Abstract
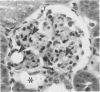
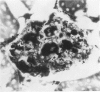
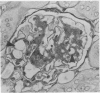
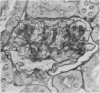
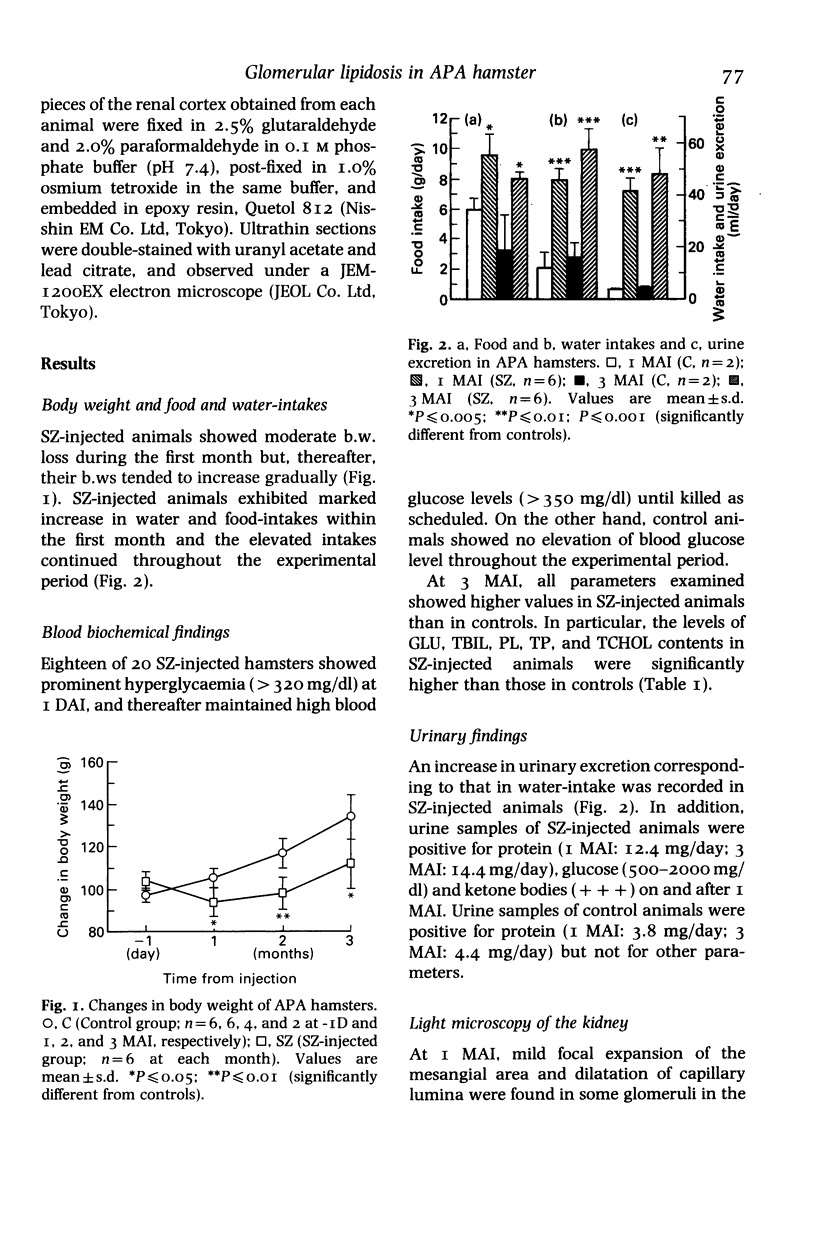
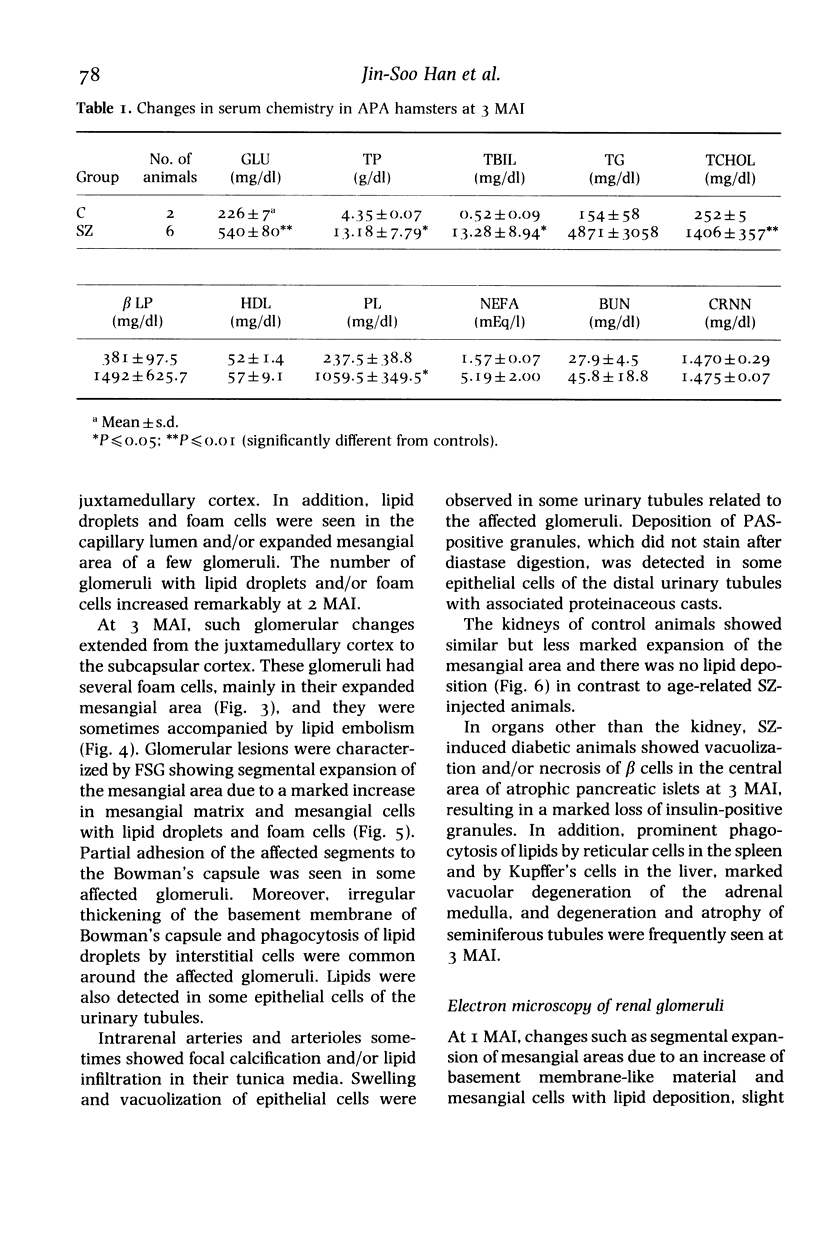
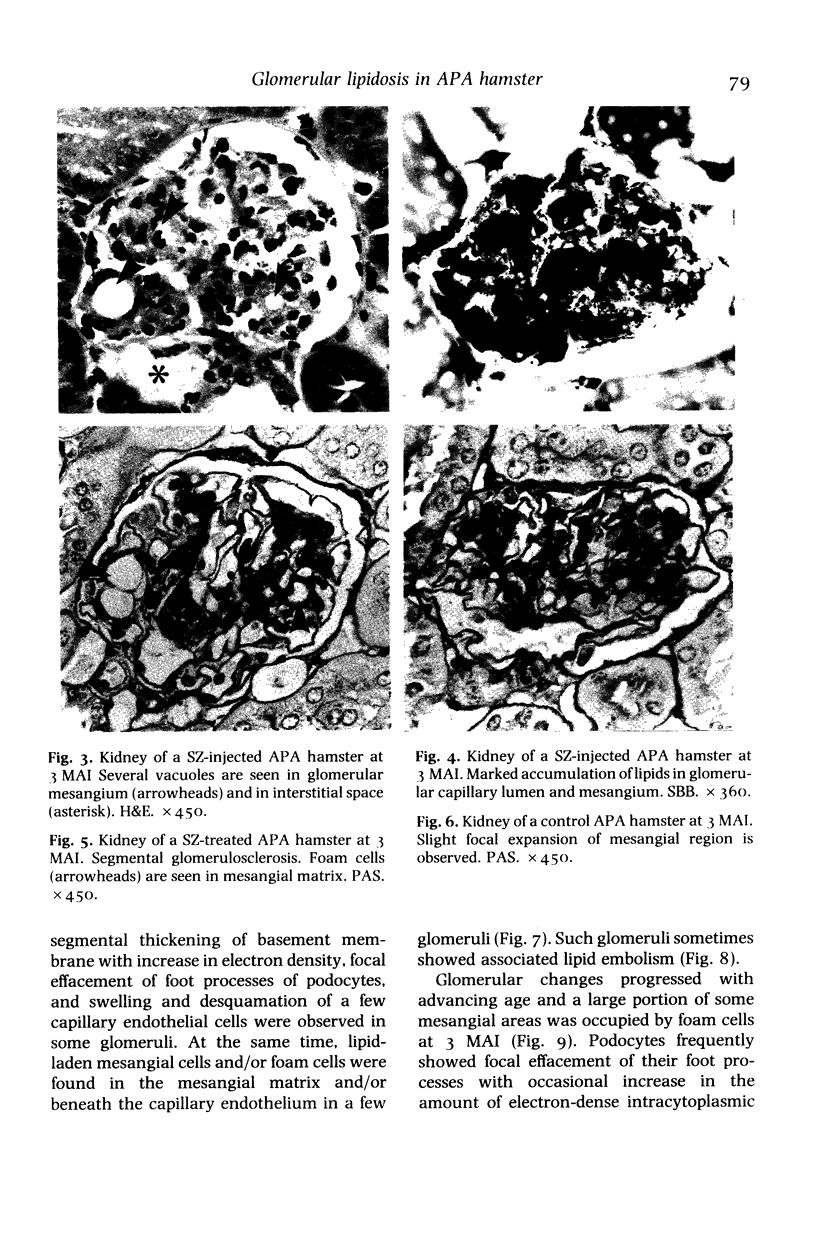
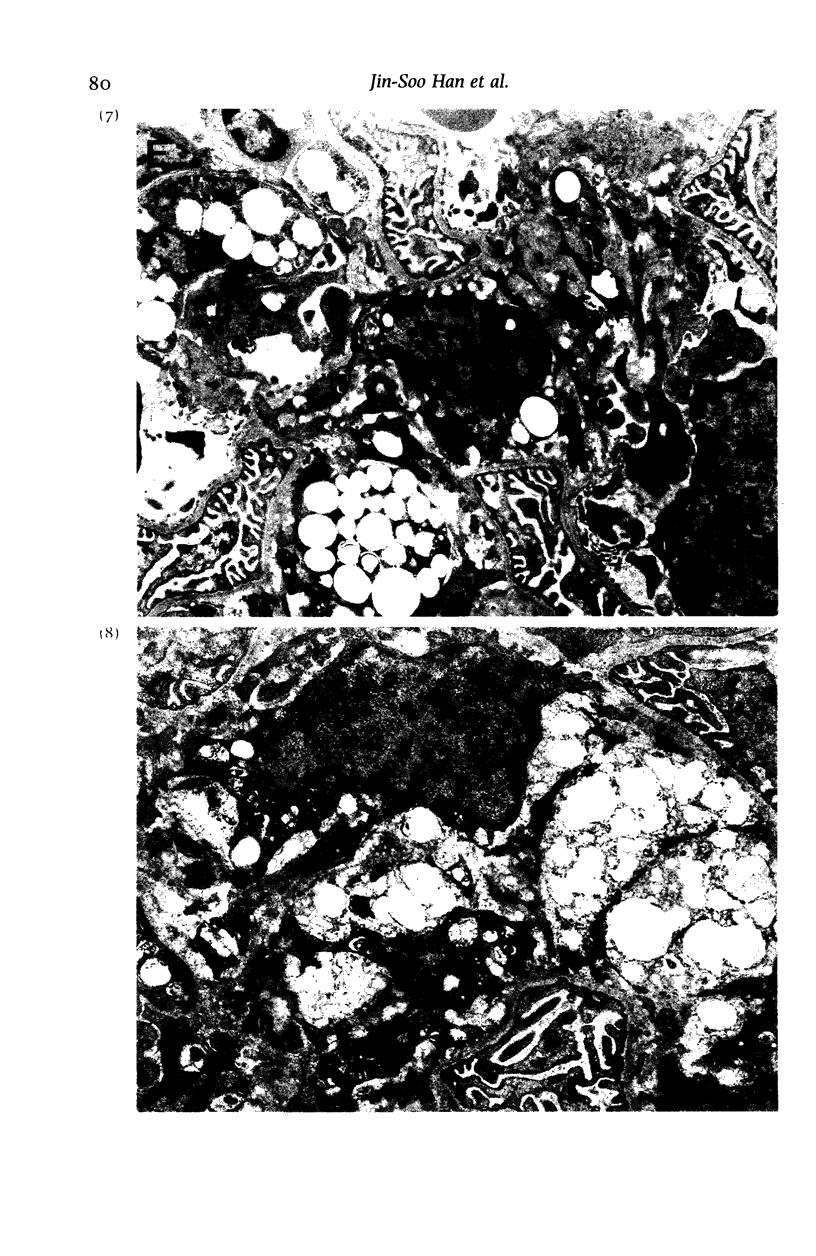
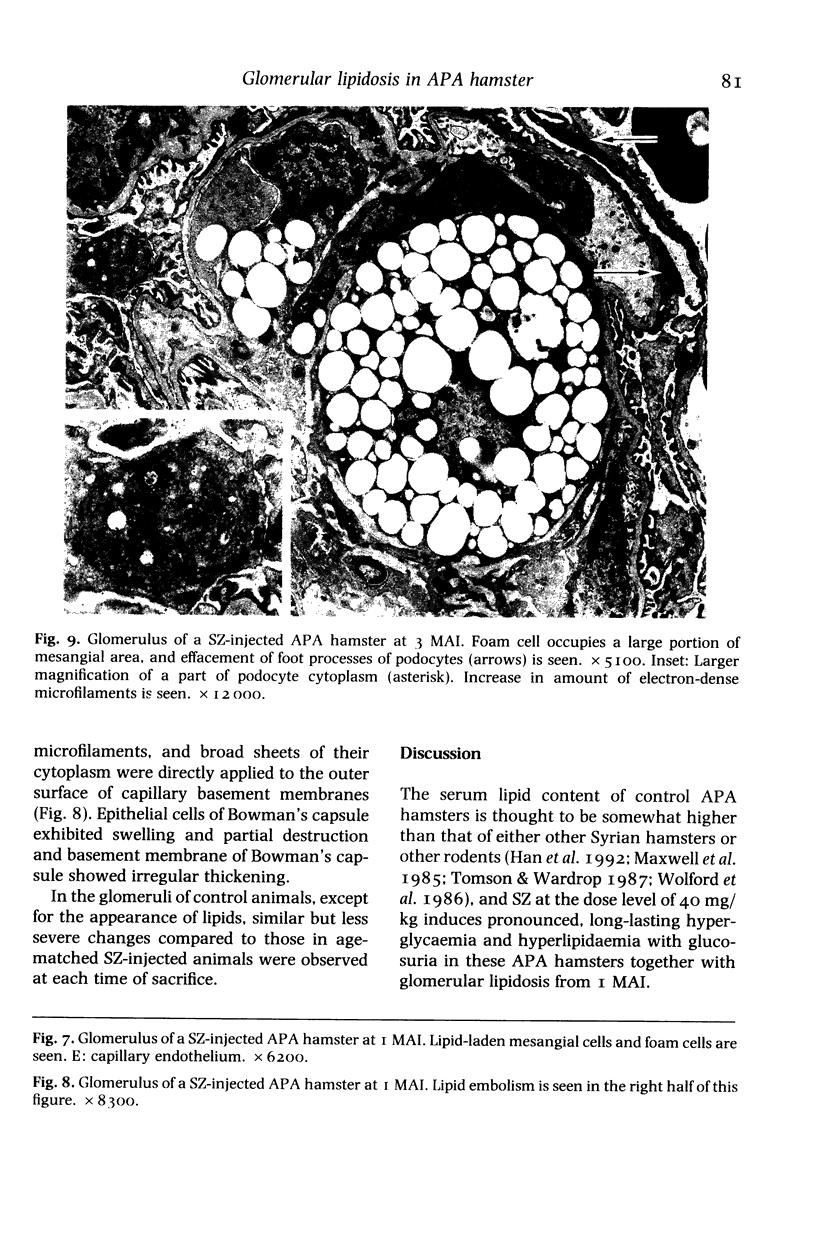
The pathology of male Syrian hamsters of APA strain which were injected intraperitoneally with 40 mg/kg body weight of streptozotocin (SZ) at 2 months of age was examined. It showed long-lasting prominent hyperglycaemia and hyperlipidaemia with glucosuria and the development of glomerular lipidosis from 1 month after SZ-injection (1 MAI). Glomerular lesions were restricted to the juxtamedullary cortex at 1 MAI and then extended to the subcapsular cortex. At 3 MAI, glomerular lesions were characterized by focal segmental glomerulosclerosis showing segmental expansion of the mesangial area due to an increase of basement membrane-like material and mesangial cells with lipid droplets and foam cells. SZ-induced diabetic APA hamsters will be a useful model for the investigation of glomerular lipidosis and focal segmental glomerulosclerosis.