Abstract
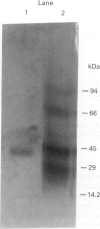
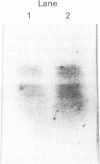
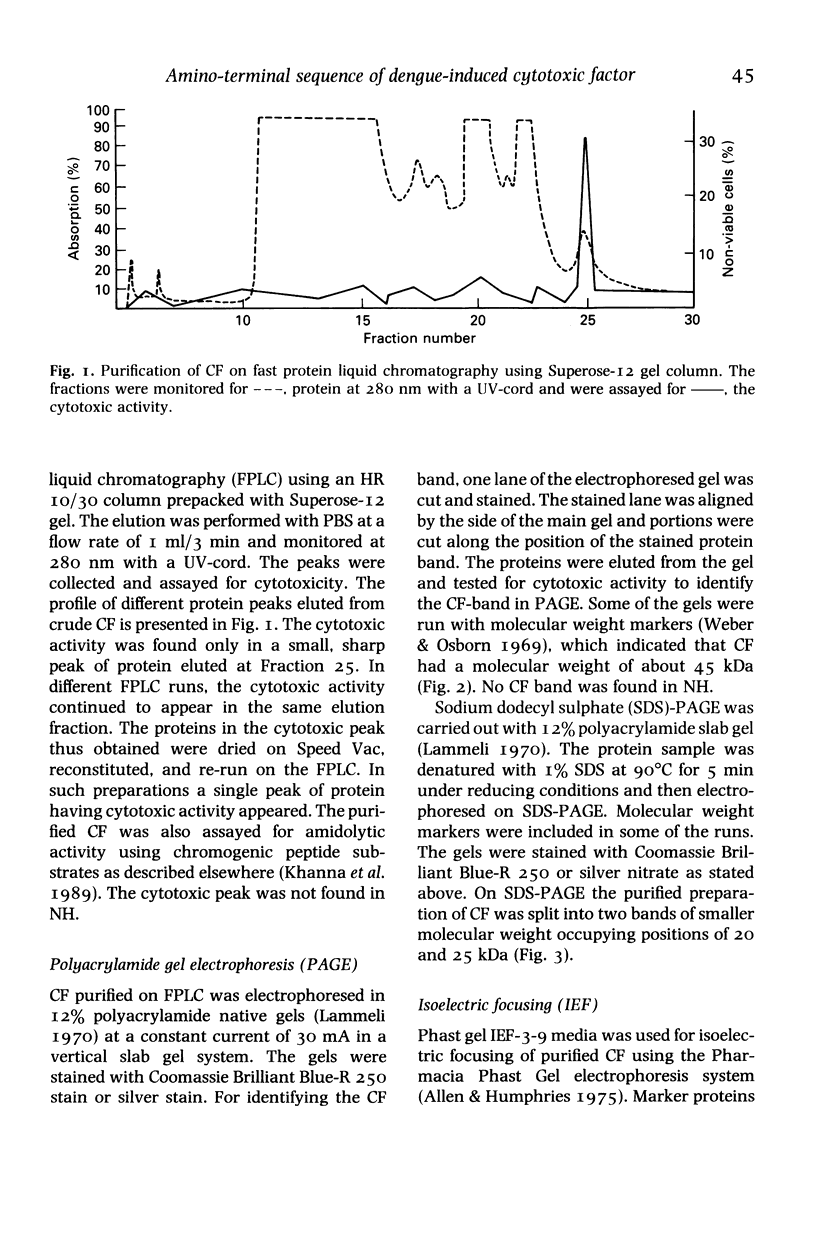
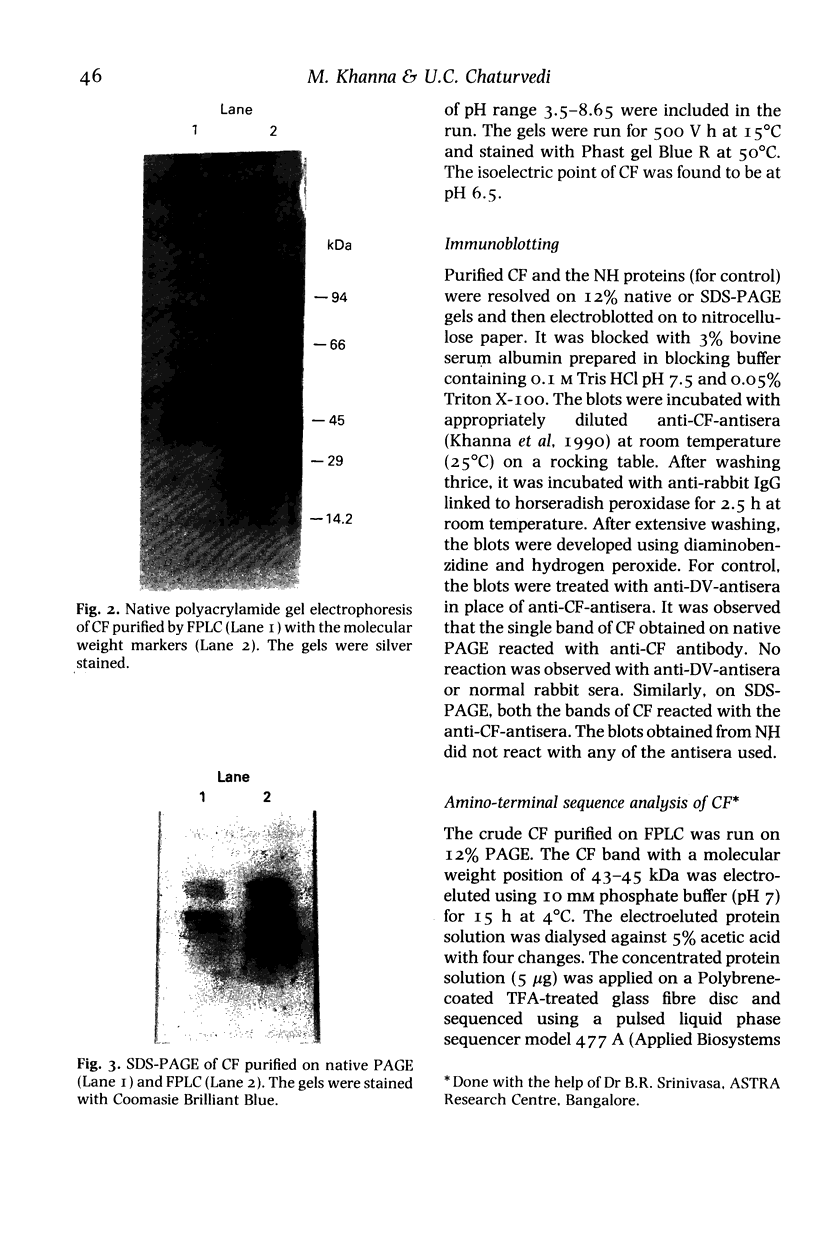
The present study was undertaken to purify the dengue type 2 virus (DV)-induced cytotoxic factor (CF) and analyse its amino-terminal sequence. Spleens collected from DV-infected moribund mice were made into a single cell suspension and cultured for 24 h. The culture supernatant was purified using fast protein liquid chromatography (FPLC) and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE). CF could be purified in a single step by FPLC and native PAGE. The isoelectric point of CF was pH 6.5. Purified CF had a molecular weight of 45 kDa on native-PAGE while on SDS-PAGE it dissociated into two bands of 20 and 25 kDa. Anti-CF-antisera reacted specifically with CF bands separated on native and SDS-PAGE in a Western blot assay. A sequence of 19 amino-acids of the N-terminus of CF was analysed which on comparison with that of other known cytotoxic proteins indicated that CF differs from them. Thus, CF appears to be a unique cytotoxic protein induced by a virus.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chaturvedi U. C., Gulati L., Mathur A. Inhibition of E-rosette formation and phagocytosis by human blood leucocytes after treatment with the dengue virus-induced cytotoxic factor. Immunology. 1982 Apr;45(4):679–685. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaturvedi U. C., Nagar R., Mathur A. Effect of dengue virus infection on Fc-receptor functions of mouse macrophages. J Gen Virol. 1983 Nov;64(Pt 11):2399–2407. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-11-2399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark W. R. Perforin--a primary or auxiliary lytic mechanism? Immunol Today. 1988 Apr;9(4):101–104. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91277-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalakoti H., Chaturvedi U. C., Mathur A. Inhibition of production of dengue virus induced cytotoxic factor by treatment with cycloheximide & mitomycin C. Indian J Exp Biol. 1982 Jan;20(1):1–3. