Abstract
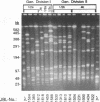
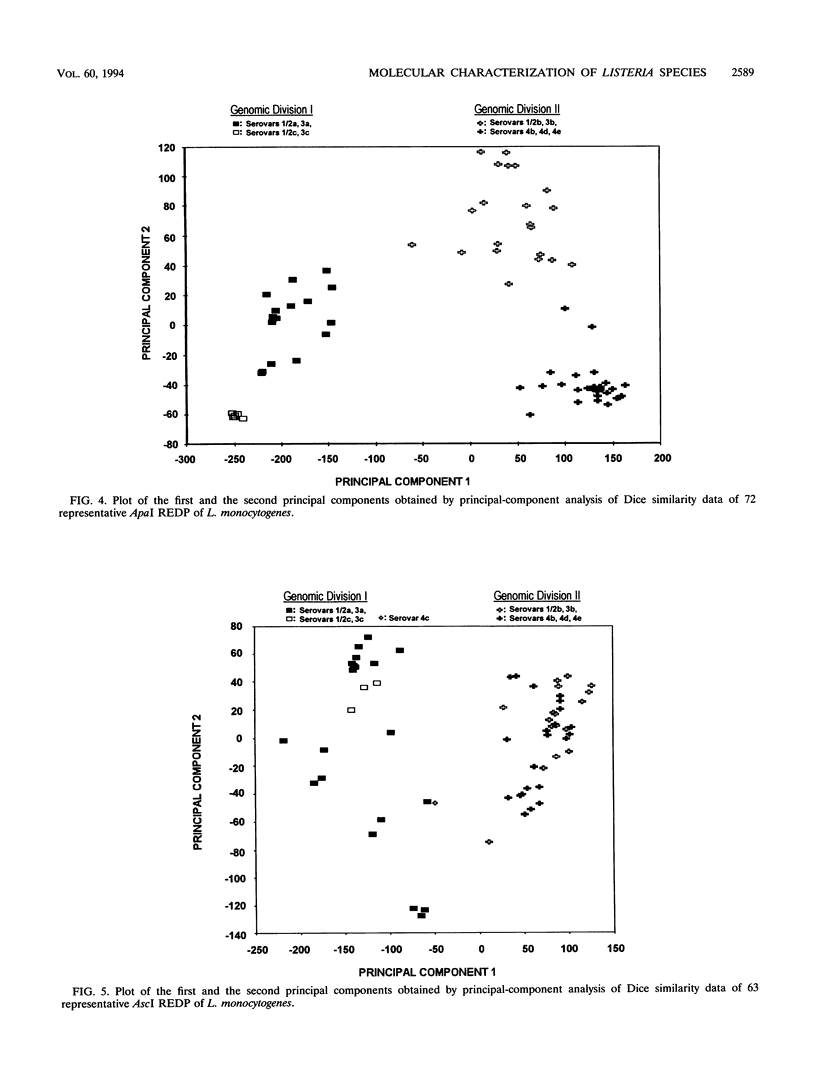
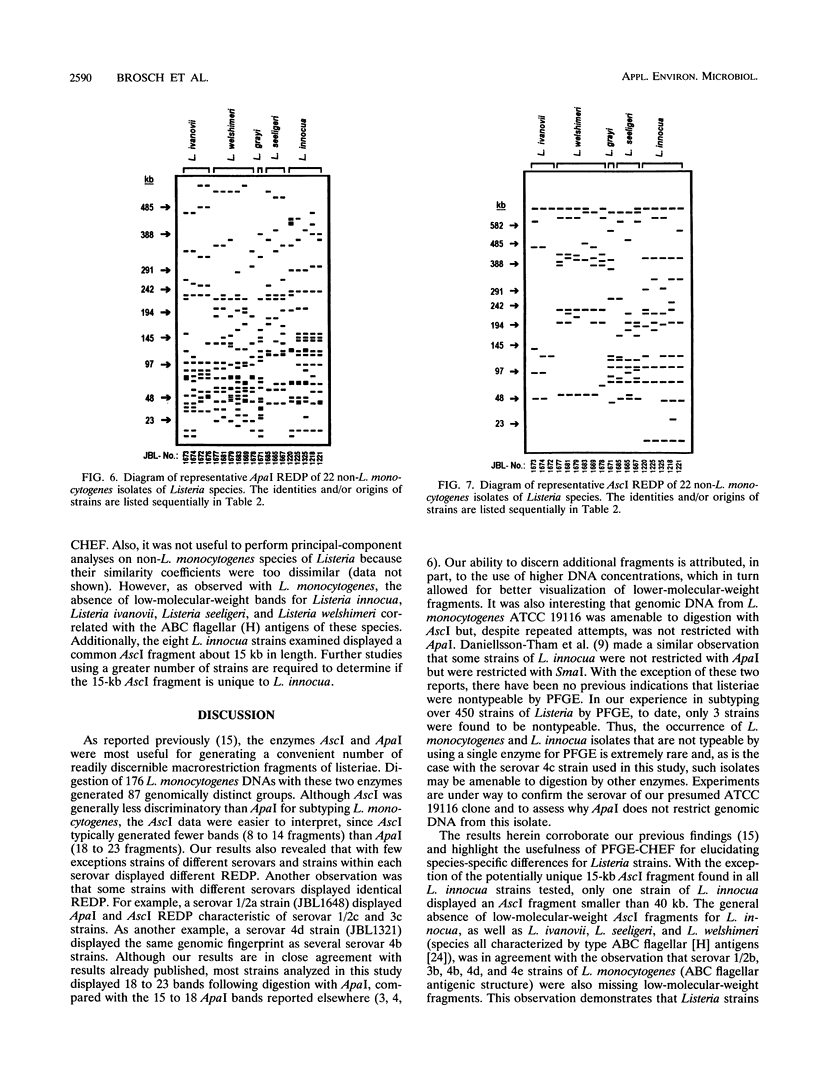
Clamped homogeneous electric field (CHEF) electrophoresis was optimized for genomic analyses of Listeria monocytogenes. Various human, animal, food, and environmental isolates, as well as strains representing other Listeria species, were separately digested with rarely cutting endonucleases. Of 176 L. monocytogenes strains analyzed, the enzymes AscI and ApaI established 63 and 72 unique restriction endonuclease digestion profiles (REDP), respectively. The 22 non-L. monocytogenes strains exhibited 18 AscI and 19 ApaI unique REDP. Statistical analyses of REDP information using the Dice coincidence index and principal component analysis revealed two distinct genomic divisions of L. monocytogenes that also correlated with the flagellar (H) antigen type: division I contained serovar 1/2a, 1/2c, 3a, and 3c stains and division II contained serovar 1/2b, 3b, 4b, 4d, and 4e strains. Division I isolates digested with ApaI were further grouped into cluster IA (serovar 1/2c and 3c) and cluster IB (serovar 1/2a and 3a) strains. Likewise, division II isolates digested with ApaI were further grouped into cluster IIA (serovar 1/2b and 3b) and cluster IIB (serovar 4b, 4d, and 4e) strains. These data indicate that genotypic data generated by CHEF can be directly related to phenotypic data generated by serotyping for establishing the overall relatedness of isolates. Moreover, these data further substantiate that CHEF analysis is a reproducible and highly discriminating method for characterizing L. monocytogenes strains at the molecular level.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brosch R., Buchrieser C., Rocourt J. Subtyping of Listeria monocytogenes serovar 4b by use of low-frequency-cleavage restriction endonucleases and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Res Microbiol. 1991 Jul-Aug;142(6):667–675. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(91)90080-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchrieser C., Brosch R., Catimel B., Rocourt J. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis applied for comparing Listeria monocytogenes strains involved in outbreaks. Can J Microbiol. 1993 Apr;39(4):395–401. doi: 10.1139/m93-058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchrieser C., Brosch R., Rocourt J. Use of pulsed field gel electrophoresis to compare large DNA-restriction fragments of Listeria monocytogenes strains belonging to serogroups 1/2 and 3. Int J Food Microbiol. 1991 Dec;14(3-4):297–304. doi: 10.1016/0168-1605(91)90121-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carriere C., Allardet-Servent A., Bourg G., Audurier A., Ramuz M. DNA polymorphism in strains of Listeria monocytogenes. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Jul;29(7):1351–1355. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.7.1351-1355.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J., Brosch R., Luchansky J. B. Isolation and characterization of Listeria monocytogenes-specific nucleotide sequences. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Dec;59(12):4367–4370. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.12.4367-4370.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielsson-Tham M. L., Bille J., Brosch R., Buchrieser C., Persson K., Rocourt J., Schwarzkopf A., Tham W., Ursing J. Characterization of Listeria strains isolated from soft cheese. Int J Food Microbiol. 1993 Apr;18(2):161–166. doi: 10.1016/0168-1605(93)90220-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Buyser M. L., Morvan A., Aubert S., Dilasser F., el Solh N. Evaluation of a ribosomal RNA gene probe for the identification of species and subspecies within the genus Staphylococcus. J Gen Microbiol. 1992 May;138(5):889–899. doi: 10.1099/00221287-138-5-889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves L. M., Swaminathan B., Reeves M. W., Wenger J. Ribosomal DNA fingerprinting of Listeria monocytogenes using a digoxigenin-labeled DNA probe. Eur J Epidemiol. 1991 Jan;7(1):77–82. doi: 10.1007/BF00221345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann J. L., Bellenger E., Perolat P., Baranton G., Saint Girons I. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis of NotI digests of leptospiral DNA: a new rapid method of serovar identification. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jul;30(7):1696–1702. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.7.1696-1702.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard P. J., Harsono K. D., Luchansky J. B. Differentiation of Listeria monocytogenes, Listeria innocua, Listeria ivanovii, and Listeria seeligeri by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Feb;58(2):709–712. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.2.709-712.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King G. J. ELBAMAP: software for management of electrophoresis banding patterns. Comput Appl Biosci. 1989 Oct;5(4):313–317. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/5.4.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefevre J. C., Faucon G., Sicard A. M., Gasc A. M. DNA fingerprinting of Streptococcus pneumoniae strains by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Oct;31(10):2724–2728. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.10.2724-2728.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazurier S. I., Wernars K. Typing of Listeria strains by random amplification of polymorphic DNA. Res Microbiol. 