Abstract
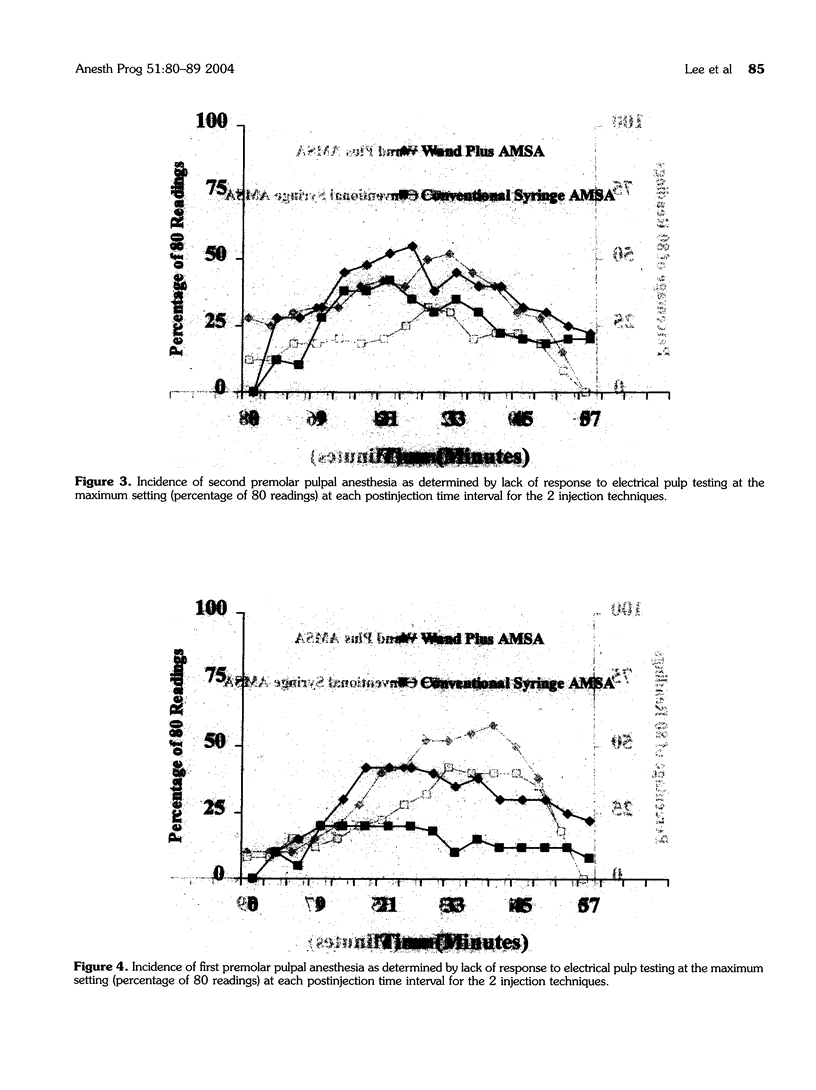
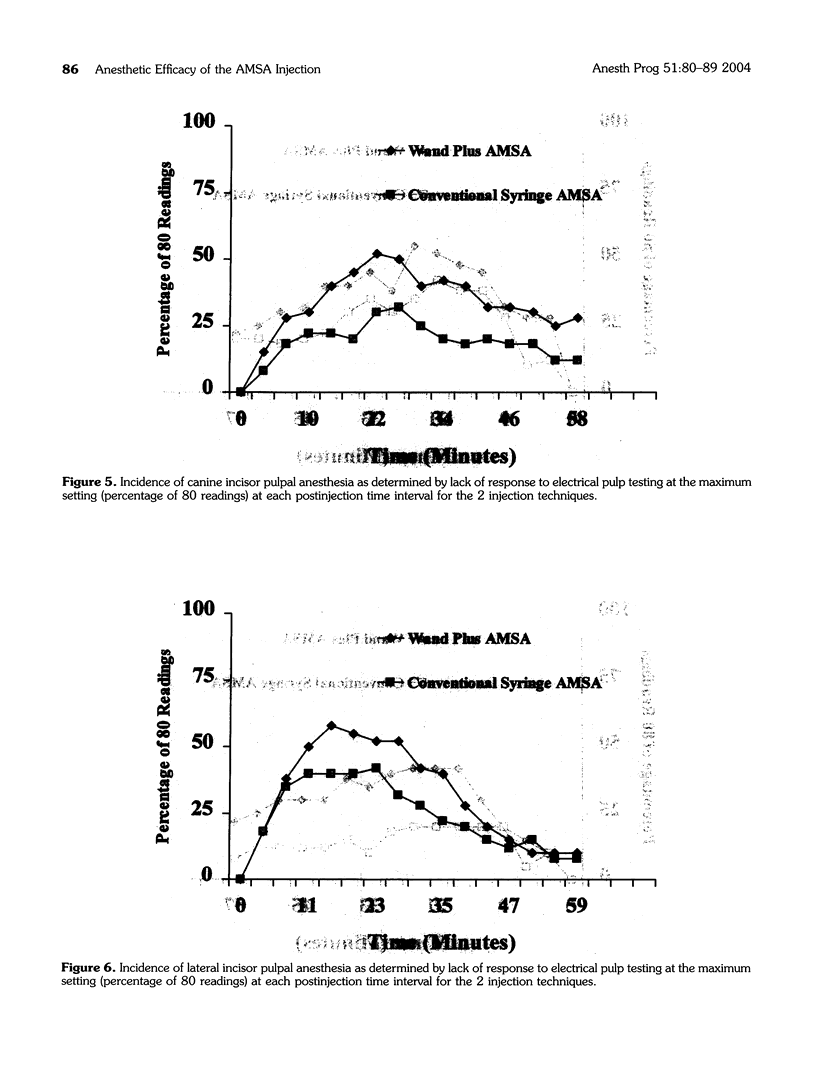
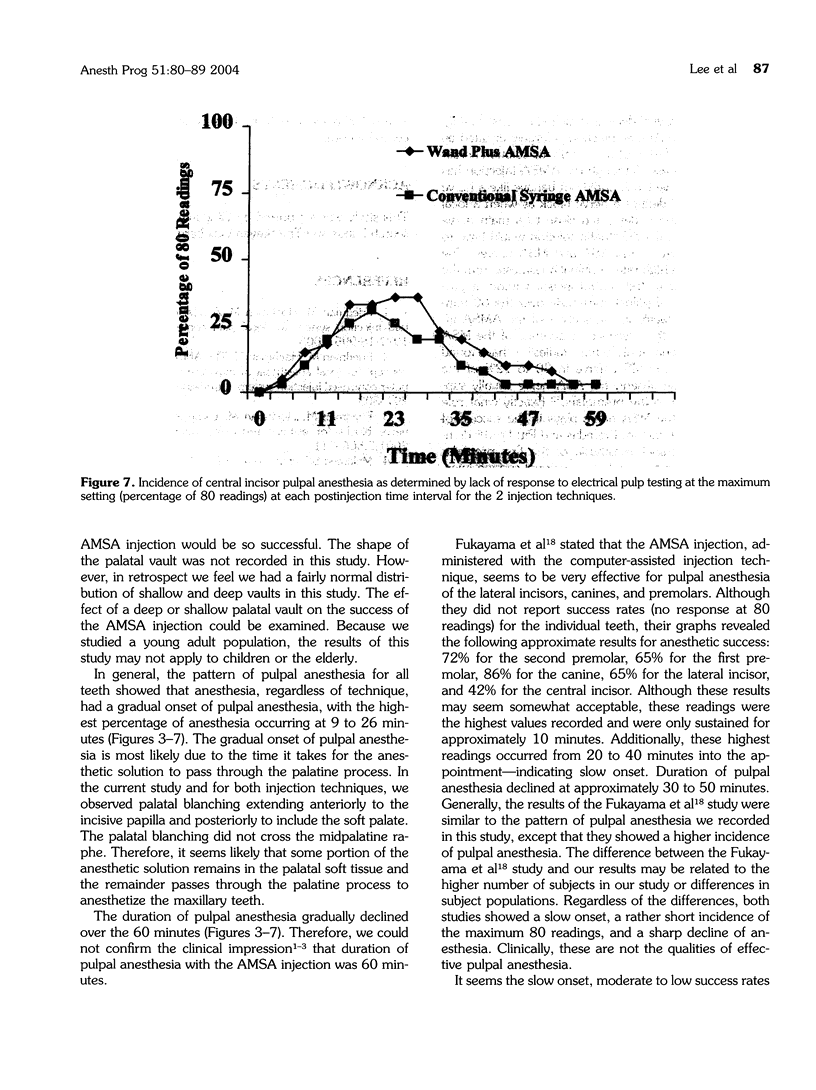
The purpose of this prospective, randomized, blinded study was to determine the anesthetic efficacy of the anterior middle superior alveolar (AMSA) injection using the computer-assisted Wand Plus injection system versus a conventional syringe. The authors, using a crossover design, randomly administered in a blind manner 2 AMSA injections utilizing the computer-assisted injection system and a conventional syringe to 40 subjects during 2 separate appointments. A pulp tester was used to test for anesthesia, in 4-minute cycles for 60 minutes, of the central and lateral incisors, canine, and first and second premolars. Anesthesia was considered successful when 2 consecutive no responses (80 readings) with the pulp tester were obtained. For all teeth, except the central incisor, the use of the computer-assisted injection system was significantly (P < .05) more likely to result in pulpal anesthesia than the use of the conventional syringe technique. For the computer-assisted injection system, successful pulpal anesthesia ranged from 35 to 58%, and for the conventional syringe, successful pulpal anesthesia ranged from 20 to 42%. For both techniques, the onset of pulpal anesthesia was slow, and duration of pulpal anesthesia declined steadily over 60 minutes. We conclude that although the AMSA injection using the computer-assisted injection system was more successful than the conventional syringe technique, the rather modest to low success rates, slow onset, and declining duration of pulpal anesthesia over 60 minutes would not ensure predictable pulpal anesthesia from the second premolar to the central incisor.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen Keith D., Kotil Darin, Larzelere Robert E., Hutfless Susan, Beiraghi Soraya. Comparison of a computerized anesthesia device with a traditional syringe in preschool children. Pediatr Dent. 2002 Jul-Aug;24(4):315–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asarch T., Allen K., Petersen B., Beiraghi S. Efficacy of a computerized local anesthesia device in pediatric dentistry. Pediatr Dent. 1999 Nov-Dec;21(7):421–424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Certosimo A. J., Archer R. D. A clinical evaluation of the electric pulp tester as an indicator of local anesthesia. Oper Dent. 1996 Jan-Feb;21(1):25–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreven L. J., Reader A., Beck M., Meyers W. J., Weaver J. An evaluation of an electric pulp tester as a measure of analgesia in human vital teeth. J Endod. 