Abstract
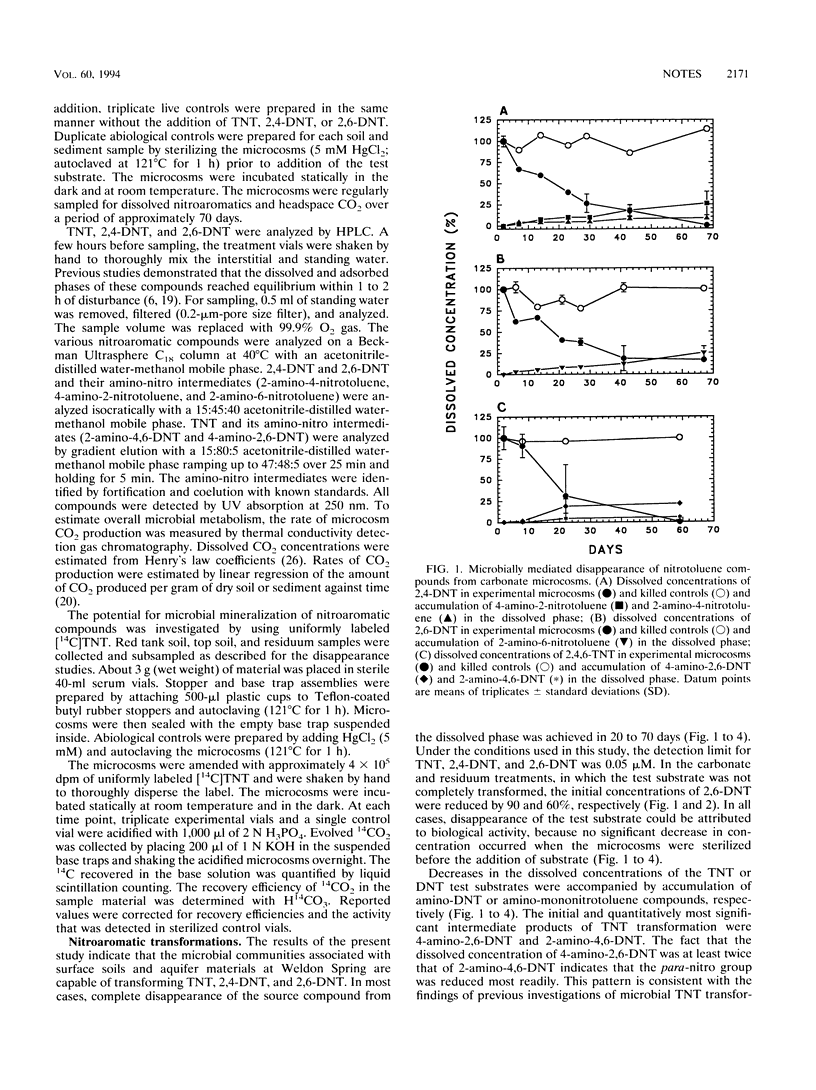
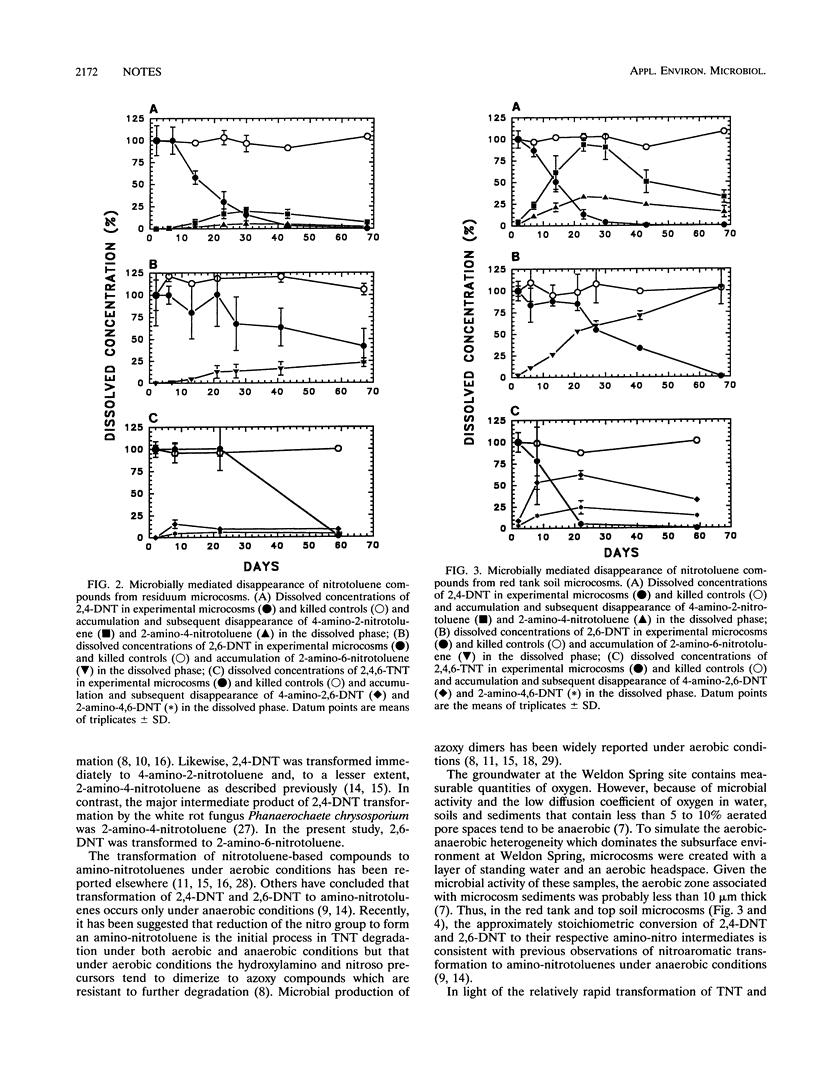
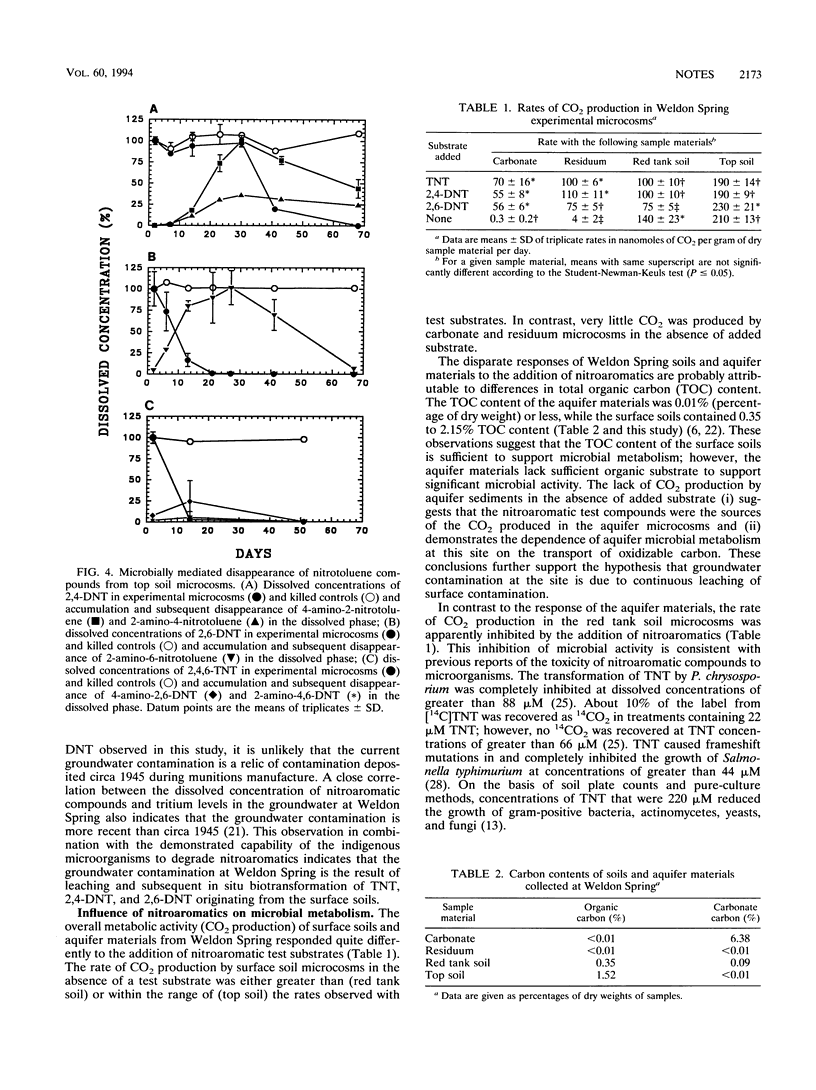
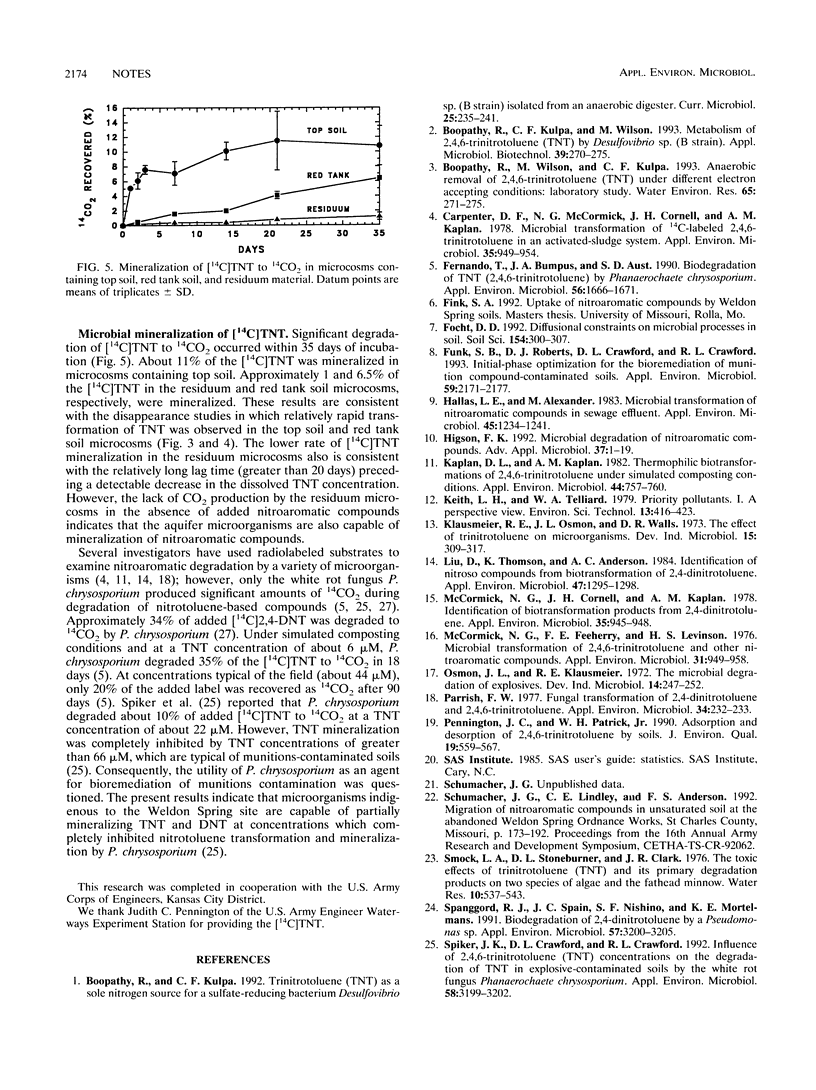
Microorganisms indigenous to surface soils and aquifer materials collected at a munitions-contaminated site transformed 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene (TNT), 2,4-dinitrotoluene (2,4-DNT), and 2,6-dinitrotoluene (2,6-DNT) to amino-nitro intermediates within 20 to 70 days. Carbon mineralization studies with both unlabeled (TNT, 2,4-DNT, and 2,6-DNT) and radiolabeled ([14C]TNT) substrates indicated that a significant fraction of these source compounds was degraded to CO2.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boopathy R., Kulpa C. F. Trinitrotoluene (TNT) as a sole nitrogen source for a sulfate-reducing bacterium Desulfovibrio sp. (B strain) isolated from an anaerobic digester. Curr Microbiol. 1992 Oct;25(4):235–241. doi: 10.1007/BF01570724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter D. F., McCormick N. G., Cornell J. H., Kaplan A. M. Microbial transformation of 14C-labeled 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene in an activated-sludge system. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 May;35(5):949–954. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.5.949-954.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernando T., Bumpus J. A., Aust S. D. Biodegradation of TNT (2,4,6-trinitrotoluene) by Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jun;56(6):1666–1671. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.6.1666-1671.