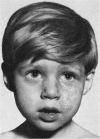
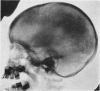
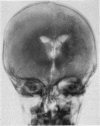
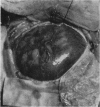
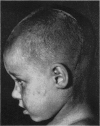
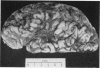
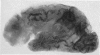
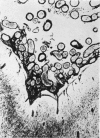
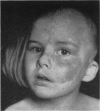
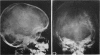
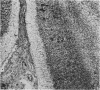
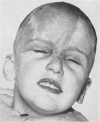
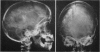
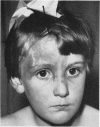
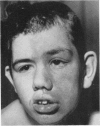
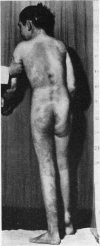
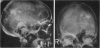
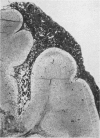
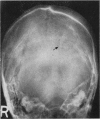
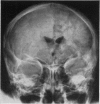
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CABIESES F., JERI R., LANDA R. Fatal brain-stem shift following hemispherectomy. J Neurosurg. 1957 Jan;14(1):74–91. doi: 10.3171/jns.1957.14.1.0074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAIRNS H., DAVIDSON M. A. Hemispherectomy in the treatment of infantile hemiplegia. Lancet. 1951 Sep 8;2(6680):411–415. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(51)91687-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRENCH L. A., JOHNSON D. R., BROWN I. A., VAN BERGEN F. B. Cerebral hemispherectomy for control of intractable convulsive seizures. J Neurosurg. 1955 Mar;12(2):154–164. doi: 10.3171/jns.1955.12.2.0154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODALL R. J. Cerebral hemispherectomy: present status and clinical indications. Neurology. 1957 Mar;7(3):151–162. doi: 10.1212/wnl.7.3.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN J. R., FOSTER J., BERENS D. L. Encephalotrigeminal angiomatosis (Sturge-Weber syndrome); with particular reference to the roentgenological aspects before and after neurosurgery. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther. 1950 Sep;64(3):391–398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROS C. Technique de l'hémisphérectomie. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1951;85(6):484–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUBER K., ZWEYMULLER E. Monosymptomatische Form des Krankheitsbildes von Sturge-Weber. Wien Z Nervenheilkd Grenzgeb. 1954;9(4):459–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRAYENBUHL H., YASARGIL G., UEHLINGER E. Klinischer und pathologischanatomischer Beitrag zur Sturge-Weber-Krab-be'schen Krankheit. Dermatologica. 1957 Oct;115(4):555–571. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRYNAUW R. A. Infantile hemiplegia treated by removing one cerebral hemisphere. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1950 Nov;13(4):243–267. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.13.4.243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LICHTENSTEIN B. W. Sturge-Weber-Dimitri syndrome, cephalic form of neurocutaneous hemangiomatosis. AMA Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1954 Mar;71(3):291–301. doi: 10.1001/archneurpsyc.1954.02320390021002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCKISSOCK W. Infantile hemiplegia. Proc R Soc Med. 1953 Jun;46(6):431–434. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAMPIGLIONE G., KERRIDGE J. E.E.G. abnormalities from the temporal lobe studied with sphenoidal electrodes. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1956 May;19(2):117–129. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.19.2.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PETERMAN A. F., HAYLES A. B., DOCKERTY M. B., LOVE J. G. Encephalotrigeminal angiomatosis (Sturge-Weber disease); clinical study of thirty-five cases. J Am Med Assoc. 1958 Aug 30;167(18):2169–2176. doi: 10.1001/jama.1958.02990350007002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLANI P. E. Encephalo-trigeminal angiomatosis (Sturge-Weber syndrome) treated by removal of the affected cerebral hemisphere. Proc R Soc Med. 1952 Dec;45(12):860–862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POSER C. M., TAVERAS J. M. Cerebral angiography in encephalo-trigeminal angiomatosis. Radiology. 1957 Mar;68(3):327–336. doi: 10.1148/68.3.327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOHLWILL F. J., YAKOVLEV P. I. Histopathology of meningo-facial angiomatosis (Sturge-Weber's disease); report of four cases. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1957 Jul;16(3):341–364. doi: 10.1097/00005072-195707000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]