Abstract
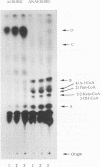
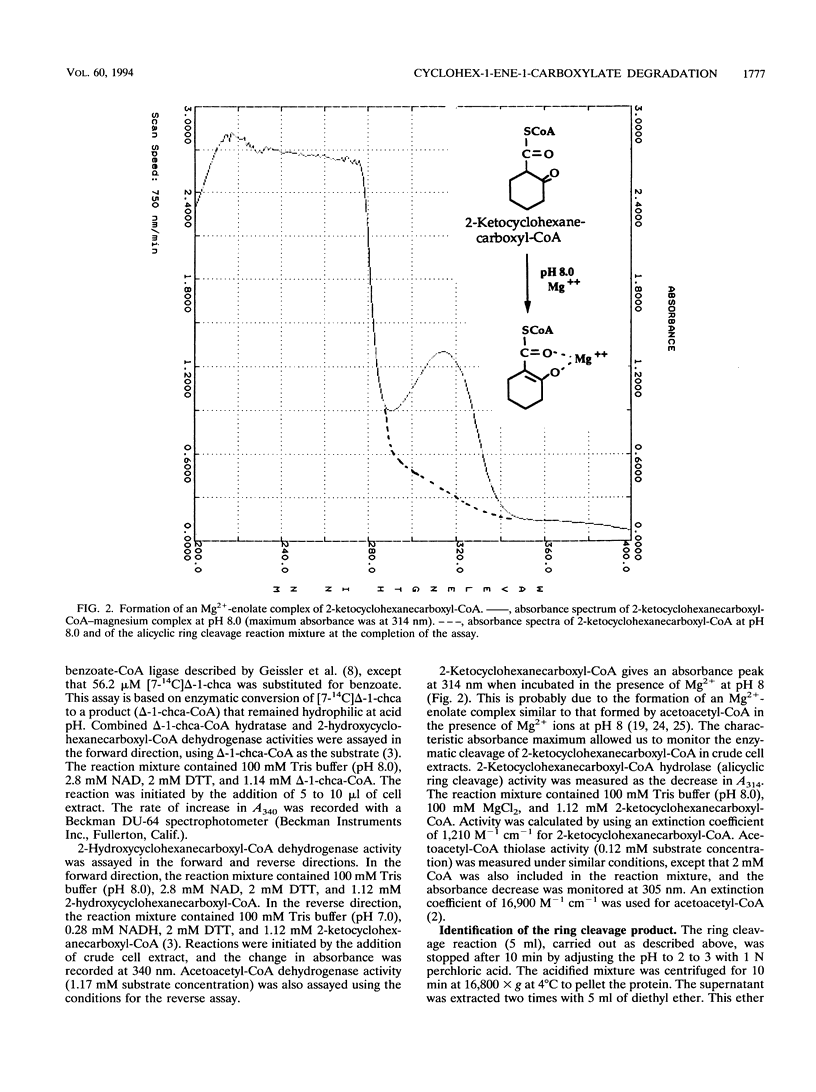
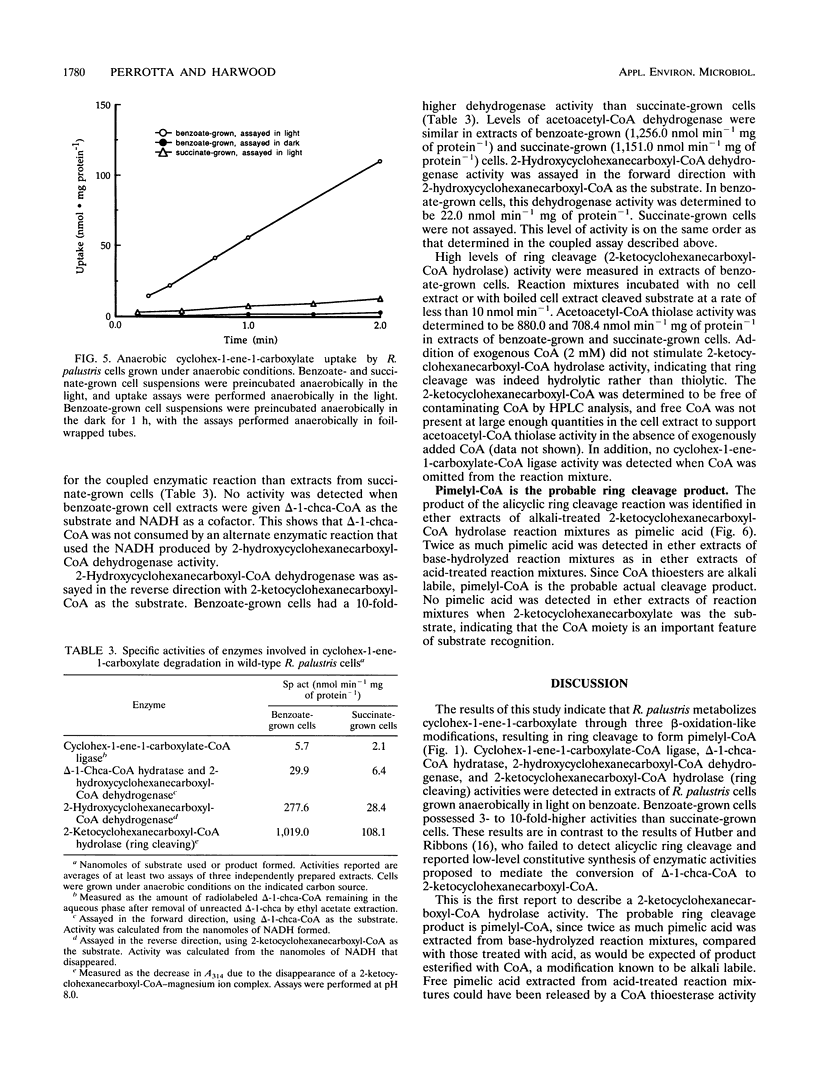
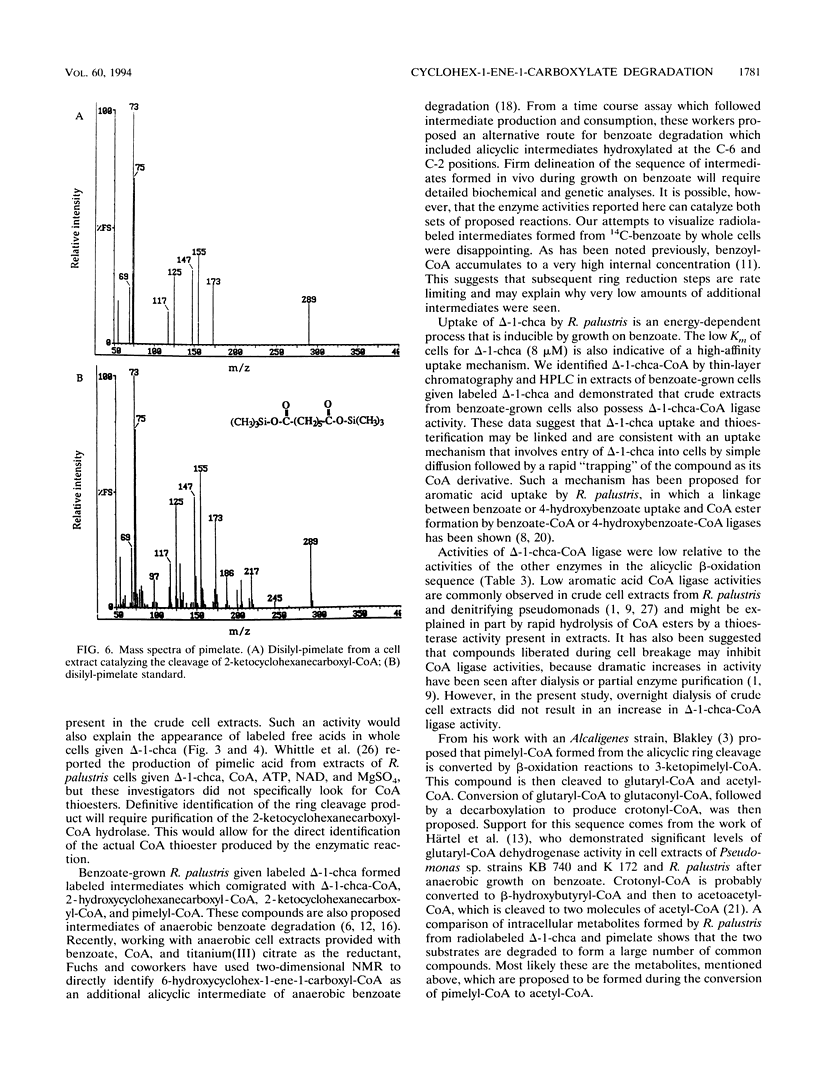
Anaerobic benzoate degradation by the phototrophic bacterium Rhodopseudomonas palustris has been proposed to proceed via aromatic ring reduction reactions leading to cyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxyl-coenzyme A (CoA) formation. The alicyclic product is then proposed to undergo three β-oxidation-like modifications resulting in ring cleavage. Illuminated suspensions of benzoate-grown cells converted [7-14C]cyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxylate to intermediates that comigrated with cyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxyl-CoA, 2-hydroxycyclohexanecar-boxyl-CoA, 2-ketocyclohexanecarboxyl-CoA, and pimelyl-CoA by thin-layer chromatography. This set of intermediates was also formed by cells grown anaerobically or aerobically on cyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxylate, indicating that benzoate-grown and cyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxylate-grown cells degrade this alicyclic acid by the same catabolic route. Four enzymatic activities proposed to be required for conversion of cyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxylate to pimelyl-CoA were detected at 3- to 10-fold-higher levels in benzoate-grown cells than in succinate-grown cells. These were cyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxylate-CoA ligase, cyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxyl-CoA hydratase, 2-hydroxycyclohexanecarboxyl-CoA dehydrogenase, and 2-ketocyclohexanecarboxyl-CoA hydrolase (ring cleaving). Pimelyl-CoA was identified in hydrolase reaction mixtures as the product of alicyclic ring cleavage. The results provide a first demonstration of an alicyclic ring cleavage activity.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altenschmidt U., Oswald B., Fuchs G. Purification and characterization of benzoate-coenzyme A ligase and 2-aminobenzoate-coenzyme A ligases from a denitrifying Pseudomonas sp. J Bacteriol. 1991 Sep;173(17):5494–5501. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.17.5494-5501.