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Al-Shebeb T., Frohlich J., Magil A. B. Glomerular disease in hypercholesterolemic guinea pigs: a pathogenetic study. Kidney Int. 1988 Feb;33(2):498–507. doi: 10.1038/ki.1988.26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashall F., Bramwell M. E., Harris H. A new marker for human cancer cells. 1 The Ca antigen and the Ca1 antibody. Lancet. 1982 Jul 3;2(8288):1–6. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91150-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhathena D. B., Weiss J. H., Holland N. H., McMorrow R. G., Curtis J. J., Lucas B. A., Luke R. G. Focal and segmental glomerular sclerosis in reflux nephropathy. Am J Med. 1980 Jun;68(6):886–892. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(80)90218-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. M., Meyer T. W., Hostetter T. H. Dietary protein intake and the progressive nature of kidney disease: the role of hemodynamically mediated glomerular injury in the pathogenesis of progressive glomerular sclerosis in aging, renal ablation, and intrinsic renal disease. N Engl J Med. 1982 Sep 9;307(11):652–659. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198209093071104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couser W. G., Stilmant M. M. Mesangial lesions and focal glomerular sclerosis in the aging rat. Lab Invest. 1975 Nov;33(5):491–501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J. R., Karnovsky M. J. Exacerbation of chronic aminonucleoside nephrosis by dietary cholesterol supplementation. Kidney Int. 1987 Nov;32(5):671–677. doi: 10.1038/ki.1987.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J. R., Karnovsky M. J. Focal and segmental glomerulosclerosis: analogies to atherosclerosis. Kidney Int. 1988 May;33(5):917–924. doi: 10.1038/ki.1988.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldszer R. C., Sweet J., Cotran R. S. Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Annu Rev Med. 1984;35:429–449. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.35.020184.002241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray J. E., van Zwieten M. J., Hollander C. F. Early light microscopic changes in chronic progressive nephrosis in several strains of aging laboratory rats. J Gerontol. 