Abstract
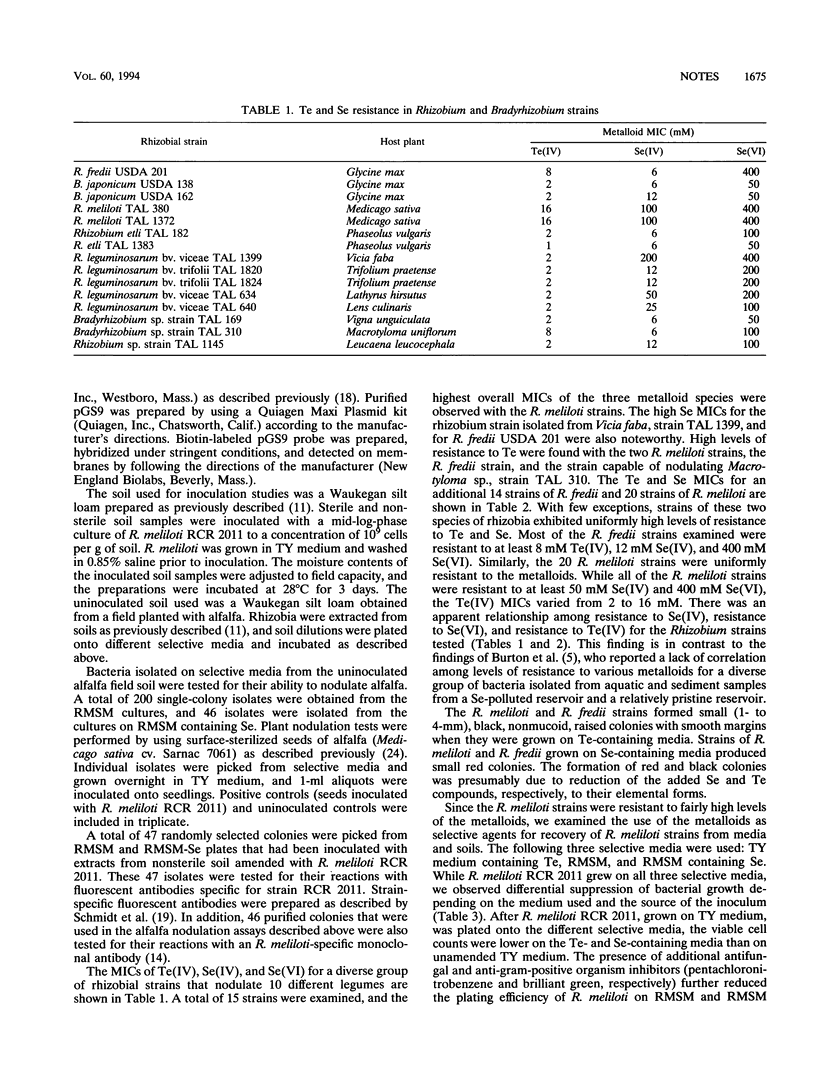
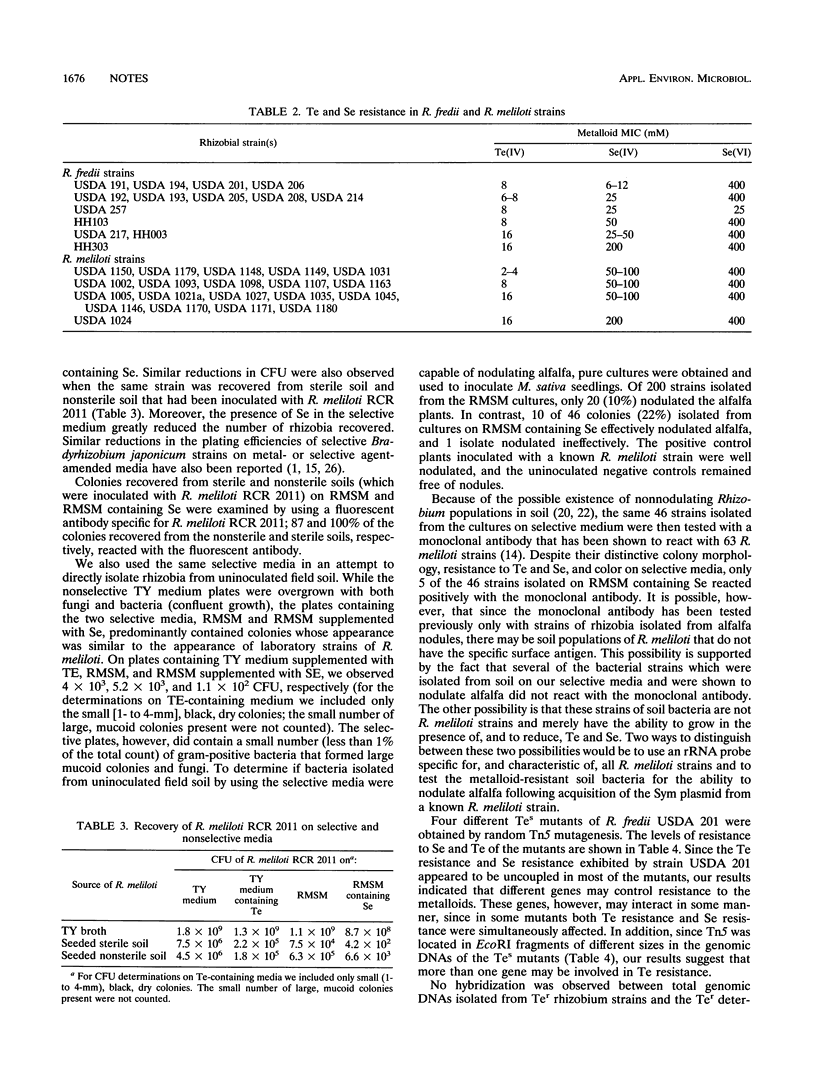
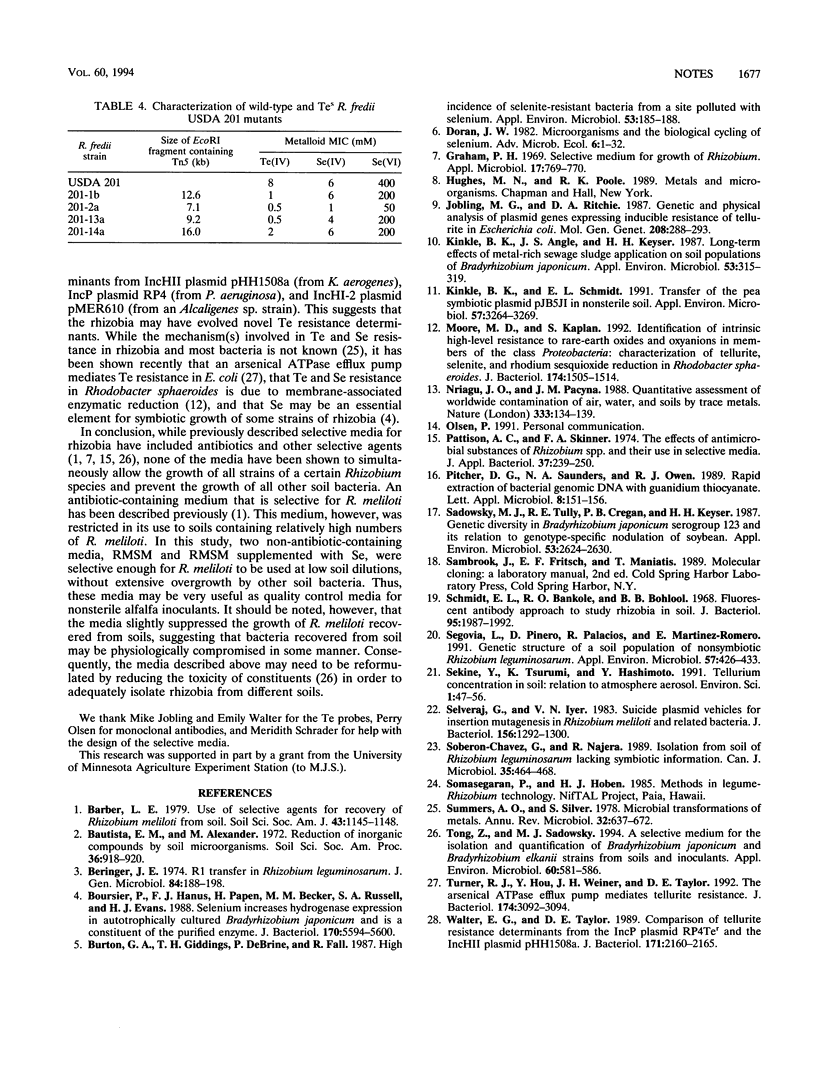
Forty-eight Rhizobium and Bradyrhizobium strains were screened for resistance to tellurite, selenite, and selenate. High levels of resistance to the metals were observed only in Rhizobium meliloti and Rhizobium fredii strains; the MICs were 2 to 8 mM for Te(IV), >200 mM for Se(VI), and 50 to 100 mM for Se(IV). Incorporation of Se and Te into growth media permitted us to directly isolate R. meliloti strains from soil. Mutant strains of rhizobia having decreased levels of Se and Te resistance were constructed by Tn5 mutagenesis and were found to have transposon insertions in DNA fragments of different sizes. Genomic DNAs from Ter rhizobium strains failed to hybridize with Ter determinants from plasmids RP4, pHH1508a, and pMER610.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beringer J. E. R factor transfer in Rhizobium leguminosarum. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Sep;84(1):188–198. doi: 10.1099/00221287-84-1-188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boursier P., Hanus F. J., Papen H., Becker M. M., Russell S. A., Evans H. J. Selenium increases hydrogenase expression in autotrophically cultured Bradyrhizobium japonicum and is a constituent of the purified enzyme. J Bacteriol. 1988 Dec;170(12):5594–5600. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.12.5594-5600.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton G. A., Jr, Giddings T. H., DeBrine P., Fall R. High incidence of selenite-resistant bacteria from a site polluted with selenium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Jan;53(1):185–188. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.1.185-188.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham P. H. Selective medium for growth of Rhizobium. Appl Microbiol. 1969 May;17(5):769–770. doi: 10.1128/am.17.5.769-770.