Abstract
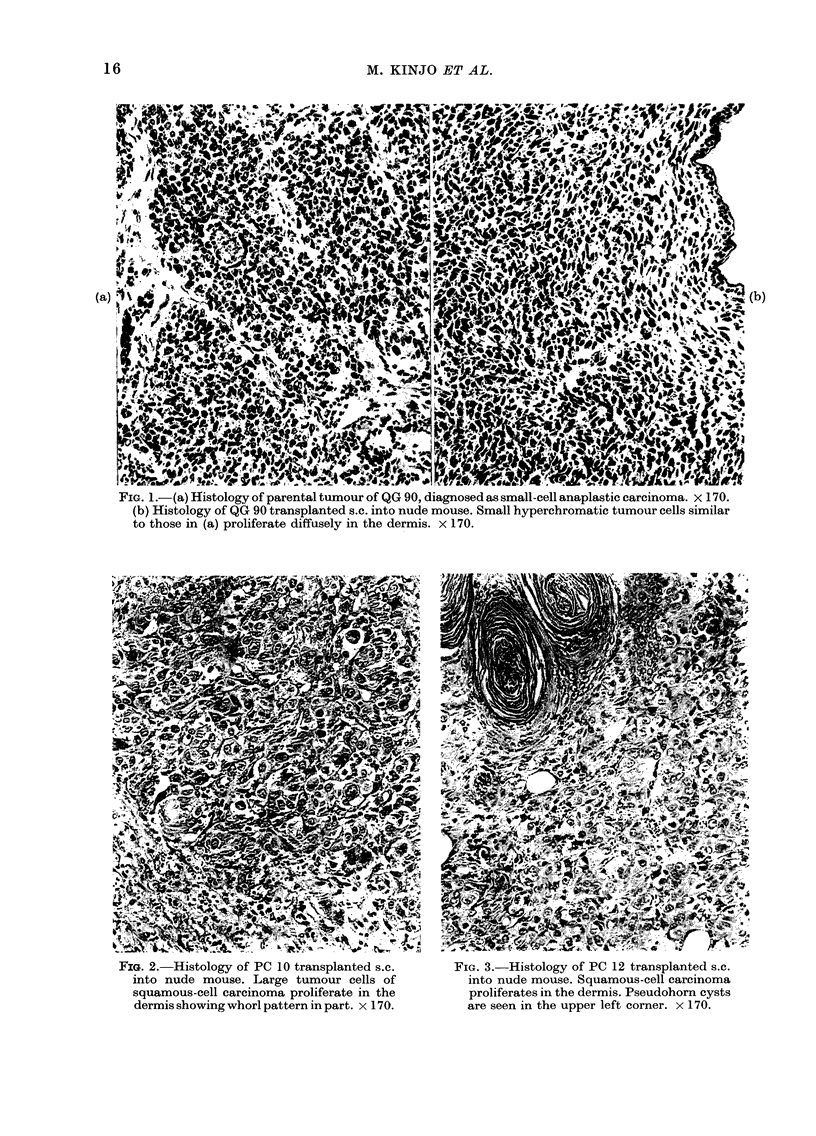
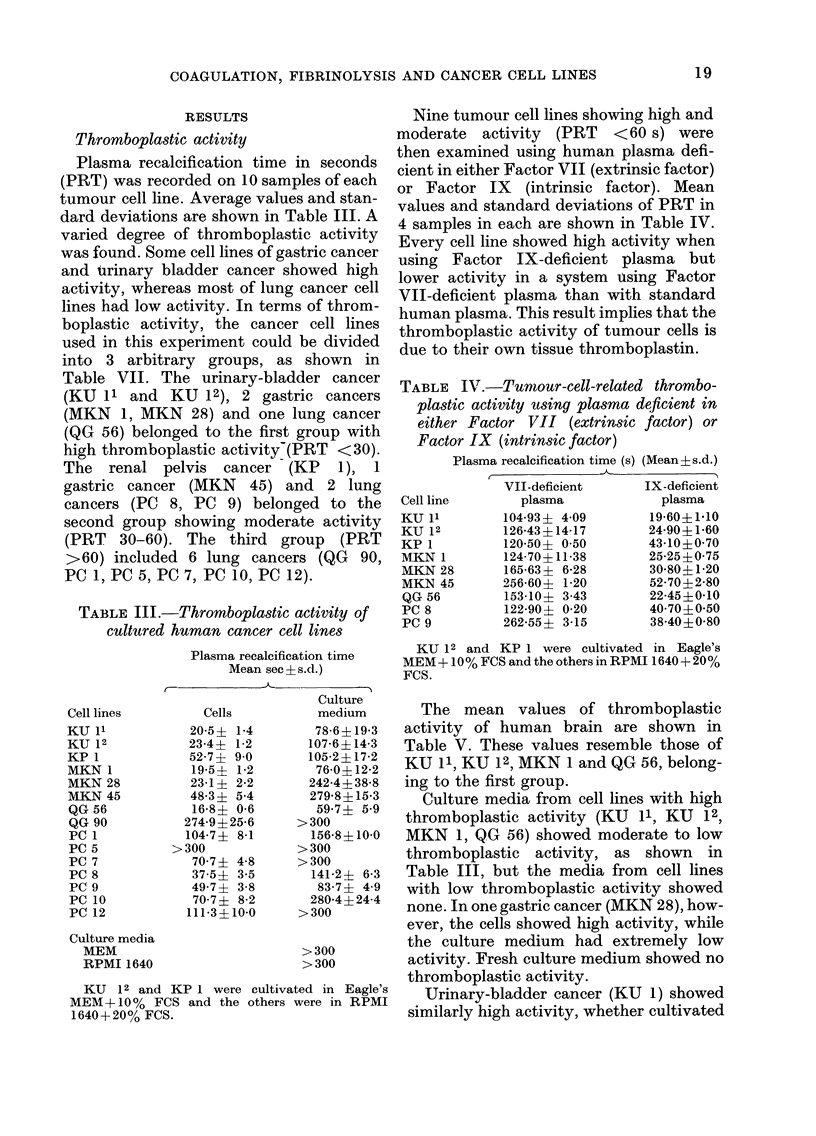
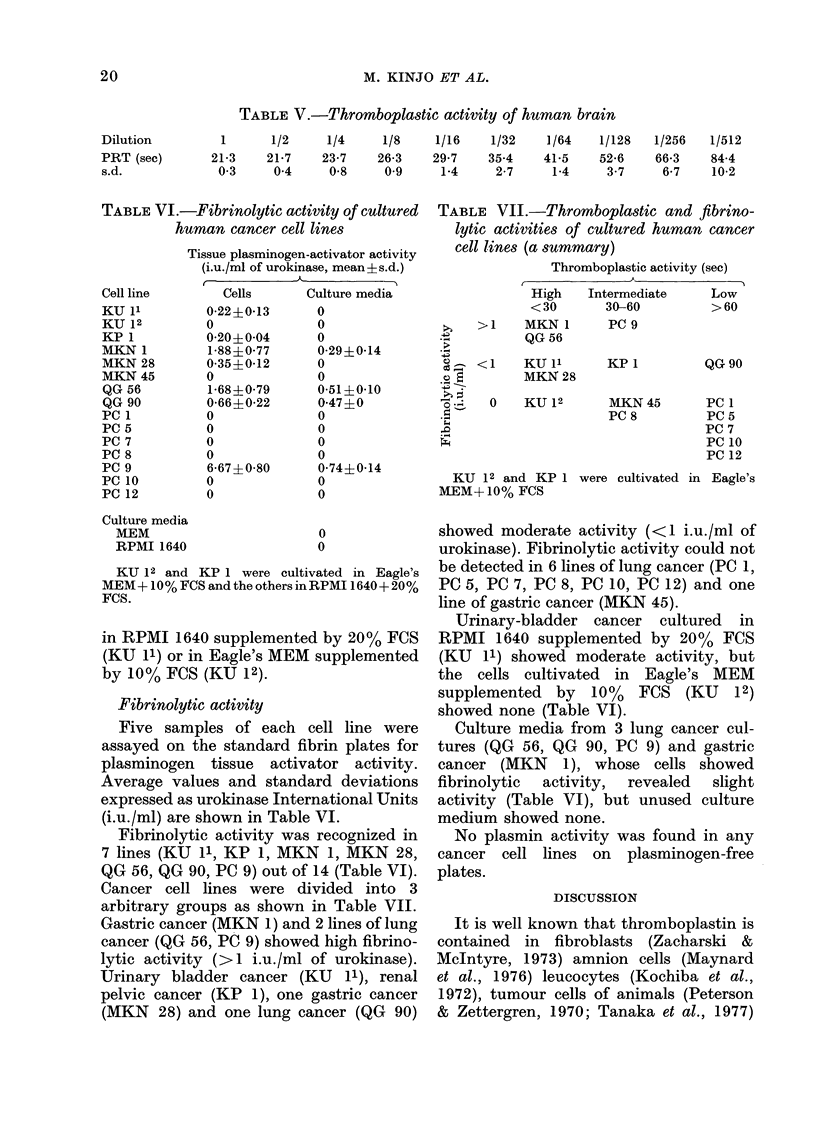
Thromboplastic and fibrinolytic activities of 14 lines of cultured human cancer cells were estimated by modified Astrup's methods. High tissue thromboplastic activity was found in one line of urinary-bladder cancer, 2 lines of gastric cancer and one line of lung cancer, but no activity was found in 6 lines of lung cancer. High fibrinolytic activity was noted in one line of gastric cancer and 2 lines of lung cancer, but no activity was seen in 6 lines of lung cancer and one line of gastric cancer. No plasmin activity was found. The tumour cell lines could be classified into 3 groups on the basis of the 2 activities. Cancer cell lines could also be classified into 2 groups: with high or low release of thromboplastin into culture media. Fibrinolytic activity was found in the culture media of all cell lines with high fibrinolytic activity. Fibrinolytic activity, but not thromboplastic activity, seemed to be influenced by the constituents of culture media. No definite correlation was found between the 2 activities and the histological types of the parent tumours of the cultured cells.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Astedt B., Holmberg L. Immunological identity of urokinase and ovarian carcinoma plasminogen activator released in tissue culture. Nature. 1976 Jun 17;261(5561):595–597. doi: 10.1038/261595a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Astrup T. Assay and content of tissue thromboplastin in different organs. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1965 Nov 15;14(3-4):401–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björlin G., Pandolfi M., Astedt B. Release of fibrinolytic activators from human tumours cultured in vitro. Experientia. 1972 Jul 15;28(7):833–834. doi: 10.1007/BF01923159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch D. G., Mertz E. T. Plasminogen: purification from human plasma by affinity chromatography. Science. 