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhawan R., Khanna M., Chaturvedi U. C., Mathur A. Effect of dengue virus-induced cytotoxin on capillary permeability. J Exp Pathol (Oxford) 1990 Feb;71(1):83–88. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulati L., Chaturvedi U. C., Mathur A. Depressed macrophage functions in dengue virus-infected mice: role of the cytotoxic factor. Br J Exp Pathol. 1982 Apr;63(2):194–202. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulati L., Chaturvedi U. C., Mathur A. Effect of dengue virus-induced macrophage cytotoxin on functions of human blood leucocytes. Indian J Med Res. 1984 Jun;79:709–715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulati L., Chaturvedi U. C., Mathur A. Plasma membrane-acting drugs inhibit the effect of dengue virus-induced cytotoxic factor. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1983 Mar-Apr;134C(2):227–235. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2625(83)80094-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khanna M., Chaturvedi U. C., Sharma M. C., Pandey V. C., Mathur A. Increased capillary permeability mediated by a dengue virus-induced lymphokine. Immunology. 1990 Mar;69(3):449–453. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khanna M., Chaturvedi U. C., Srinivasa B. R., Swaminathan K. R., Mathur A. Proteinase-like activity in the cytotoxic factor produced by T cells during dengue virus infection. Immunology. 1989 May;67(1):32–37. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagar R., Chaturvedi U. C., Mathur A. Effect of dengue virus-induced cytotoxic factor on Fc-receptor functions of mouse macrophages. Br J Exp Pathol. 1984 Feb;65(1):11–17. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nath P., Tandon P., Gulati L., Chaturvedi U. C. Histological & ultrastructural study of spleen during dengue virus infection of mice. Indian J Med Res. 1983 Jul;78:83–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]