1987 May;13(5):233–238. doi: 10.1016/s0099-2399(87)80097-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman M. J., Hochman M. N. A 21st century computerized injection system for local pain control. Compend Contin Educ Dent. 1997 Oct;18(10):995-1000, 1002-3; quiz 1004. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman M. J., Hochman M. N. The AMSA injection: a new concept for local anesthesia of maxillary teeth using a computer-controlled injection system. Quintessence Int. 1998 May;29(5):297–303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman M. J., Hochman M. N. Using AMSA and P-ASA nerve blocks for esthetic restorative dentistry. Gen Dent. 2001 Sep-Oct;49(5):506–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukayama Haruhisa, Yoshikawa Fumihiro, Kohase Hikaru, Umino Masahiro, Suzuki Nagaaki. Efficacy of anterior and middle superior alveolar (AMSA) anesthesia using a new injection system: the Wand. Quintessence Int. 2003 Jul-Aug;34(7):537–541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson R. S., Allen K., Hutfless S., Beiraghi S. The Wand vs. traditional injection: a comparison of pain related behaviors. Pediatr Dent. 2000 Nov-Dec;22(6):458–462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodell G. G., Gallagher F. J., Nicoll B. K. Comparison of a controlled injection pressure system with a conventional technique. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2000 Jul;90(1):88–94. doi: 10.1067/moe.2000.107365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heasman P. A. Clinical anatomy of the superior alveolar nerves. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1984 Dec;22(6):439–447. doi: 10.1016/0266-4356(84)90051-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochman M., Chiarello D., Hochman C. B., Lopatkin R., Pergola S. Computerized local anesthetic delivery vs. traditional syringe technique. Subjective pain response. N Y State Dent J. 1997 Aug-Sep;63(7):24–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loetscher C. A., Walton R. E. Patterns of innervation of the maxillary first molar: a dissection study. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1988 Jan;65(1):86–90. doi: 10.1016/0030-4220(88)90198-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCDANIEL W. L. Variation in nerve distributions of the maxillary teeth. J Dent Res. 1956 Dec;35(6):916–921. doi: 10.1177/00220345560350061301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson J. W., Berry T. G., Summitt J. B., Yuan C. H., Witten T. M. Pain perception and utility: a comparison of the syringe and computerized local injection techniques. Gen Dent. 2001 Mar-Apr;49(2):167–173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLSEN N. H., TEUSCHER G. W., VEHE K. L. A study of the nerve supply to the upper anterior teeth. J Dent Res. 1955 Jun;34(3):413–420. doi: 10.1177/00220345550340031701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Premdas C. E., Pitt Ford T. R. Effect of palatal injections on pulpal blood flow in premolars. Endod Dent Traumatol. 1995 Dec;11(6):274–278. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-9657.1995.tb00503.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Primosch Robert E., Brooks Richard. Influence of anesthetic flow rate delivered by the Wand Local Anesthetic System on pain response to palatal injections. Am J Dent. 2002 Feb;15(1):15–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg Edwin S. A computer-controlled anesthetic delivery system in a periodontal practice: patient satisfaction and acceptance. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2002;14(1):39–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1708-8240.2002.tb00146.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saloum F. S., Baumgartner J. C., Marshall G., Tinkle J. A clinical comparison of pain perception to the Wand and a traditional syringe. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2000 Jun;89(6):691–695. doi: 10.1067/moe.2000.106333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan P. Y., Vukasin P., Chin I. D., Ciona C. J., Ortega A. E., Anthone G. J., Corman M. L., Beart R. W., Jr The WAND local anesthetic delivery system: a more pleasant experience for anal anesthesia. Dis Colon Rectum. 2001 May;44(5):686–689. doi: 10.1007/BF02234567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- True Robert H., Fabfp, Abhrs, Elliott Robert M., Abhrs Microprocessor-controlled local anesthesia versus the conventional syringe technique in hair transplantation. Dermatol Surg. 2002 Jun;28(6):463–468. doi: 10.1046/j.1524-4725.2002.01270.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