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funk S. B., Roberts D. J., Crawford D. L., Crawford R. L. Initial-phase optimization for bioremediation of munition compound-contaminated soils. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Jul;59(7):2171–2177. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.7.2171-2177.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallas L. E., Alexander M. Microbial transformation of nitroaromatic compounds in sewage effluent. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Apr;45(4):1234–1241. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.4.1234-1241.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higson F. K. Microbial degradation of nitroaromatic compounds. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1992;37:1–19. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(08)70250-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. L., Kaplan A. M. Thermophilic biotransformations of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene under simulated composting conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Sep;44(3):757–760. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.3.757-760.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu D., Thomson K., Anderson A. C. Identification of nitroso compounds from biotransformation of 2,4-dinitrotoluene. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Jun;47(6):1295–1298. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.6.1295-1298.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick N. G., Cornell J. H., Kaplan A. M. Identification of biotransformation products from 2,4-dinitrotoluene. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 May;35(5):945–948. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.5.945-948.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick N. G., Feeherry F. E., Levinson H. S. Microbial transformation of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene and other nitroaromatic compounds. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Jun;31(6):949–958. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.6.949-958.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrish F. W. Fungal transformation of 2,4-dinitrotoluene and 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Aug;34(2):232–233. doi: 10.1128/aem.34.2.232-233.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spanggord R. J., Spain J. C., Nishino S. F., Mortelmans K. E. Biodegradation of 2,4-dinitrotoluene by a Pseudomonas sp. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Nov;57(11):3200–3205. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.11.3200-3205.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiker J. K., Crawford D. L., Crawford R. L. Influence of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene (TNT) concentration on the degradation of TNT in explosive-contaminated soils by the white rot fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Sep;58(9):3199–3202. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.9.3199-3202.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Won W. D., Heckly R. J., Glover D. J., Hoffsommer J. C. Metabolic disposition of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Mar;27(3):513–516. doi: 10.1128/am.27.3.513-516.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