1970 Dec 4;170(3962):1095–1096. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasic G. J., Koch P. A., Hsu B., Gasic T. B., Niewiarowski S. Thrombogenic activity of mouse and human tumors: effects on platelets, coagulation, and fibrinolysis, and possible significance for metastases. Z Krebsforsch Klin Onkol Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1976 Aug 30;86(3):263–277. doi: 10.1007/BF00286945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinjo M. Lodgement and extravasation of tumour cells in blood-borne metastasis: an electron microscope study. Br J Cancer. 1978 Aug;38(2):293–301. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1978.201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kociba G. J., Loeb W. F., Wall R. L. Development of procoagulant (tissue thromboplastin) activity in cultured leukocytes. J Lab Clin Med. 1972 May;79(5):778–787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maynard J. R., Fintel D. J., Pitlick F. A., Nemerson Y. Tissue factor in cultured cells: metabolic control. Lab Invest. 1976 Dec;35(6):542–549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mott D. M., Fabisch P. H., Sani B. P., Sorof S. Lack of correlation between fibrinolysis and the transformed state of cultured mammalian cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Nov 27;61(2):621–627. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)91002-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy B., Ban J., Brdar B. Fibrinolysis associated with human neoplasia: production of plasminogen activator by human tumours. Int J Cancer. 1977 May 15;19(5):614–620. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910190504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ossowski L., Unkeless J. C., Tobia A., Quigley J. P., Rifkin D. B., Reich E. An enzymatic function associated with transformation of fibroblasts by oncogenic viruses. II. Mammalian fibroblast cultures transformed by DNA and RNA tumor viruses. J Exp Med. 1973 Jan 1;137(1):112–126. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.1.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peck S. D., Reiquam C. W. Disseminated intravascular coagulation in cancer patients: supportive evidence. Cancer. 1973 May;31(5):1114–1119. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197305)31:5<1114::aid-cncr2820310512>3.0.co;2-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson H. I., Larsson S., Zettergren L. Fibrinolysis in human Bronchogenic Carcinoma. Eur J Cancer. 1975 Apr;11(4):277–279. doi: 10.1016/0014-2964(75)90008-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson H. I., Zettergren L. Thromboplastic and fibrinolytic properties of three transplantable rat tumours. Acta Chir Scand. 1970;136(5):365–368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifkin D. B., Loeb J. N., Moore G., Reich E. Properties of plasminogen activators formed by neoplastic human cell cultures. J Exp Med. 1974 May 1;139(5):1317–1328. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.5.1317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf B. A., Goldberg A. R. Rous-sarcoma-virus-transformed fibroblasts having low levels of plasminogen activator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3613–3617. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu M., Arimura G. K., Yunis A. A. Purification and characterization of a plasminogen activator secreted by cultured human pancreatic carcinoma cells. Biochemistry. 1977 May 3;16(9):1908–1913. doi: 10.1021/bi00628a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasumoto K., Ohta M., Nomoto K. Cytotoxic activity of lymphocytes to bronchogenic carcinoma cells in patients with lung cancer. Gan. 1976 Aug;67(4):505–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zacharski L. R., McIntyre O. R. Membrane-mediated synthesis of tissue factor (thromboplastin) in cultured fibroblasts. Blood. 1973 May;41(5):679–685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