1992 Jun;143(5):499–505. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(92)90096-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nørrung B., Gerner-Smidt P. Comparison of multilocus enzyme electrophoresis (MEE), ribotyping, restriction enzyme analysis (REA) and phage typing for typing of Listeria monocytogenes. Epidemiol Infect. 1993 Aug;111(1):71–79. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800056697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piffaretti J. C., Kressebuch H., Aeschbacher M., Bille J., Bannerman E., Musser J. M., Selander R. K., Rocourt J. Genetic characterization of clones of the bacterium Listeria monocytogenes causing epidemic disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3818–3822. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen O. F., Beck T., Olsen J. E., Dons L., Rossen L. Listeria monocytogenes isolates can be classified into two major types according to the sequence of the listeriolysin gene. Infect Immun. 1991 Nov;59(11):3945–3951. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.11.3945-3951.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocourt J., Audurier A., Courtieu A. L., Durst J., Ortel S., Schrettenbrunner A., Taylor A. G. A multi-centre study on the phage typing of Listeria monocytogenes. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1985 Jul;259(4):489–497. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(85)80081-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux V., Raoult D. Genotypic identification and phylogenetic analysis of the spotted fever group rickettsiae by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. J Bacteriol. 1993 Aug;175(15):4895–4904. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.15.4895-4904.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabouret M., de Rycke J., Dubray G. Analysis of surface proteins of Listeria in relation to species, serovar and pathogenicity. J Gen Microbiol. 1992 Apr;138(4):743–753. doi: 10.1099/00221287-138-4-743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torensma R., Visser M. J., Aarsman C. J., Poppelier M. J., Fluit A. C., Verhoef J. Monoclonal antibodies that react with live Listeria spp. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Aug;59(8):2713–2716. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.8.2713-2716.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wesley I. V., Ashton F. Restriction enzyme analysis of Listeria monocytogenes strains associated with food-borne epidemics. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Apr;57(4):969–975. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.4.969-975.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]