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jobling M. G., Ritchie D. A. Genetic and physical analysis of plasmid genes expressing inducible resistance of tellurite in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Jun;208(1-2):288–293. doi: 10.1007/BF00330455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinkle B. K., Angle J. S., Keyser H. H. Long-Term Effects of Metal-Rich Sewage Sludge Application on Soil Populations of Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Feb;53(2):315–319. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.2.315-319.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinkle B. K., Schmidt E. L. Transfer of the Pea Symbiotic Plasmid pJB5JI in Nonsterile Soil. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Nov;57(11):3264–3269. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.11.3264-3269.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M. D., Kaplan S. Identification of intrinsic high-level resistance to rare-earth oxides and oxyanions in members of the class Proteobacteria: characterization of tellurite, selenite, and rhodium sesquioxide reduction in Rhodobacter sphaeroides. J Bacteriol. 1992 Mar;174(5):1505–1514. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.5.1505-1514.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nriagu J. O., Pacyna J. M. Quantitative assessment of worldwide contamination of air, water and soils by trace metals. Nature. 1988 May 12;333(6169):134–139. doi: 10.1038/333134a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattison A. C., Skinner F. A. The effects of antimicrobial substances on Rhizobium spp. and their use in selective media. J Appl Bacteriol. 1974 Jun;37(2):239–250. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1974.tb00435.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowsky M. J., Tully R. E., Cregan P. B., Keyser H. H. Genetic Diversity in Bradyrhizobium japonicum Serogroup 123 and Its Relation to Genotype-Specific Nodulation of Soybean. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Nov;53(11):2624–2630. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.11.2624-2630.