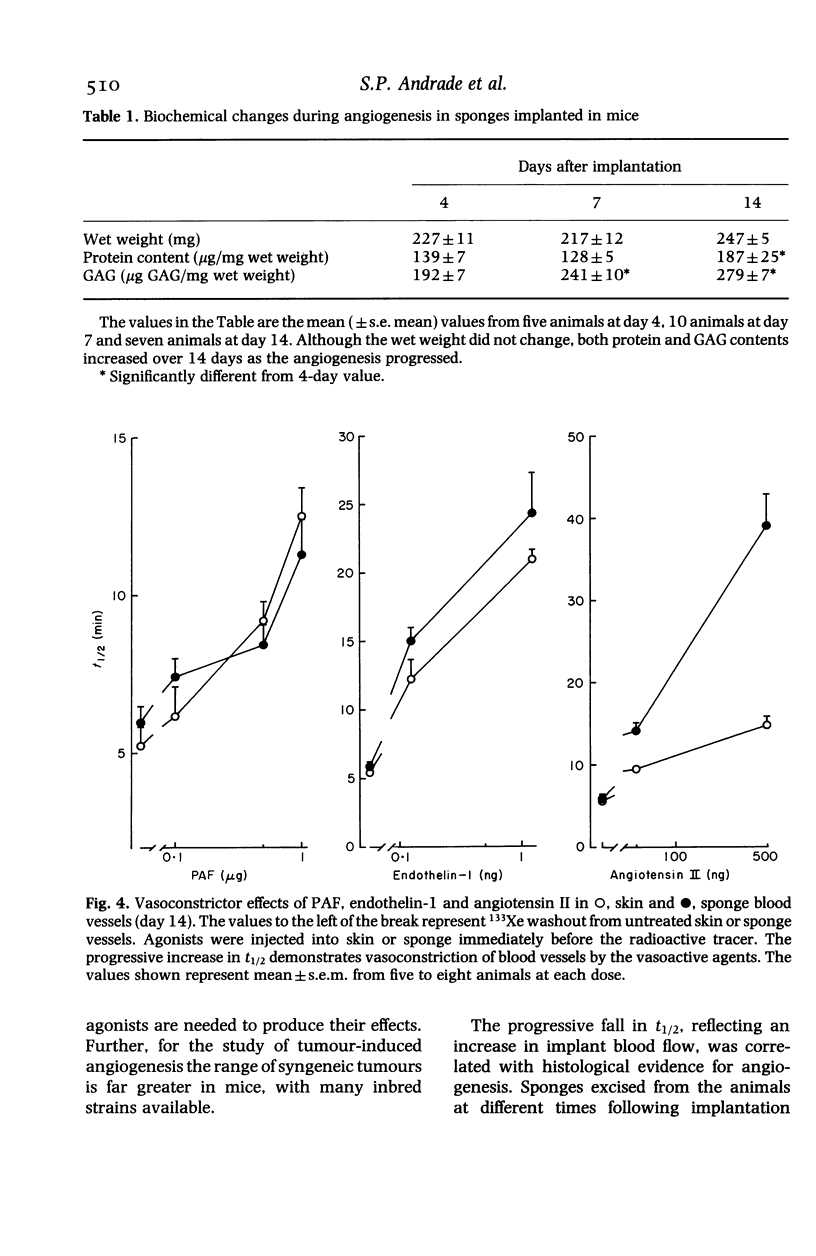
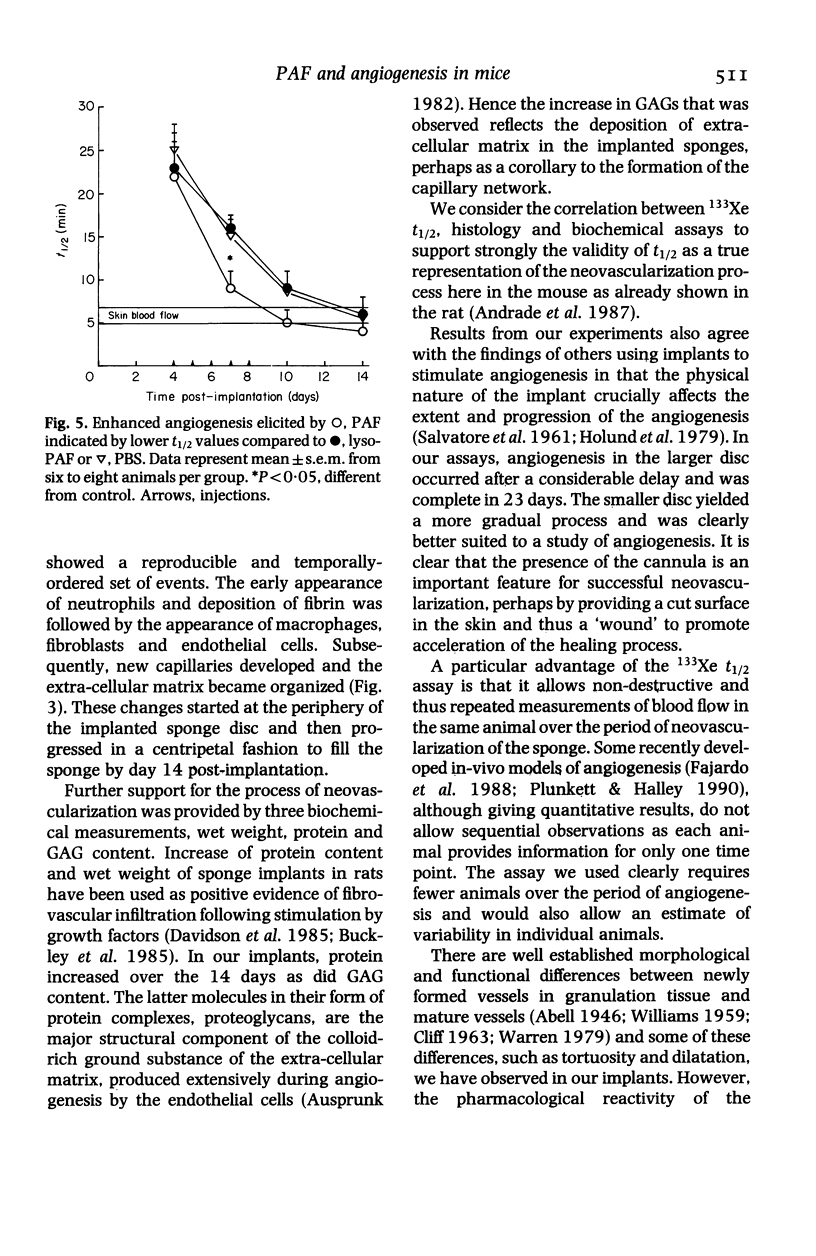
The combination of sponge implant and 133Xe washout technique described in this paper provides a model to study neovascularization in mice which can be observed over several days in the same animal. The local blood flow within the ingrowing granulation tissue has been determined by measuring the washout rate of 133Xe injected into the implants. Tissue infiltration of the sponges was assessed by histological examination and by measurement of sponge wet weight, protein and glycosaminoglycans (GAG) content. The newly formed blood vessels, despite having abnormal configuration, responded to platelet activating factor (PAF) and to endothelin-1 (ET-1) similarly to the normal mature vessels in adjacent skin. However, the sponge blood vessels were more sensitive to angiotensin II than the skin blood vessels. Using this model we have also demonstrated an angiogenic activity of PAF substantiated by increased blood flow and biochemical variables in the implanted sponges.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrade S. P., Fan T. P., Lewis G. P. Quantitative in-vivo studies on angiogenesis in a rat sponge model. Br J Exp Pathol. 1987 Dec;68(6):755–766. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ausprunk D. H. Synthesis of glycoproteins by endothelial cells in embryonic blood vessels. Dev Biol. 1982 Mar;90(1):79–90. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90213-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOLLET A. J., GOODWIN J. F., SIMPSON W. F., ANDERSON D. V. Mucopolysaccharide, protein and desoxyribosenucleic acid concentration of granulation tissue induced by polyvinyl sponges. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1958 Nov;99(2):418–421. doi: 10.3181/00379727-99-24369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley A., Davidson J. M., Kamerath C. D., Wolt T. B., Woodward S. C. Sustained release of epidermal growth factor accelerates wound repair. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7340–7344. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiarugi V., Ruggiero M., Porciatti F., Vannucchi S., Ziche M. Cooperation of heparin with other angiogenetic effectors. Int J Tissue React. 1986;8(2):129–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson J. M., Klagsbrun M., Hill K. E., Buckley A., Sullivan R., Brewer P. S., Woodward S. C. Accelerated wound repair, cell proliferation, and collagen accumulation are produced by a cartilage-derived growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;100(4):1219–1227. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.4.1219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDWARDS R. H., SARMENTA S. S., HASS G. M. Stimulation of granulation tissue growth by tissue extracts. Study in intramuscular wounds in rabbits. Arch Pathol. 1960 Mar;69:286–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fajardo L. F., Kowalski J., Kwan H. H., Prionas S. D., Allison A. C. The disc angiogenesis system. Lab Invest. 1988 Jun;58(6):718–724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farndale R. W., Sayers C. A., Barrett A. J. A direct spectrophotometric microassay for sulfated glycosaminoglycans in cartilage cultures. Connect Tissue Res. 1982;9(4):247–248. doi: 10.3109/03008208209160269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez L. A., Twickler J., Mead A. Neovascularization produced by angiotensin II. J Lab Clin Med. 1985 Feb;105(2):141–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Klagsbrun M. Angiogenic factors. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):442–447. doi: 10.1126/science.2432664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRINDLAY J. H., WAUGH J. M. Plastic sponge which acts as a framework for living tissue; experimental studies and preliminary report of use to reinforce abdominal aneurysms. AMA Arch Surg. 1951 Sep;63(3):288–297. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1951.01250040294003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hølund B., Clemmensen I., Junker P., Lyon H. Fibronectin in experimental granulation tissue. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand A. 1982 May;90(3):159–165. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1982.tb00077_90a.