Abstract
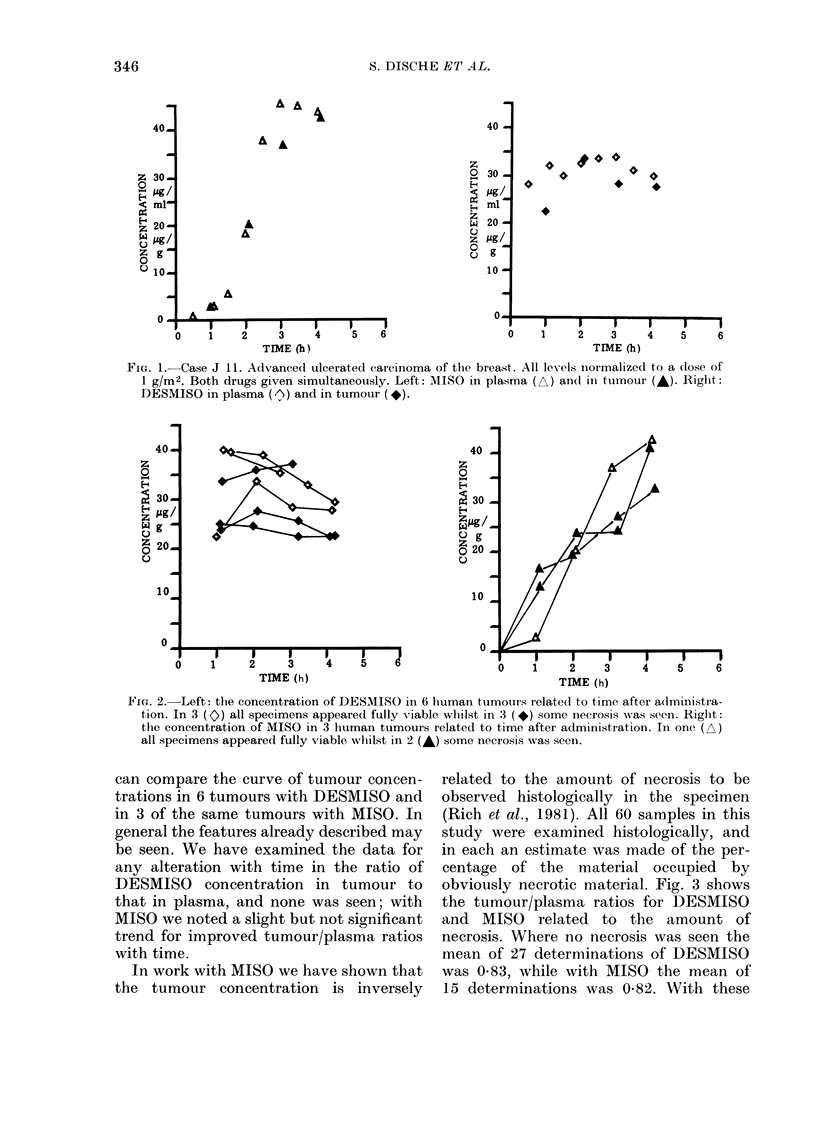
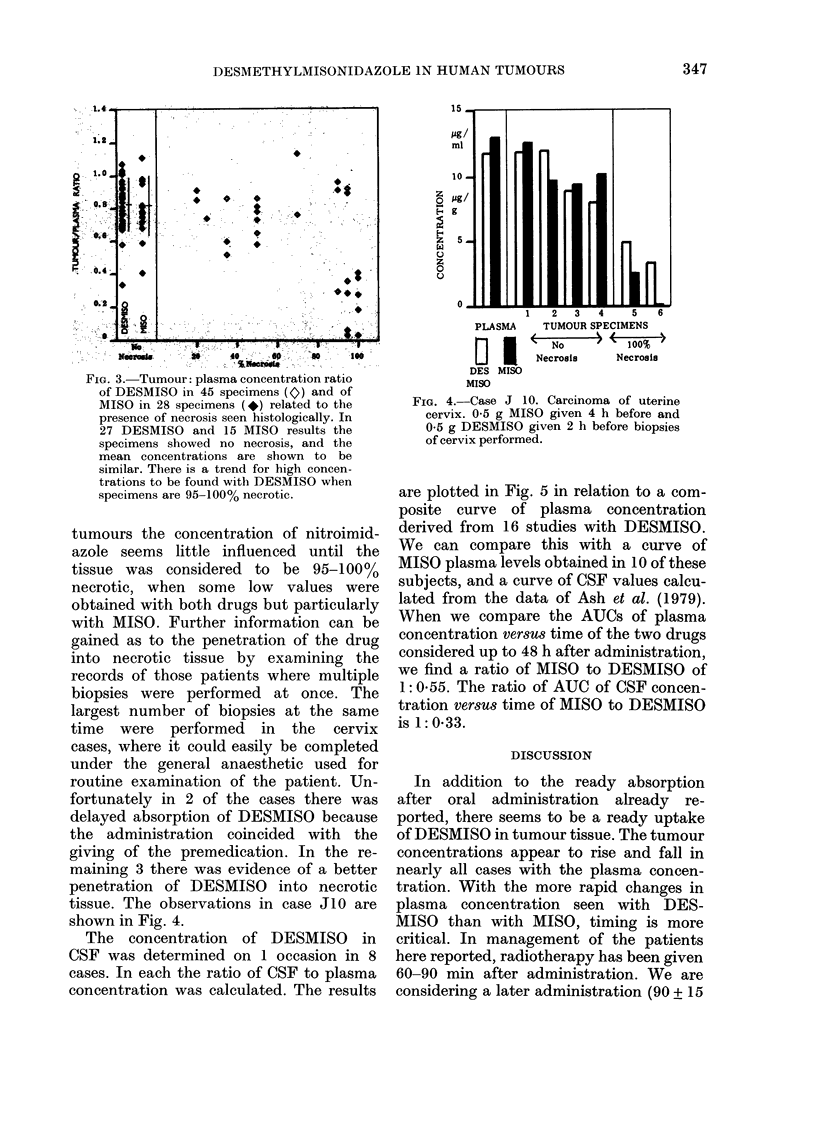
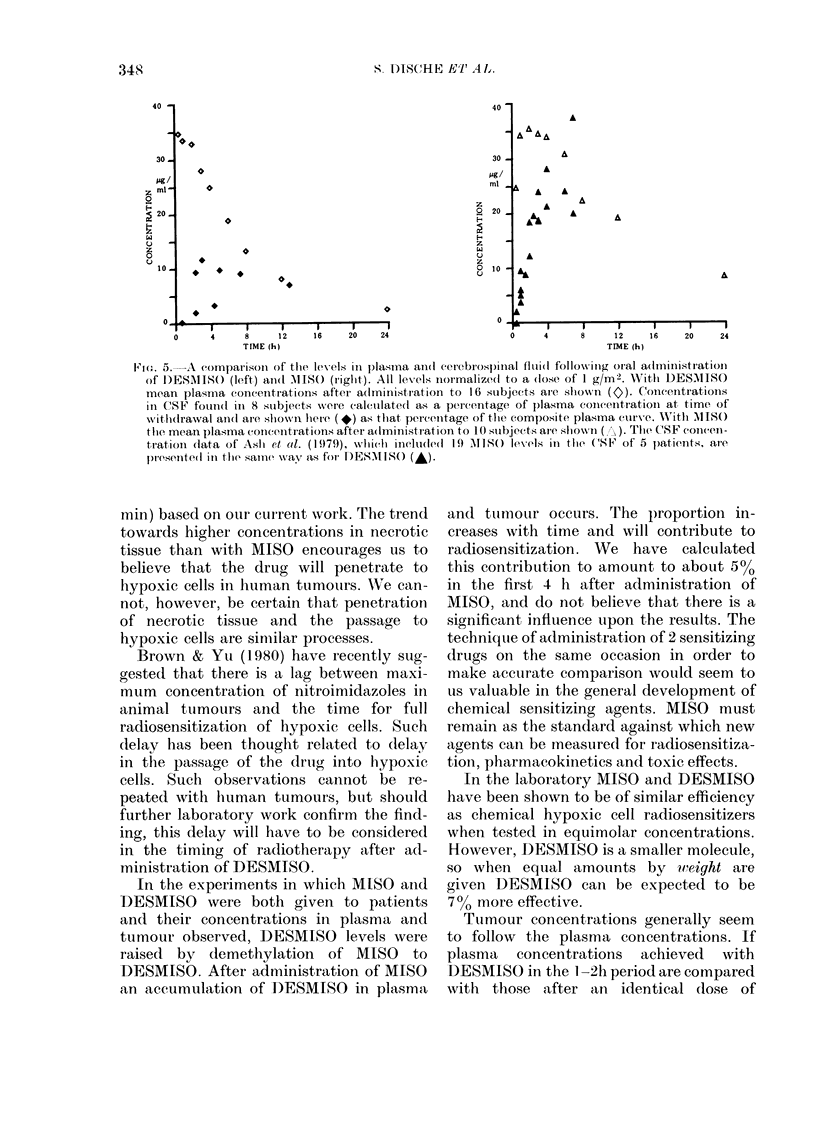
The concentration of desmethylmisonidazole (DESMISO) was determined in 60 biopsy samples taken from 13 human tumours and in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from 8 patients after oral administration. In comparison with misonidazole (MISO), peak concentrations in plasma were reached at earlier times and half-lives were shorter, so that the area under the curve of plasma concentration with time (AUC) was reduced by 45%; the AUC of CSF concentration with time was reduced by 67%. Between 1 and 2 h after administration of DESMISO, concentrations in tumours were generally 85-90% of those of MISO estimated approximately 4 h after it was given. The two drugs when tested in equimolar concentrations have been found in laboratory experiment to be equally potent as hypoxic cell radiosensitizers. Recognizing the lower mol. wt of DESMISO and the trend to higher concentrations in the more necrotic areas of the tumours studied equal doses by weight of the two drugs given orally may give equal radiosensitization of hypoxic cells in human tumours.