Abstract
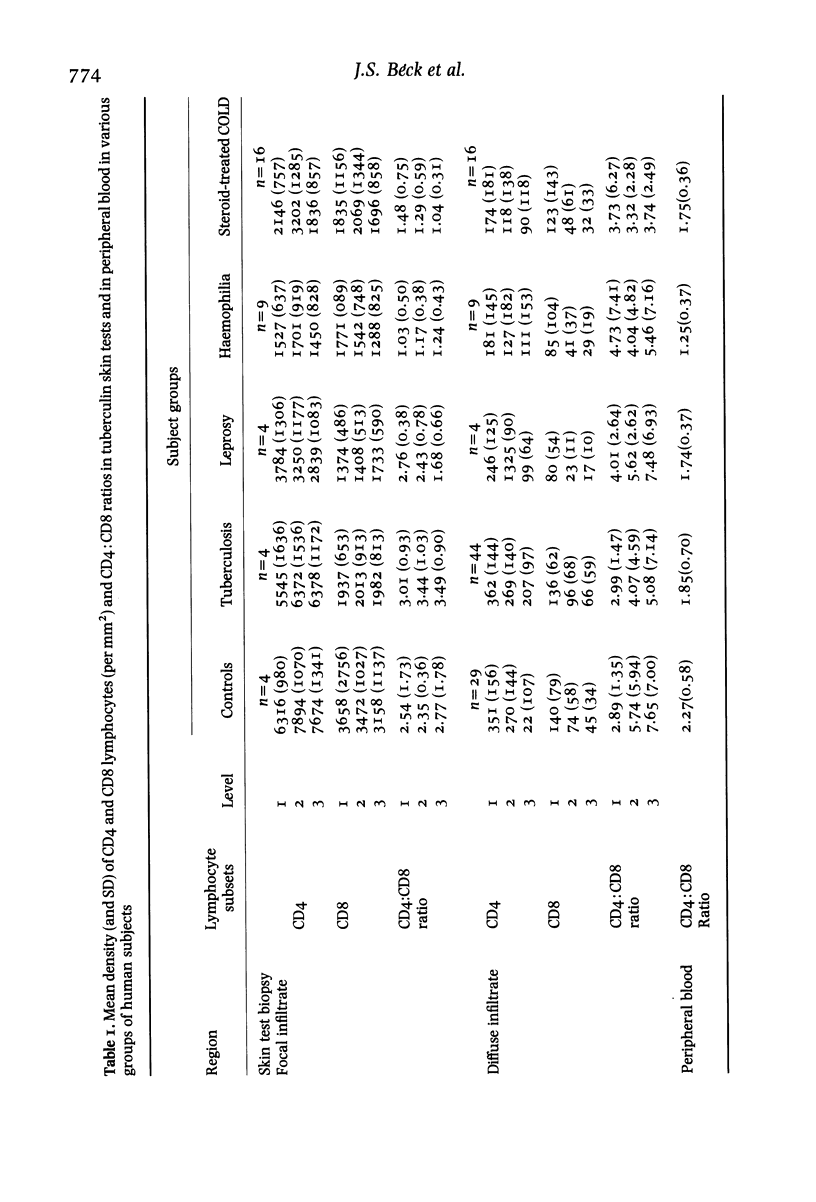
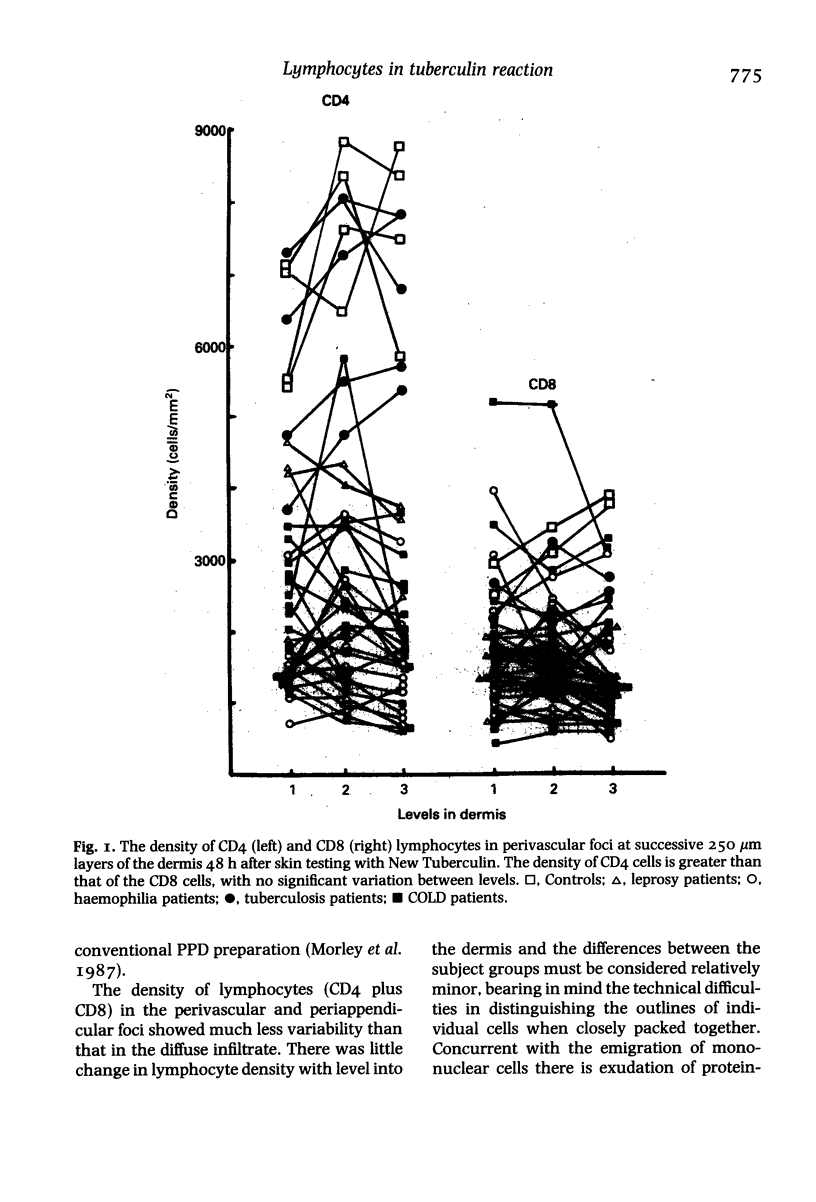
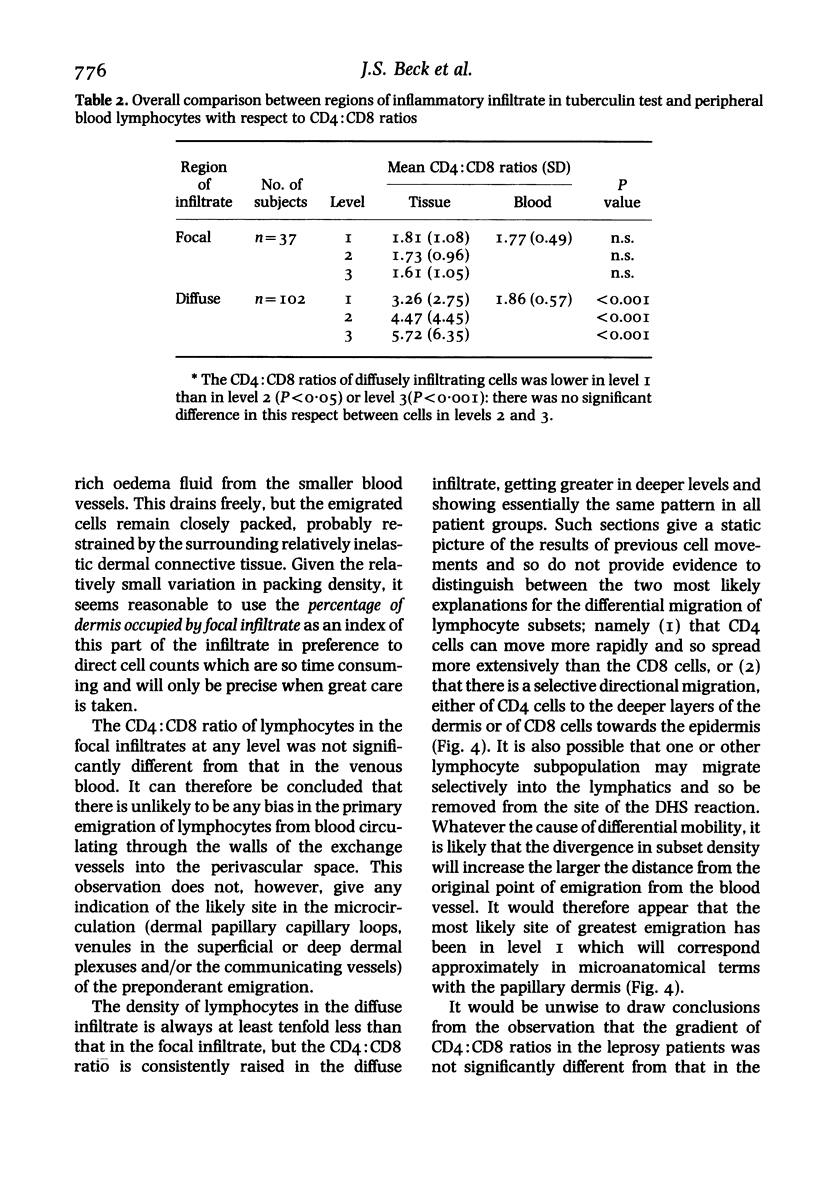
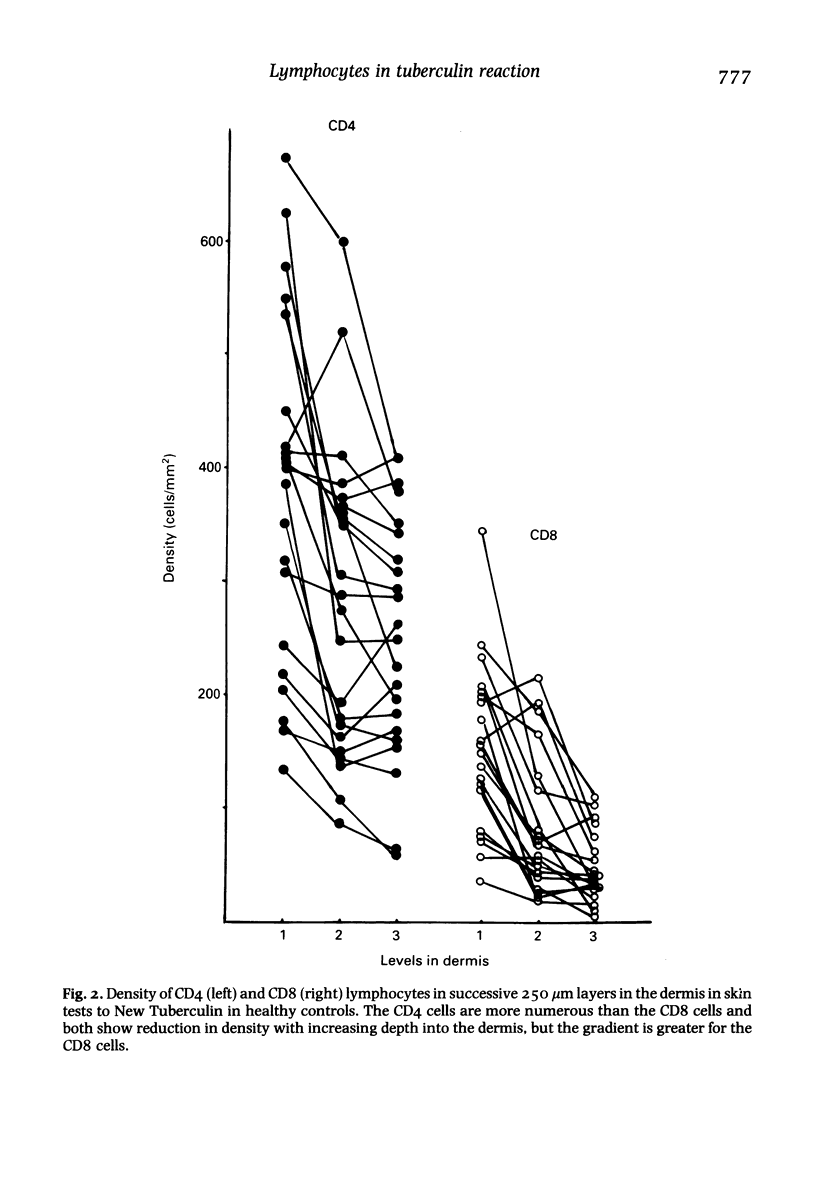
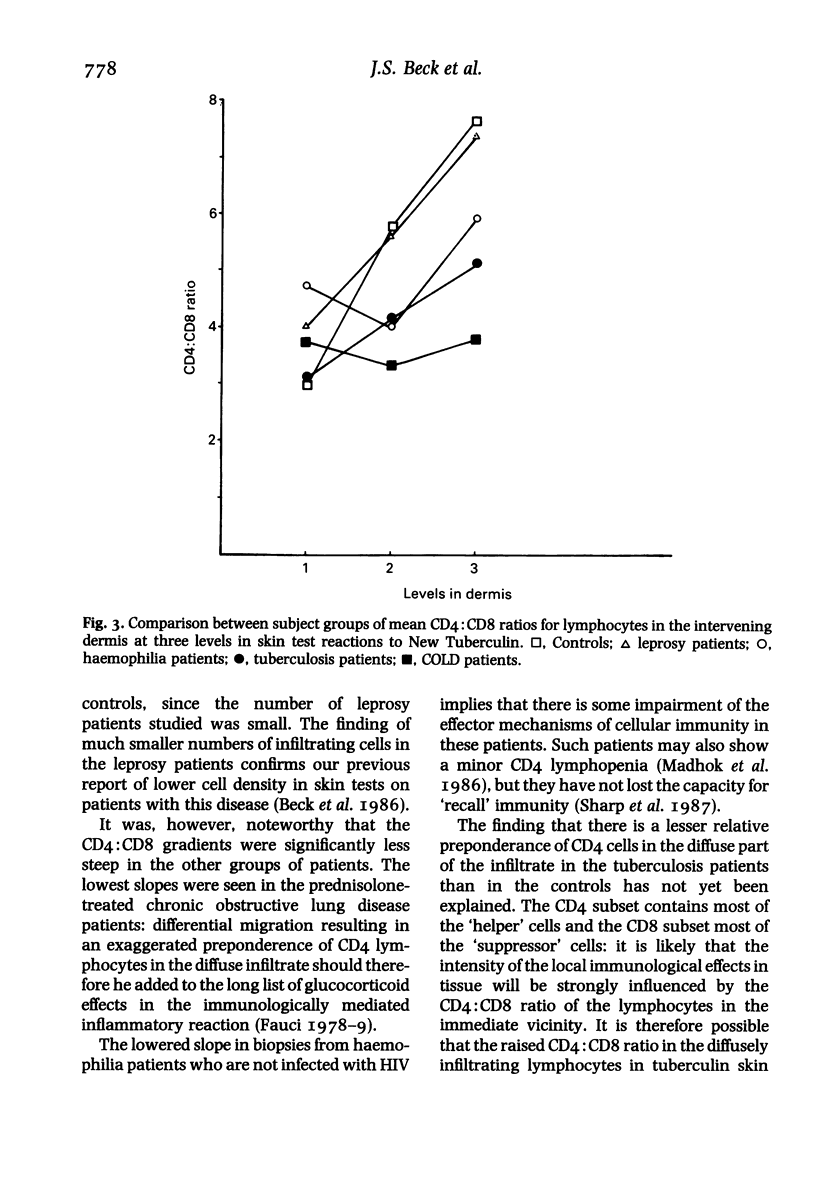
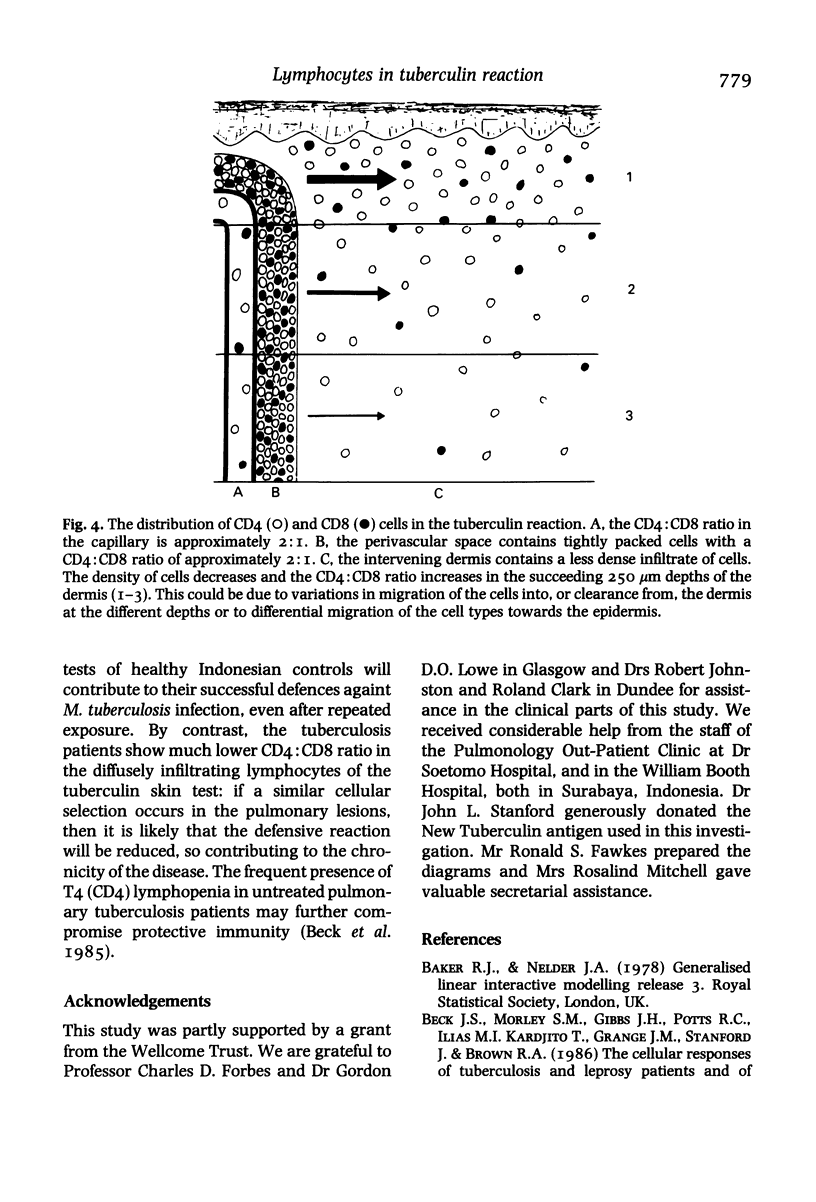
The lymphocytes in the perivascular foci of tuberculin skin tests have a similar CD4:CD8 ratio to those in the peripheral blood, suggesting that these subsets do not show bias in their initial emigration. By contrast, the diffusely infiltrating lymphocytes show a relative preponderance of CD4 cells which is progressively greater in successive 250 micron layers into the dermis. A generally similar pattern is seen in healthy controls and in patients with untreated pulmonary tuberculosis, treated leprosy, haemophilia A and