Abstract
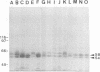
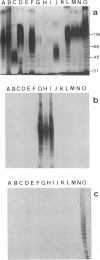
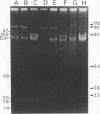
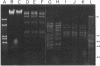
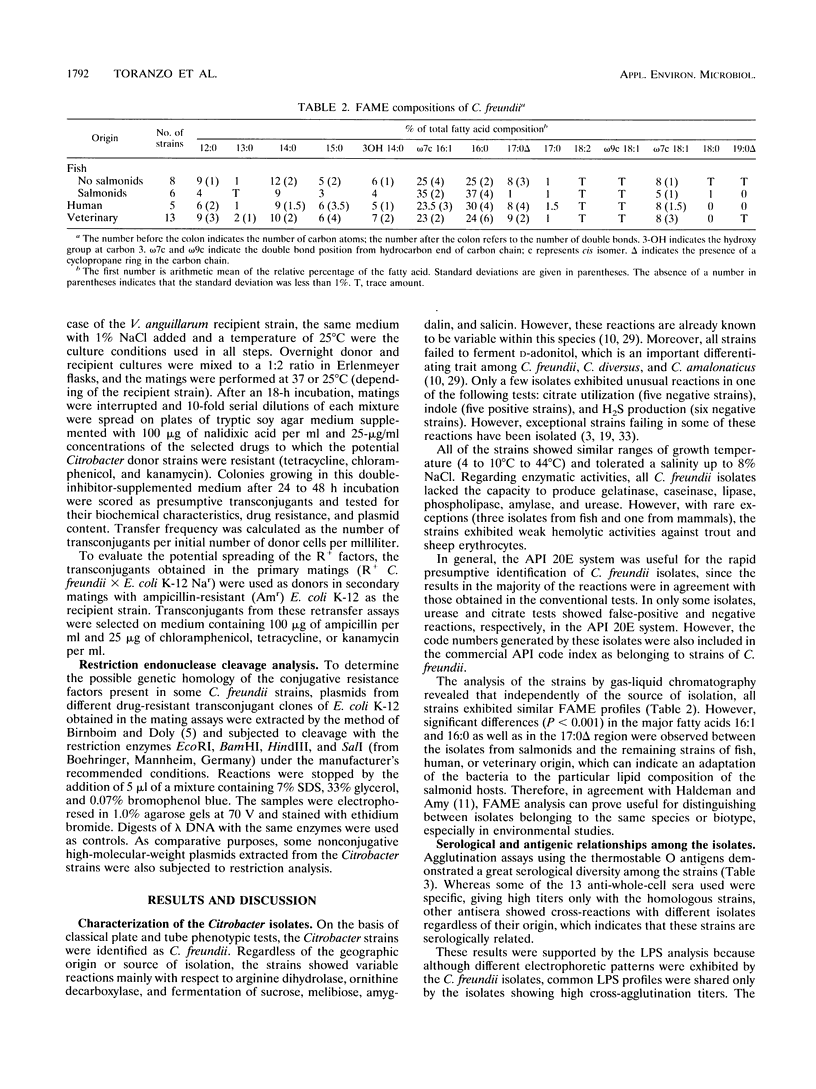
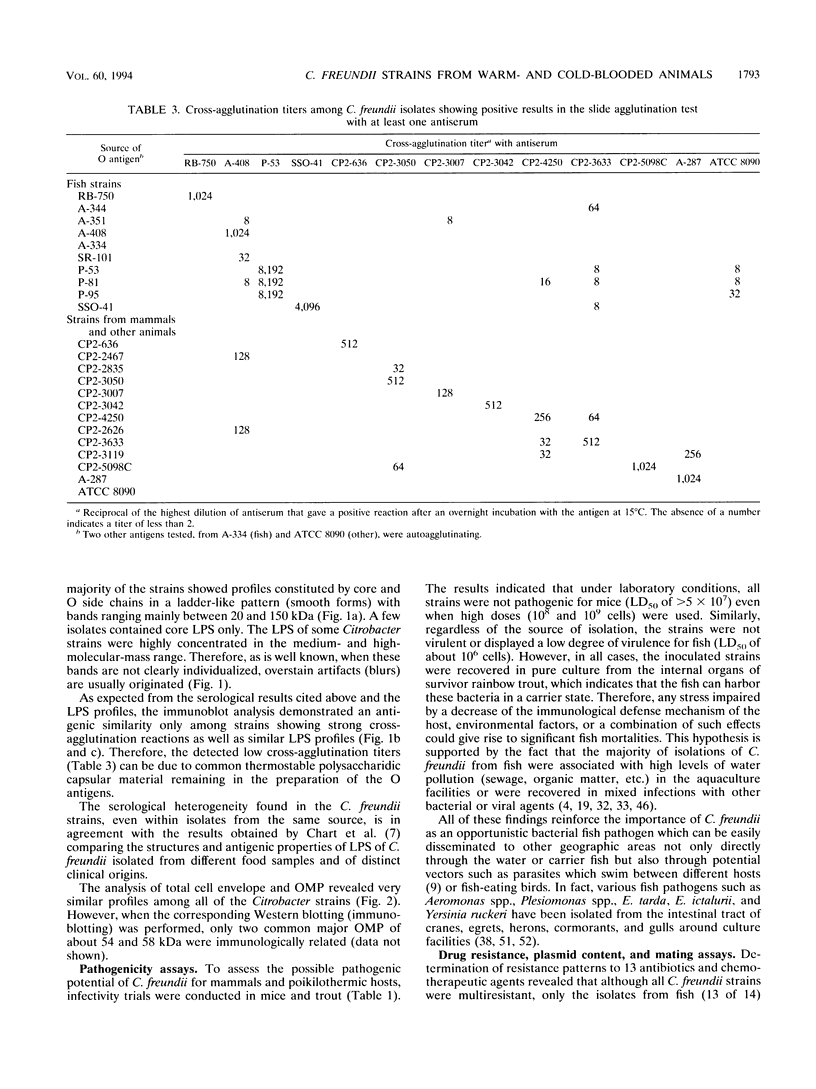
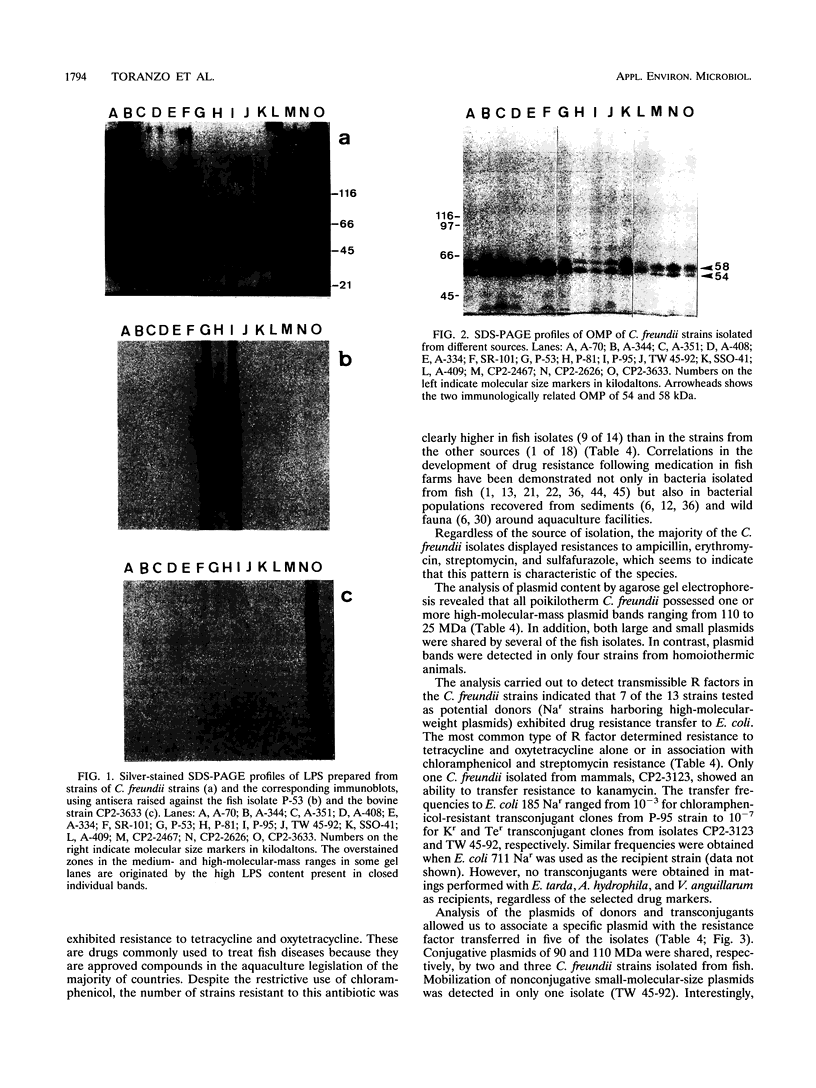
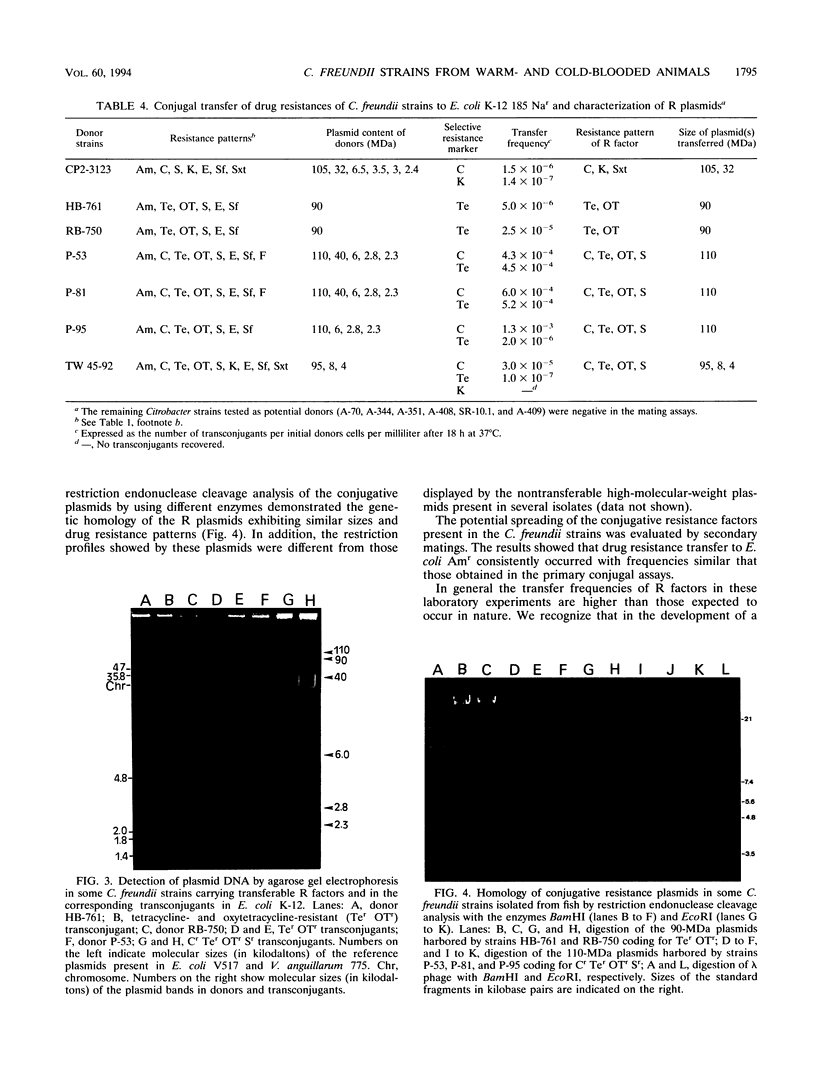
In this study, the phenotypic, antigenic, and virulence characteristics of 32 Citrobacter freundii strains of fish, human, and veterinary origin were comparatively analyzed. In addition, the spread of drug resistance factors by conjugation was investigated. Regardless of the source of isolation, the strains exhibited variable reactions mainly for arginine dihydrolase, ornithine decarboxylase, and fermentation of sucrose, melibiose, amygdalin, and salicin. Total fatty acid methyl ester analysis by gas chromatography proved to be useful for an intratypic differentiation within the C. freundii strains studied. In fact, although all of the isolates exhibited similar fatty acid methyl ester profiles, significant differences in the major fatty acids 16:1 and 16:0 and in the 17:0 delta region were observed between the isolates from salmonids and the remaining strains. Serological studies using agglutination tests, analysis of lipopolysaccharides (LPS), and the corresponding immunoblots with 13 antisera indicated a great antigenic diversity among the strains. Common LPS patterns were shared only by some isolates showing high cross-agglutination titers. In contrast, although all strains exhibited very similar surface protein patterns, only two common outer membrane proteins of 54 and 58 kDa were