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvi R. J., Ahroon W., Saunders S. S., Arnold S. A. Evoked potentials: computer-automated threshold-tracking procedure using an objective detection criterion. Ear Hear. 1987 Jun;8(3):151–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt E. L., Bakole R. O., Bohlool B. B. Fluorescent-antibody approach to study of rhizobia in soil. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):1987–1992. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.1987-1992.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segovia L., Piñero D., Palacios R., Martínez-Romero E. Genetic structure of a soil population of nonsymbiotic Rhizobium leguminosarum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Feb;57(2):426–433. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.2.426-433.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraj G., Iyer V. N. Suicide plasmid vehicles for insertion mutagenesis in Rhizobium meliloti and related bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1983 Dec;156(3):1292–1300. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.3.1292-1300.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers A. O., Silver S. Microbial transformations of metals. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1978;32:637–672. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.32.100178.003225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong Z., Sadowsky M. J. A Selective Medium for the Isolation and Quantification of Bradyrhizobium japonicum and Bradyrhizobium elkanii Strains from Soils and Inoculants. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1994 Feb;60(2):581–586. doi: 10.1128/aem.60.2.581-586.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R. J., Hou Y., Weiner J. H., Taylor D. E. The arsenical ATPase efflux pump mediates tellurite resistance. J Bacteriol. 1992 May;174(9):3092–3094. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.9.3092-3094.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter E. G., Taylor D. E. Comparison of tellurite resistance determinants from the IncP alpha plasmid RP4Ter and the IncHII plasmid pHH1508a. J Bacteriol. 1989 Apr;171(4):2160–2165. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.4.2160-2165.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