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ash D. V., Smith M. R., Bugden R. D. Distribution of misonidazole in human tumours and normal tissues. Br J Cancer. 1979 May;39(5):503–509. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1979.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartal A. H., Cohen Y., Robinson E. Malignant melanoma arising at tattoo sites used for radiotherapy field marking. Br J Radiol. 1980 Sep;53(633):913–914. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-53-633-913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. M., Workman P. Partition coefficient as a guide to the development of radiosensitizers which are less toxic than misonidazole. Radiat Res. 1980 Apr;82(1):171–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dische S., Fowler J. F., Saunders M. I., Stratford M. R., Anderson P., Minchinton A. I., Lee M. E. A drug for improved radiosensitization in radiotherapy. Br J Cancer. 1980 Jul;42(1):153–155. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1980.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dische S., Saunders M. I., Flockhart I. R., Lee M. E., Anderson P. Misonidazole-a drug for trial in radiotherapy and oncology. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1979 Jun;5(6):851–860. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(79)90070-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dische S., Saunders M. I., Lee M. E., Adams G. E., Flockhart I. R. Clinical testing of the radiosensitizer Ro 07-0582: experience with multiple doses. Br J Cancer. 1977 May;35(5):567–579. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1977.90. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler J. F., Adams G. E., Denekamp J. Radiosensitizers of hypoxic cells in solid tumors. Cancer Treat Rev. 1976 Dec;3(4):227–256. doi: 10.1016/s0305-7372(76)80012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. A., Workman P. Pharmacokinetic and tumour-penetration properties of the hypoxic cell radiosensitizer desmethylmisonidazole (Ro 05-Ro-9963) in dogs. Br J Cancer. 1980 Feb;41(2):268–276. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1980.39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