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binstock J. F., Schulz H. Fatty acid oxidation complex from Escherichia coli. Methods Enzymol. 1981;71(Pt 100):403–411. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)71051-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakley E. R. The microbial degradation of cyclohexanecarboxylic acid by a beta-oxidation pathway with simultaneous induction to the utilization of benzoate. Can J Microbiol. 1978 Jul;24(7):847–855. doi: 10.1139/m78-141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutton P. L., Evans W. C. The metabolism of aromatic compounds by Rhodopseudomonas palustris. A new, reductive, method of aromatic ring metabolism. Biochem J. 1969 Jul;113(3):525–536. doi: 10.1042/bj1130525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geissler J. F., Harwood C. S., Gibson J. Purification and properties of benzoate-coenzyme A ligase, a Rhodopseudomonas palustris enzyme involved in the anaerobic degradation of benzoate. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1709–1714. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1709-1714.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson J., Dispensa M., Fogg G. C., Evans D. T., Harwood C. S. 4-Hydroxybenzoate-coenzyme A ligase from Rhodopseudomonas palustris: purification, gene sequence, and role in anaerobic degradation. J Bacteriol. 1994 Feb;176(3):634–641. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.3.634-641.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson K. J., Gibson J. Potential early intermediates in anaerobic benzoate degradation by Rhodopseudomonas palustris. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Feb;58(2):696–698. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.2.696-698.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyer M., Hegeman G. Evidence for a reductive pathway for the anaerobic metabolism of benzoate. J Bacteriol. 1969 Sep;99(3):906–907. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.3.906-907.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwood C. S., Gibson J. Anaerobic and aerobic metabolism of diverse aromatic compounds by the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodopseudomonas palustris. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Mar;54(3):712–717. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.3.712-717.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwood C. S., Gibson J. Uptake of benzoate by Rhodopseudomonas palustris grown anaerobically in light. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):504–509. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.504-509.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Härtel U., Eckel E., Koch J., Fuchs G., Linder D., Buckel W. Purification of glutaryl-CoA dehydrogenase from Pseudomonas sp., an enzyme involved in the anaerobic degradation of benzoate. Arch Microbiol. 1993;159(2):174–181. doi: 10.1007/BF00250279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch J., Eisenreich W., Bacher A., Fuchs G. Products of enzymatic reduction of benzoyl-CoA, a key reaction in anaerobic aromatic metabolism. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Feb 1;211(3):649–661. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb17593.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LYNEN F., OCHOA S. Enzymes of fatty acid metabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1953 Sep-Oct;12(1-2):299–314. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(53)90149-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merkel S. M., Eberhard A. E., Gibson J., Harwood C. S. Involvement of coenzyme A thioesters in anaerobic metabolism of 4-hydroxybenzoate by Rhodopseudomonas palustris. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):1–7. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.1-7.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ploux O., Marquet A. The 8-amino-7-oxopelargonate synthase from Bacillus sphaericus. Purification and preliminary characterization of the cloned enzyme overproduced in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1992 Apr 15;283(Pt 2):327–331. doi: 10.1042/bj2830327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittle P. J., Lunt D. O., Evans W. C. Anaerobic photometabolism of aromatic compounds by Rhodopseudomonas sp. Biochem Soc Trans. 1976;4(3):490–491. doi: 10.1042/bst0040490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]