Abstract
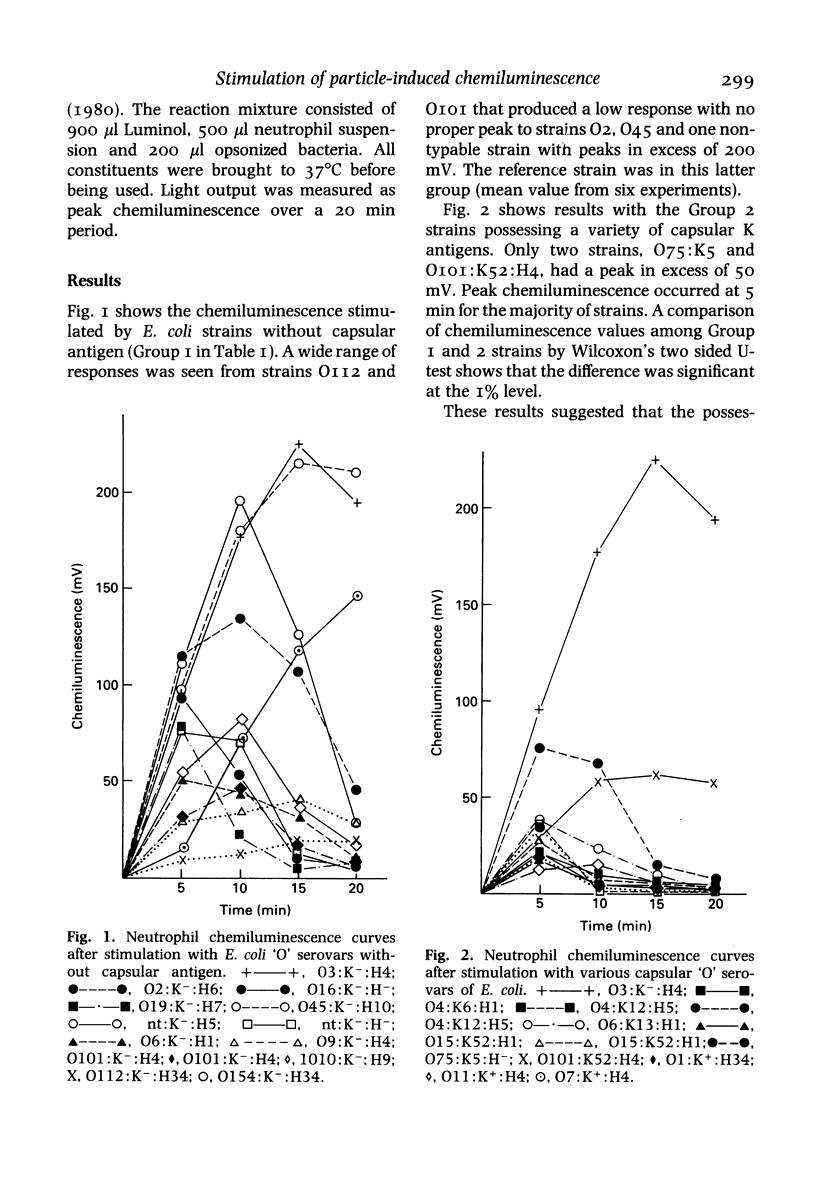
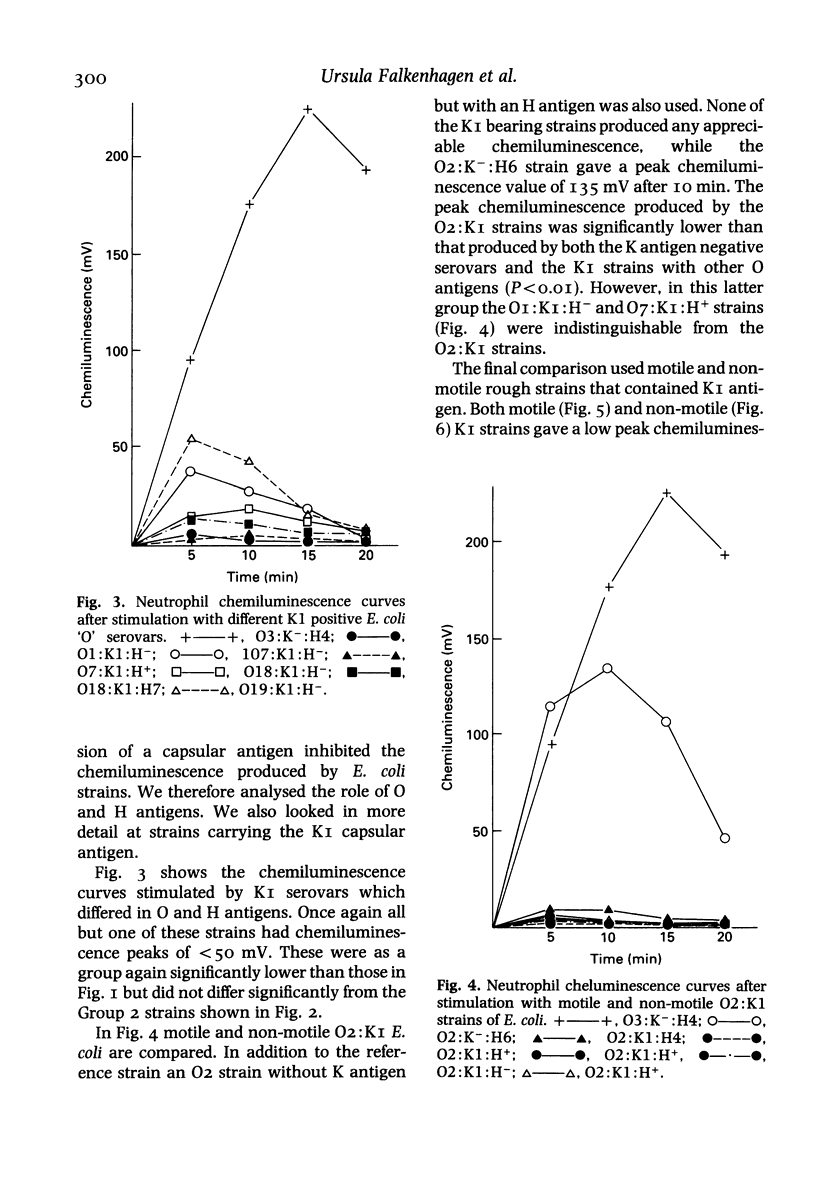
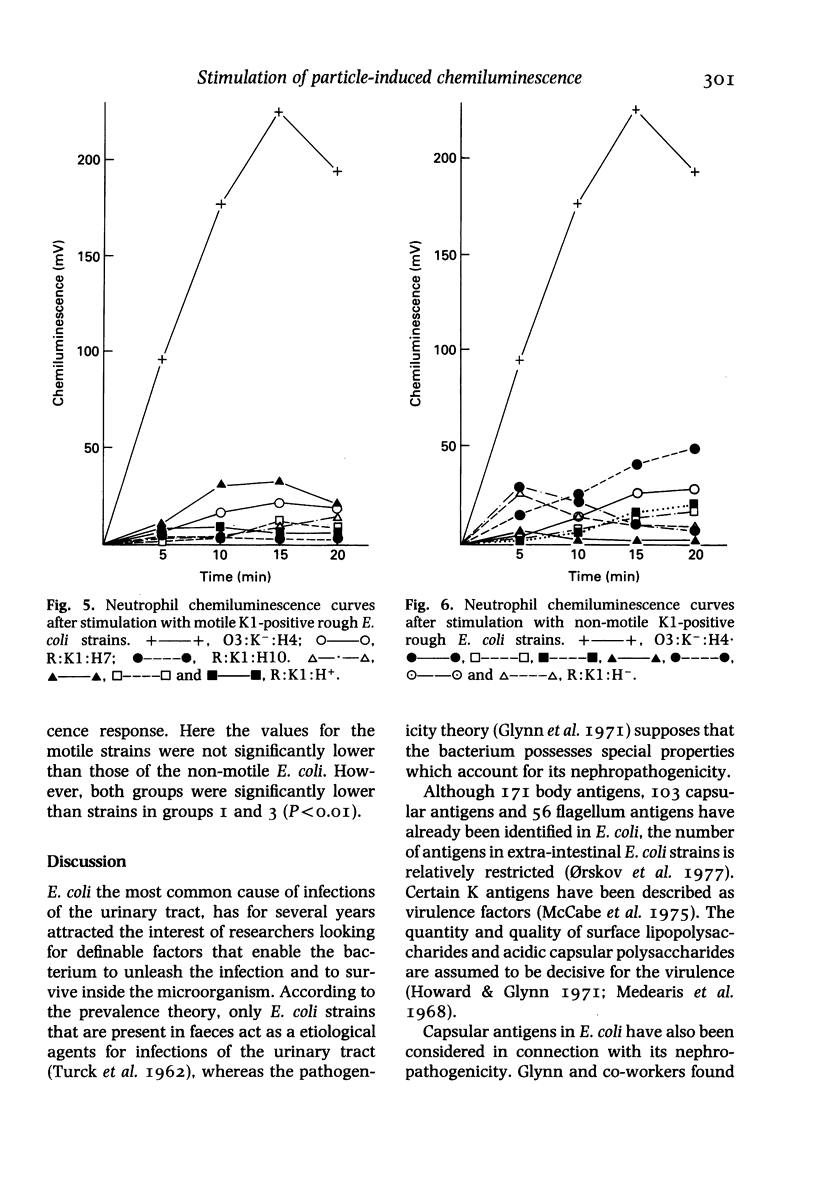
The patterns of neutrophil chemiluminescence stimulated by groups of E. coli strains opsonized with pooled normal human serum were compared. All strains of E. coli were obtained from patients with chronic pyelonephritis. 'O' serovars which lacked capsular (K) antigen produced significantly higher chemiluminescence than strains possessing a variety of K antigens. Chemiluminescence produced by a range 'O' serovars bearing the K1 antigen did not differ significantly from those containing other K antigens. The lowest chemiluminescence values were obtained with a group of O2:K1 strains. Rough strains containing K1 antigen were also poor stimulators of chemiluminescence.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen R. C., Loose L. D. Phagocytic activation of a luminol-dependent chemiluminescence in rabbit alveolar and peritoneal macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Mar 8;69(1):245–252. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80299-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen R. C., Stjernholm R. L., Steele R. H. Evidence for the generation of an electronic excitation state(s) in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes and its participation in bactericidal activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 May 26;47(4):679–684. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90545-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bortolussi R., Ferrieri P., Björkstén B., Quie P. G. Capsular K1 polysaccharide of Escherichia coli: relationship to virulence in newborn rats and resistance to phagocytosis. Infect Immun. 1979 Jul;25(1):293–298. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.1.293-298.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross R. J., Cheasty T., Rowe B. Isolation of bacteriophages specific for the K1 polysaccharide antigen of Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Dec;6(6):548–550. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.6.548-550.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard C. J., Glynn A. A. The virulence for mice of strains of Escherichia coli related to the effects of K antigens on their resistance to phagocytosis and killing by complement. Immunology. 1971 May;20(5):767–777. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medearis D. N., Jr, Camitta B. M., Heath E. C. Cell wall composition and virulence in Escherichia coli. J Exp Med. 1968 Sep 1;128(3):399–414. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.3.399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dijk W. C., Verbrugh H. A., Peters R., Van Der Tol M. E., Peterson P. K., Verhoef J. Escherichia coli K antigen in relation to serum-induced lysis and phagocytosis. J Med Microbiol. 1979 Feb;12(1):123–130. doi: 10.1099/00222615-12-1-123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein R., Young L. S. Phagocytic resistance of Escherichia coli K-1 isolates and relationship to virulence. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Dec;8(6):748–755. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.6.748-755.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


