Abstract
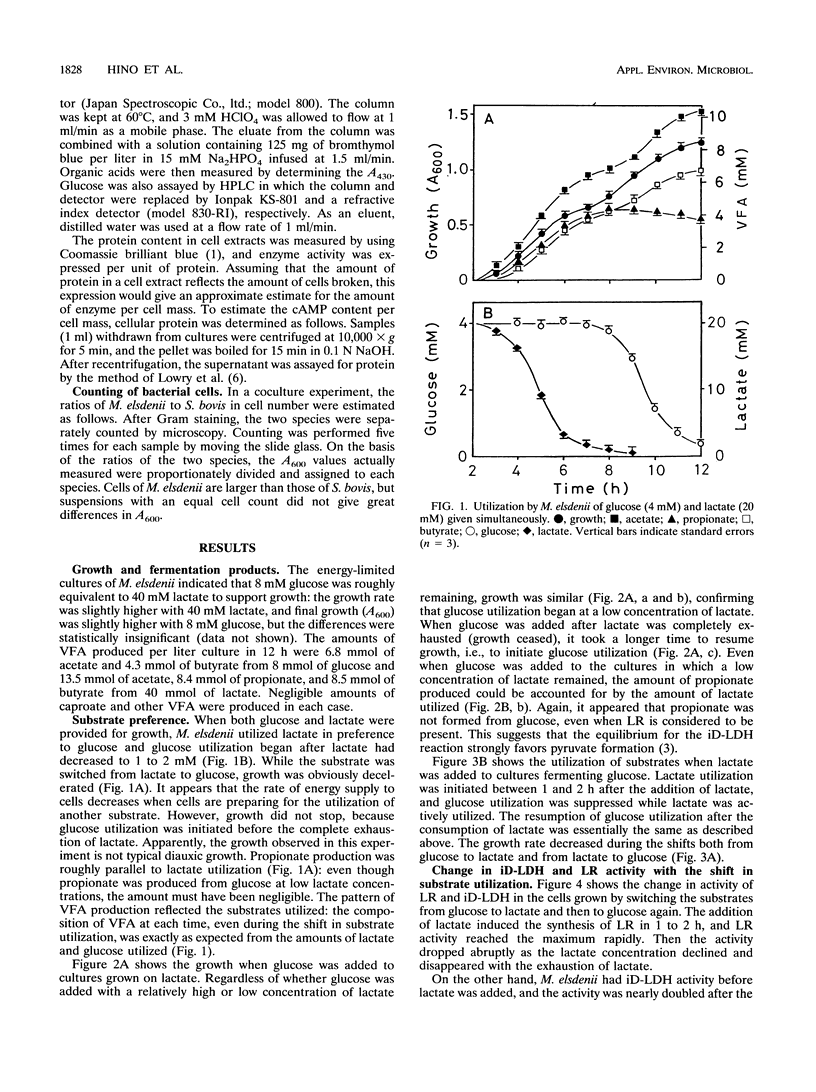
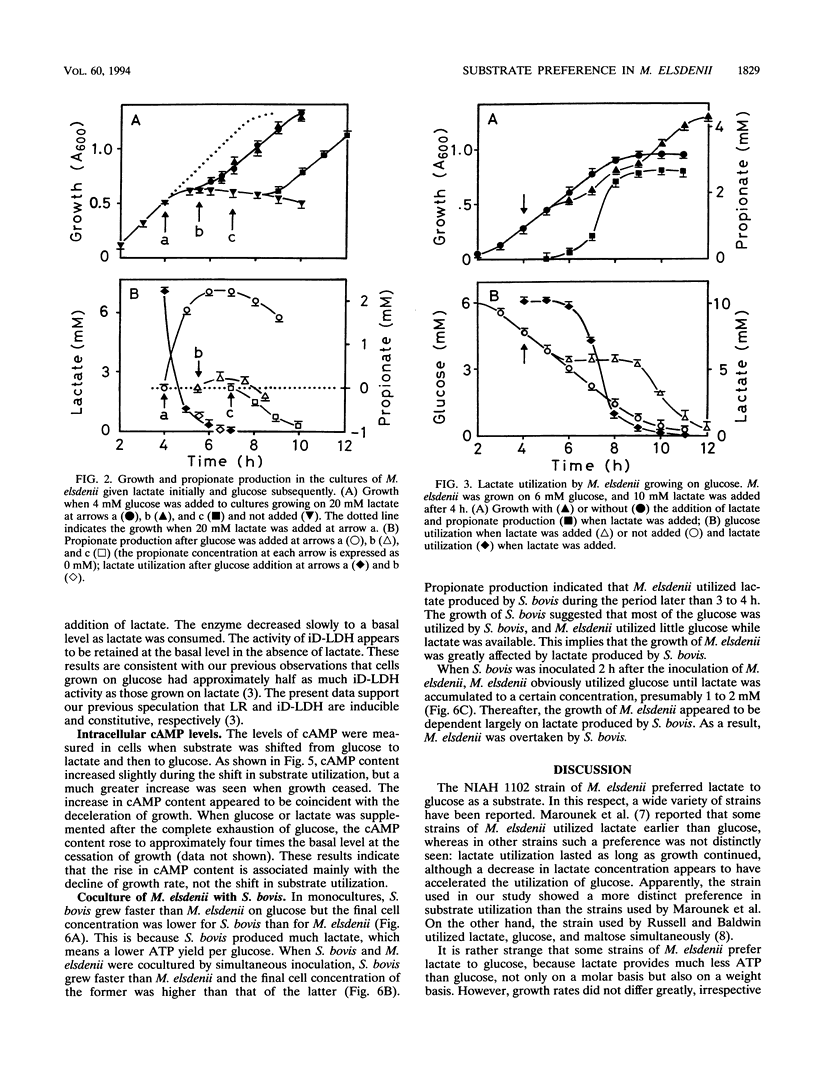
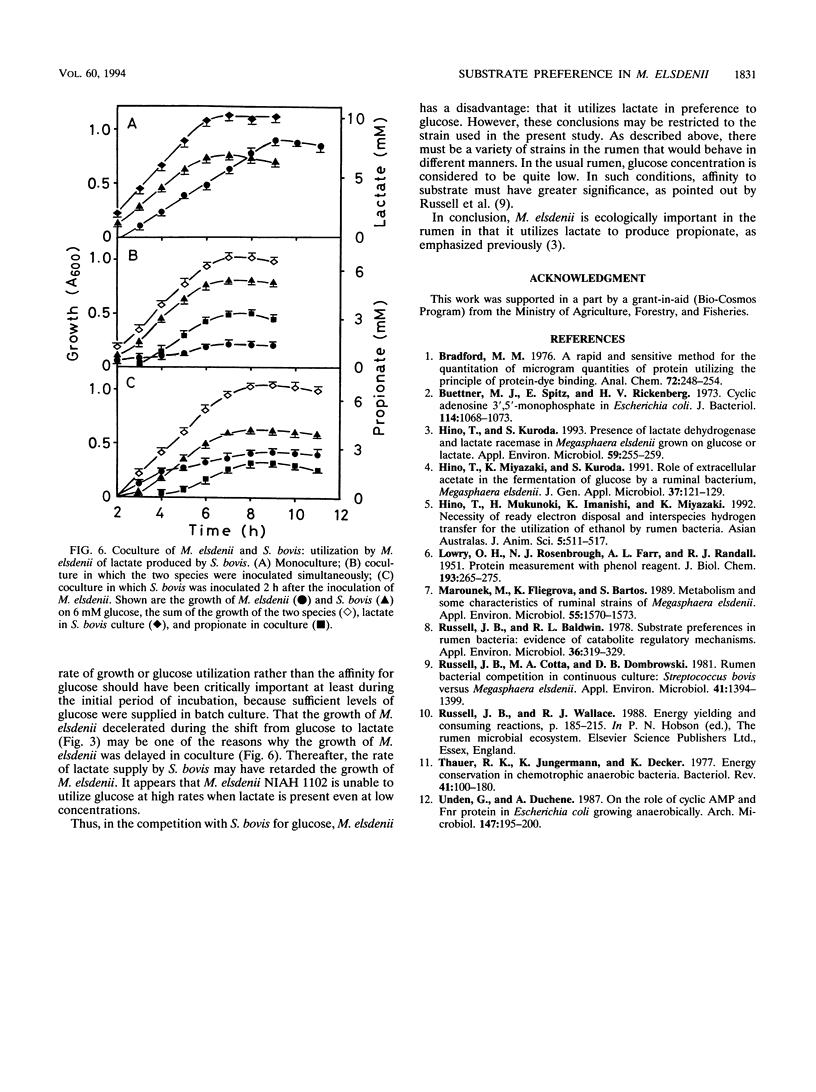
The NIAH 1102 strain of Megasphaera elsdenii utilized lactate in preference to glucose when the two substrates were present. Even when lactate was supplied to cells fermenting glucose, the cells switched substrate utilization from glucose to lactate and did not utilize glucose until lactate decreased to a low concentration (1 to 2 mM). Since substrate utilization was shifted gradually without intermittence, typical diauxic growth was not seen. The cyclic AMP content did not rise markedly with the shift in substrate utilization, suggesting that this nucleotide is not involved in the regulation of the shift. It was unlikely that propionate was produced from glucose, which was explicable by the fact that lactate racemase activity dropped rapidly with the exhaustion of lactate and cells actively fermenting glucose did not possess this enzyme. A coculture experiment indicated that M. elsdenii NIAH 1102 is overcome by Streptococcus bovis JB1 in the competition for glucose, mainly because M. elsdenii NIAH 1102 is obliged to utilize lactate produced by S. bovis JB1; i.e., glucose utilization by M. elsdenii NIAH 1102 is suppressed by the coexistence of S. bovis JB1.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buettner M. J., Spitz E., Rickenberg H. V. Cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):1068–1073. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.1068-1073.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hino T., Kuroda S. Presence of lactate dehydrogenase and lactate racemase in Megasphaera elsdenii grown on glucose or lactate. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Jan;59(1):255–259. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.1.255-259.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marounek M., Fliegrova K., Bartos S. Metabolism and some characteristics of ruminal strains of Megasphaera elsdenii. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jun;55(6):1570–1573. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.6.1570-1573.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. B., Baldwin R. L. Substrate preferences in rumen bacteria: evidence of catabolite regulatory mechanisms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Aug;36(2):319–329. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.2.319-329.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. B., Cotta M. A., Dombrowski D. B. Rumen Bacterial Competition in Continuous Culture: Streptococcus bovis Versus Megasphaera elsdenii. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jun;41(6):1394–1399. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.6.1394-1399.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thauer R. K., Jungermann K., Decker K. Energy conservation in chemotrophic anaerobic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Mar;41(1):100–180. doi: 10.1128/br.41.1.100-180.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unden G., Duchene A. On the role of cyclic AMP and the Fnr protein in Escherichia coli growing anaerobically. Arch Microbiol. 1987 Mar;147(2):195–200. doi: 10.1007/BF00415284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


