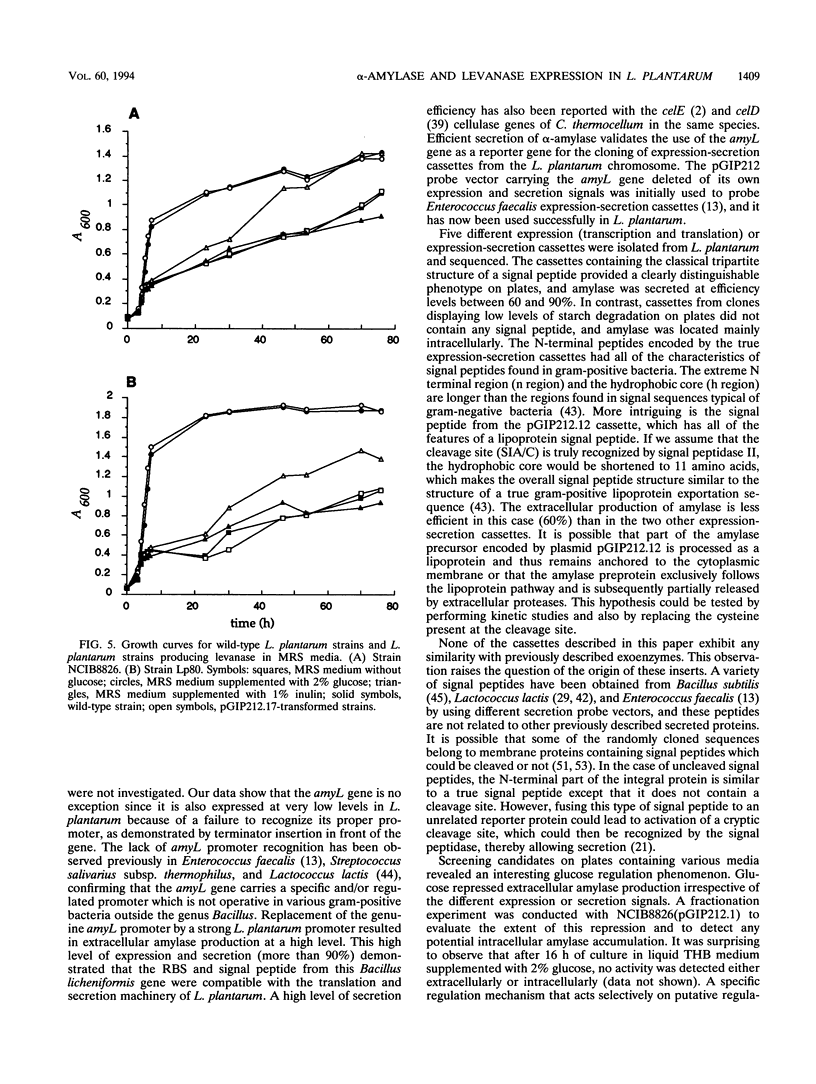
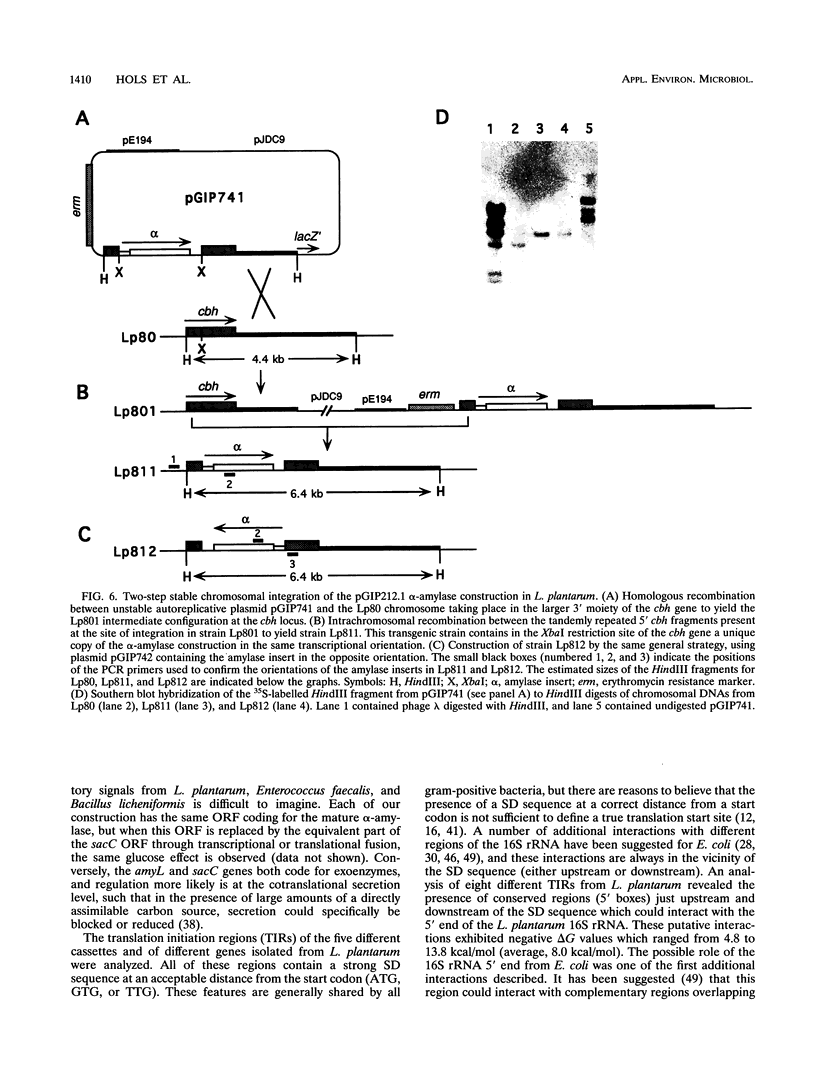
Abstract
The genuine alpha-amylase gene from Bacillus licheniformis (amyL) is not expressed in Lactobacillus plantarum, but replacement of the amyL promoter by a strong L. plantarum promoter leads to efficient expression of the gene and secretion of more than 90% of the alpha-amylase into the culture supernatant. A series of L. plantarum genetic cassettes (transcription and translation with or without secretion) were cloned by translation fusion of random DNA fragments to the silent amyL coding frame in the pGIP212 probe vector (P. Hols, A. Baulard, D. Garmyn, B. Delplace, S. Hogan, and J. Delcour, Gene 118:21-30, 1992). Five different cassettes were sequenced and found to harbor genetic signals similar to those of other gram-positive bacteria. The functions of the cloned cassettes and the cassettes isolated previously from Enterococcus faecalis were compared in E. faecalis and L. plantarum, respectively. All signals were well recognized in L. plantarum, but cassettes isolated from L. plantarum led to a low level of amylase production in E. faecalis, suggesting that the L. plantarum signals are more species specific. Six transcriptional or translational fusions were constructed to express the Bacillus subtilis levanase gene (sacC) in L. plantarum. All of these constructions were capable of inducing levanase production and secretion in the culture supernatant, and, furthermore, L. plantarum strains harboring the most efficient fusions could grow in MRS medium containing inulin as the major carbon source. Finally, a two-step chromosomal integration procedure was used to achieve efficient stabilization of an amylase construction without any residual resistance marker or vector sequence.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bates E. E., Gilbert H. J., Hazlewood G. P., Huckle J., Laurie J. I., Mann S. P. Expression of a Clostridium thermocellum endoglucanase gene in Lactobacillus plantarum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Aug;55(8):2095–2097. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.8.2095-2097.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouia A., Bringel F., Frey L., Belarbi A., Guyonvarch A., Kammerer B., Hubert J. C. Cloning and structure of the pyrE gene of Lactobacillus plantarum CCM 1904. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Jun 1;57(3):233–238. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(90)90072-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bringel F., Frey L., Hubert J. C. Characterization, cloning, curing, and distribution in lactic acid bacteria of pLP1, a plasmid from Lactobacillus plantarum CCM 1904 and its use in shuttle vector construction. Plasmid. 1989 Nov;22(3):193–202. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(89)90002-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. D., Morrison D. A. Cloning of Streptococcus pneumoniae DNA fragments in Escherichia coli requires vectors protected by strong transcriptional terminators. Gene. 1987;55(2-3):179–187. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiaens H., Leer R. J., Pouwels P. H., Verstraete W. Cloning and expression of a conjugated bile acid hydrolase gene from Lactobacillus plantarum by using a direct plate assay. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Dec;58(12):3792–3798. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.12.3792-3798.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferain T., Garmyn D., Bernard N., Hols P., Delcour J. Lactobacillus plantarum ldhL gene: overexpression and deletion. J Bacteriol. 1994 Feb;176(3):596–601. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.3.596-601.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hager P. W., Rabinowitz J. C. Inefficient translation of T7 late mRNA by Bacillus subtilis ribosomes. Implications for species-specific translation. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15163–15167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hols P., Baulard A., Garmyn D., Delplace B., Hogan S., Delcour J. Isolation and characterization of genetic expression and secretion signals from Enterococcus faecalis through the use of broad-host-range alpha-amylase probe vectors. Gene. 1992 Sep 1;118(1):21–30. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90244-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hols P., de Halleux S., Delcour J. A strategy to construct vector-free amylolytic strains through nondisruptive homologous recombination: application to Enterococcus faecalis. Gene. 1992 Sep 1;118(1):31–38. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90245-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ike Y., Craig R. A., White B. A., Yagi Y., Clewell D. B. Modification of Streptococcus faecalis sex pheromones after acquisition of plasmid DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5369–5373. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacques N., Dreyfus M. Translation initiation in Escherichia coli: old and new questions. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Jul;4(7):1063–1067. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00679.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S., Warner P. J. Cloning and expression of alpha-amylase from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens in a stable plasmid vector in Lactobacillus plantarum. Lett Appl Microbiol. 1990 Oct;11(4):214–219. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-765x.1990.tb00164.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josson K., Scheirlinck T., Michiels F., Platteeuw C., Stanssens P., Joos H., Dhaese P., Zabeau M., Mahillon J. Characterization of a gram-positive broad-host-range plasmid isolated from Lactobacillus hilgardii. Plasmid. 1989 Jan;21(1):9–20. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(89)90082-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leer R. J., Christiaens H., Verstraete W., Peters L., Posno M., Pouwels P. H. Gene disruption in Lactobacillus plantarum strain 80 by site-specific recombination: isolation of a mutant strain deficient in conjugated bile salt hydrolase activity. Mol Gen Genet. 1993 May;239(1-2):269–272. doi: 10.1007/BF00281627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipp J., Dobberstein B. The membrane-spanning segment of invariant chain (I gamma) contains a potentially cleavable signal sequence. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1103–1112. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90710-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig W., Seewaldt E., Kilpper-Bälz R., Schleifer K. H., Magrum L., Woese C. R., Fox G. E., Stackebrandt E. The phylogenetic position of Streptococcus and Enterococcus. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Mar;131(3):543–551. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-3-543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin I., Debarbouille M., Klier A., Rapoport G. Induction and metabolite regulation of levanase synthesis in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1989 Apr;171(4):1885–1892. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.4.1885-1892.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin I., Débarbouillé M., Ferrari E., Klier A., Rapoport G. Characterization of the levanase gene of Bacillus subtilis which shows homology to yeast invertase. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Jun;208(1-2):177–184. doi: 10.1007/BF00330439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin J. R., Murray C. L., Rabinowitz J. C. Unique features in the ribosome binding site sequence of the gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus beta-lactamase gene. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):11283–11291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melançon P., Leclerc D., Brakier-Gingras L. A deletion mutation at the 5' end of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Aug 27;1050(1-3):98–103. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90148-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olins P. O., Rangwala S. H. A novel sequence element derived from bacteriophage T7 mRNA acts as an enhancer of translation of the lacZ gene in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):16973–16976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Martinez G., Kok J., Venema G., van Dijl J. M., Smith H., Bron S. Protein export elements from Lactococcus lactis. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Sep;234(3):401–411. doi: 10.1007/BF00538699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen G. B., Stockwell P. A., Hill D. F. Messenger RNA recognition in Escherichia coli: a possible second site of interaction with 16S ribosomal RNA. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3957–3962. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03282.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piggott R. P., Rossiter A., Ortlepp S. A., Pembroke J. T., Ollington J. F. Cloning in Bacillus subtilis of an extremely thermostable alpha amylase: comparison with other cloned heatstable alpha amylases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jul 18;122(1):175–183. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90456-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posno M., Leer R. J., van Luijk N., van Giezen M. J. F., Heuvelmans P. T. H. M., Lokman B. C., Pouwels P. H. Incompatibility of Lactobacillus Vectors with Replicons Derived from Small Cryptic Lactobacillus Plasmids and Segregational Instability of the Introduced Vectors. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Jun;57(6):1822–1828. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.6.1822-1828.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz P. J., Beckwith J. Genetic analysis of protein export in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Genet. 1990;24:215–248. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.24.120190.001243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheirlinck T., Mahillon J., Joos H., Dhaese P., Michiels F. Integration and expression of alpha-amylase and endoglucanase genes in the Lactobacillus plantarum chromosome. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Sep;55(9):2130–2137. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.9.2130-2137.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer G. F., Walkinshaw M. D., Arnott S., Morré D. J. The ribosome binding sites recognized by E. coli ribosomes have regions with signal character in both the leader and protein coding segments. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Sep 11;8(17):3895–3907. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.17.3895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibakov M., Koivula T., von Wright A., Palva I. Secretion of TEM beta-lactamase with signal sequences isolated from the chromosome of Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Feb;57(2):341–348. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.2.341-348.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonen M., Palva I. Protein secretion in Bacillus species. Microbiol Rev. 1993 Mar;57(1):109–137. doi: 10.1128/mr.57.1.109-137.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H., de Jong A., Bron S., Venema G. Characterization of signal-sequence-coding regions selected from the Bacillus subtilis chromosome. Gene. 1988 Oct 30;70(2):351–361. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90207-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suominen I., Karp M., Lähde M., Kopio A., Glumoff T., Meyer P., Mäntsälä P. Extracellular production of cloned alpha-amylase by Escherichia coli. Gene. 1987;61(2):165–176. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90111-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Borer P. N., Dengler B., Levin M. D., Uhlenbeck O. C., Crothers D. M., Bralla J. Improved estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):40–41. doi: 10.1038/newbio246040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerial M., Melancon P., Schneider C., Garoff H. The transmembrane segment of the human transferrin receptor functions as a signal peptide. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1543–1550. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04395.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Knippenberg P. H. A possible role of the 5' terminal sequence of 16S ribosomal RNA in the recognition of initiation sequences for protein synthesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1975 Jan;2(1):79–85. doi: 10.1093/nar/2.1.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Transcending the impenetrable: how proteins come to terms with membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jun 9;947(2):307–333. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(88)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