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hølund B., Junker P., Garbarsch C., Christoffersen P., Lorenzen I. Formation of granulation tissue in subcutaneously implanted sponges in rats. A comparison between granulation tissue developed in viscose cellulose sponges (Visella) and in polyvinyl alcohol sponges (Ivalon). Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand A. 1979 Sep;87A(5):367–374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim R. C., Jr, Zederfeldt B., Lewis D. H. Metabolic and blood flow changes in healing wounds: a measurement of microcirculatory development. Bibl Anat. 1969;10:328–333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plunkett M. L., Hailey J. A. An in vivo quantitative angiogenesis model using tumor cells entrapped in alginate. Lab Invest. 1990 Apr;62(4):510–517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polverini P. J., Cotran P. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Unanue E. R. Activated macrophages induce vascular proliferation. Nature. 1977 Oct 27;269(5631):804–806. doi: 10.1038/269804a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALVATORE J. E., GILMER W. S., Jr, KASHGARIAN M., BARBEE W. R. An experimental study of the influence of pore size of implanted polyurethane sponges upon subsequent tissue formation. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1961 Apr;112:463–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidky Y. A., Auerbach R. Lymphocyte-induced angiogenesis: a quantitative and sensitive assay of the graft-vs.-host reaction. J Exp Med. 1975 May 1;141(5):1084–1100. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.5.1084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIBER A. Studies in vascularisation of healing wounds with radioactive isotopes. Acta Chir Scand Suppl. 1959;116(Suppl 237):1–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS R. G. Experiments on the growth of blood vessels in thin tissue and in small autografts. Anat Rec. 1959 Mar;133(3):465–485. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091330302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