chronic obstructive lung disease (COLD) patients treated with prednisolone, but the gradient of increasing CD4:CD8 ratio with depth into the dermis is significantly less steep in patients with tuberculosis, haemophilia and prednisolone-treated COLD than in the healthy controls. Selective migration results in a relative preponderance of CD4 cells in the diffuse infiltrate and it is suggested that this is a mechanism likely to potentiate defensive reaction to Mycobacterium tuberculosis: any deficiency in selective migration may make immunological defences less effective and so contribute to the chronicity of the lesions of tuberculosis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beck J. S., Potts R. C., Kardjito T., Grange J. M. T4 lymphopenia in patients with active pulmonary tuberculosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Apr;60(1):49–54. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coghill G., Gibbs J. H., Lowe J. G., Swanson Beck J. Cryopreservation with glycerol during cryostat sectioning for localisation of lymphocytes and accessory cell phenotypic subsets in tissue biopsies. J Clin Pathol. 1985 Jul;38(7):840–842. doi: 10.1136/jcp.38.7.840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cree I. A., McDougall A. C., Coghill G., Beck J. S. Quantitation of the granuloma fraction in leprosy skin biopsies by planimetry. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1985 Dec;53(4):582–586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madhok R., Gracie A., Lowe G. D., Burnett A., Froebel K., Follett E., Forbes C. D. Impaired cell mediated immunity in haemophilia in the absence of infection with human immunodeficiency virus. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Oct 18;293(6553):978–980. doi: 10.1136/bmj.293.6553.978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morley S. M., Beck J. S., Grange J. M., Brown R. A., Kardjito T. The method of preparation of an antigen may influence the cellular reaction to it in skin tests for delayed hypersensitivity: comparison between responses to two different reagents prepared from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Sep;69(3):584–590. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt J. L., Grant B. W., Eddy A. A., Michael A. F. Immune cell populations in cutaneous delayed-type hypersensitivity. J Exp Med. 1983 Oct 1;158(4):1227–1242. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.4.1227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulter L. W., Seymour G. J., Duke O., Janossy G., Panayi G. Immunohistological analysis of delayed-type hypersensitivity in man. Cell Immunol. 1982 Dec;74(2):358–369. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(82)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp R. A., Morley S. M., Beck J. S., Urquhart G. E. Unresponsiveness to skin testing with bacterial antigens in patients with haemophilia A not apparently infected with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). J Clin Pathol. 1987 Aug;40(8):849–852. doi: 10.1136/jcp.40.8.849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


