Abstract
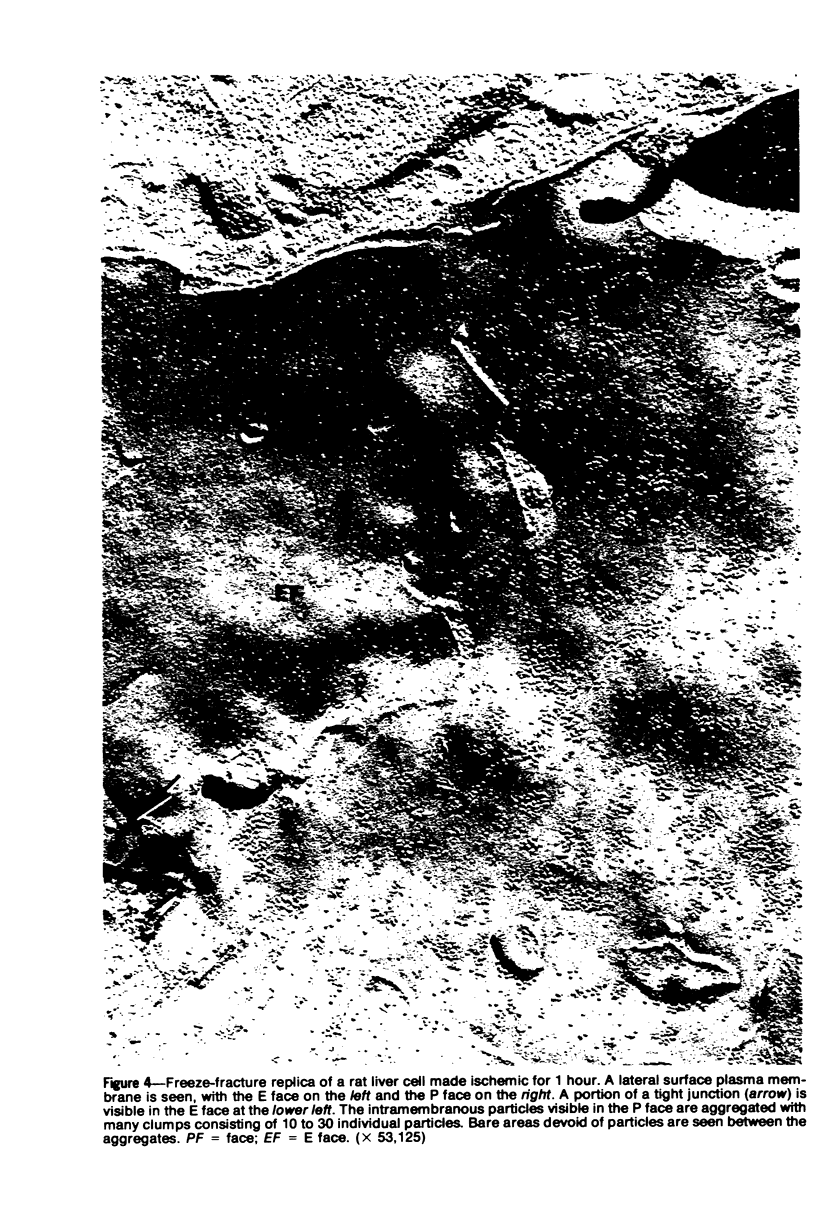
Ischemic rat liver tissue has been shown previously to exhibit a markedly accelerated rate of phospholipid degradation, producing a loss of almost one half the total cellular phospholipid with 3 hours of ischemia. Pretreatment of the rats with chlorpromazine completely prevented the disturbed phospholipid metabolism at the same time that it prevented the cell death associated with as much as 3 hours of ischemia. Lipid-depleted microsomal membranes were shown previously to manifest alterations in their structure and function. The present report documents that similar structural alterations are evident in ischemic liver cell plasma membranes. The technique of freeze-fracture electron microscopy was used to examine the morphology of ischemic liver cell plasma membranes. Freeze-fracture replicas of whole tissue fragments exhibited a diffuse aggregation of the intramembranous particles in the P face of the plasma membranes. The incidence of this change correlated with the duration of ischemia. Pretreatment of the rats with chlorpromazine (20 mg/kg) for 30 minutes before inducing ischemia prevented the aggregation of the membrane-associated particles. These findings establish the existence of plasma membrane alterations in ischemic liver cells. The time course of these changes, their prevention by chlorpromazine, and their similarity to the previously described structural alterations in the microsomal membranes suggest that they are related to the loss of liver cell phospholipid. The data in the present report support the hypothesis that an accelerated phospholipid degradation and its resultant membrane dysfunction are the critical alterations that produce irreversible liver cell injury and, ultimately, cell death in ischemia.