immunologically related. Infectivity trials performed in mice and rainbow trout indicated that all of the C. freundii strains were not pathogenic for mice (50% lethal dose of > 5 x 10(7)). Although the isolates displayed a low degree of virulence for trout, inoculated strains were always recovered from the survivors in pure culture.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chart H., Willshaw G. A., Cheasty T., Rowe B. Structure and antigenic properties of Citrobacter freundii lipopolysaccharides. J Appl Bacteriol. 1993 May;74(5):583–587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughter J. P., Stewart G. J. Genetic exchange in the environment. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1989;55(1):15–22. doi: 10.1007/BF02309615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haldeman D. L., Amy P. S. Diversity within a Colony Morphotype: Implications for Ecological Research. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Mar;59(3):933–935. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.3.933-935.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J., Brown T. M. Morphological heterogeneity among Salmonella lipopolysaccharide chemotypes in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):269–277. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.269-277.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kado C. I., Liu S. T. Rapid procedure for detection and isolation of large and small plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1365–1373. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1365-1373.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss C. W., Wallace P. L., Hollis D. G., Weaver R. E. Cultural and chemical characterization of CDC groups EO-2, M-5, and M-6, Moraxella (Moraxella) species, Oligella urethralis, Acinetobacter species, and Psychrobacter immobilis. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Mar;26(3):484–492. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.3.484-492.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima T., Suzuki M., Harada K., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. Transmission of R plasmids in vibrio anguillarum to Vibrio cholerae. Microbiol Immunol. 1983;27(2):195–198. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1983.tb03584.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavia A. T., Bryan J. A., Maher K. L., Hester T. R., Jr, Farmer J. J., 3rd Vibrio carchariae infection after a shark bite. Ann Intern Med. 1989 Jul 1;111(1):85–86. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-111-1-85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson M. H., Clarke I. R., Coghlan J. D., Gill O. N. Leptospirosis in trout farmers. Lancet. 1981 Sep 19;2(8247):626–627. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92757-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shotts E. B., Jr Bacterial diseases of fish associated with human health. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract. 1987 Jan;17(1):241–247. doi: 10.1016/s0195-5616(87)50615-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stotzky G., Zeph L. R., Devanas M. A. Factors affecting the transfer of genetic information among microorganisms in soil. Biotechnology. 1991;15:95–122. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-409-90199-3.50012-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toranzo A. E., Barja J. L., Colwell R. R., Hetrick F. M. Characterization of plasmids in bacterial fish pathogen. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):184–192. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.184-192.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toranzo A. E., Barja J. L., Potter S. A., Colwell R. R., Hetrick F. M., Crosa J. H. Molecular factors associated with virulence of marine vibrios isolated from striped bass in Chesapeake Bay. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1220–1227. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1220-1227.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toranzo A. E., Combarro P., Lemos M. L., Barja J. L. Plasmid coding for transferable drug resistance in bacteria isolated from cultured rainbow trout. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Oct;48(4):872–877. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.4.872-877.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandepitte J., Lemmens P., de Swert L. Human Edwardsiellosis traced to ornamental fish. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jan;17(1):165–167. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.1.165-167.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White F. H., Simpson C. F., Williams L. E., Jr Isolation of Edwardsiella tarda from aquatic animal species and surface waters in Florida. J Wildl Dis. 1973 Jul;9(3):204–208. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-9.3.204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]