1982 Mar;37(2):142–150. doi: 10.1093/geronj/37.2.142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gröne H. J., Walli A., Gröne E., Niedmann P., Thiery J., Seidel D., Helmchen U. Induction of glomerulosclerosis by dietary lipids. A functional and morphologic study in the rat. Lab Invest. 1989 Mar;60(3):433–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman L. R., Burkholder P. M. Focal sclerosing glomerulonephropathy with segmental hyalinosis. A clinicopathologic analysis. Lab Invest. 1973 May;28(5):533–544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keane W. F., Kasiske B. L., O'Donnell M. P. Lipids and progressive glomerulosclerosis. A model analogous to atherosclerosis. Am J Nephrol. 1988;8(4):261–271. doi: 10.1159/000167599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magil A. B., Cohen A. H. Monocytes and focal glomerulosclerosis. Lab Invest. 1989 Oct;61(4):404–409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell K. O., Wish C., Murphy J. C., Fox J. G. Serum chemistry reference values in two strains of Syrian hamsters. Lab Anim Sci. 1985 Feb;35(1):67–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mezza L. E., Quimby F. W., Durham S. K., Lewis R. M. Characterization of spontaneous amyloidosis of Syrian hamsters using the potassium permanganate method. Lab Anim Sci. 1984 Aug;34(4):376–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norimatsu M., Doi K., Itagaki S., Honjo K., Mitsuoka T. Glomerular lipidosis in a Syrian hamster of the APA strain. Lab Anim. 1990 Jan;24(1):48–52. doi: 10.1258/002367790780890383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. M., Lewis E. J. Focal segmental glomerular sclerosis: the cellular lesion. Kidney Int. 1985 Dec;28(6):968–974. doi: 10.1038/ki.1985.225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimamura T. Relationship of dietary intake to the development of glomerulosclerosis in obese Zucker rats. Exp Mol Pathol. 1982 Jun;36(3):423–424. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(82)90071-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verani R. R., Hawkins E. P. Recurrent focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. A pathological study of the early lesion. Am J Nephrol. 1986;6(4):263–270. doi: 10.1159/000167173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wehner H., Höhn D., Faix-Schade U., Huber H., Walzer P. Glomerular changes in mice with spontaneous hereditary diabetes. Lab Invest. 1972 Sep;27(3):331–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]