Full text
PDF
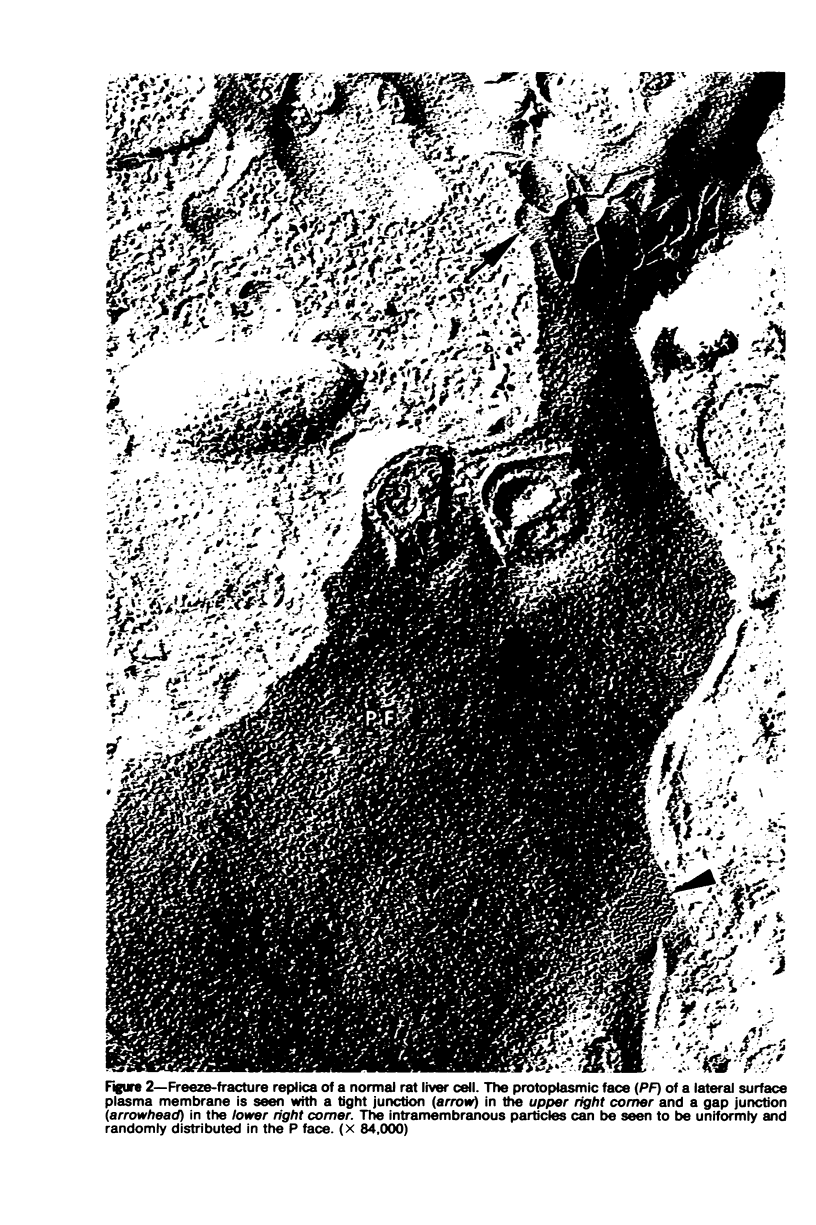
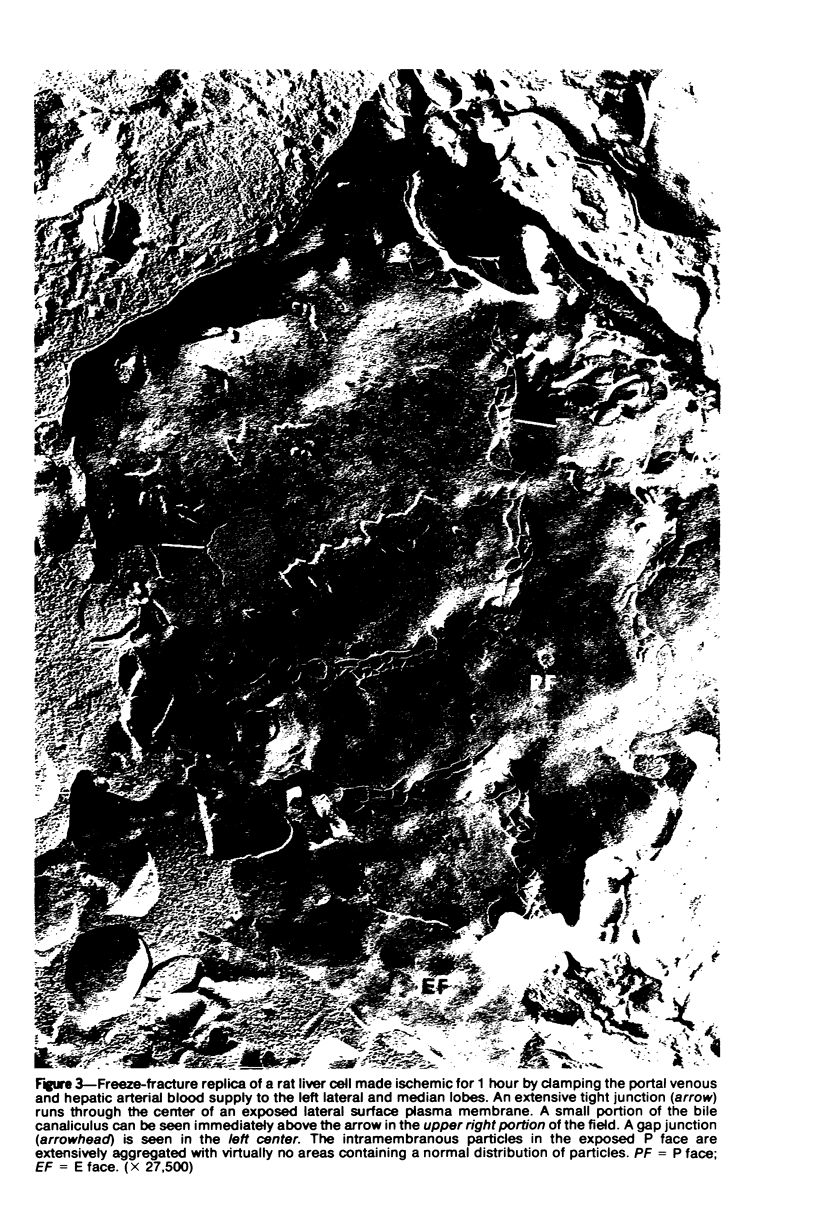
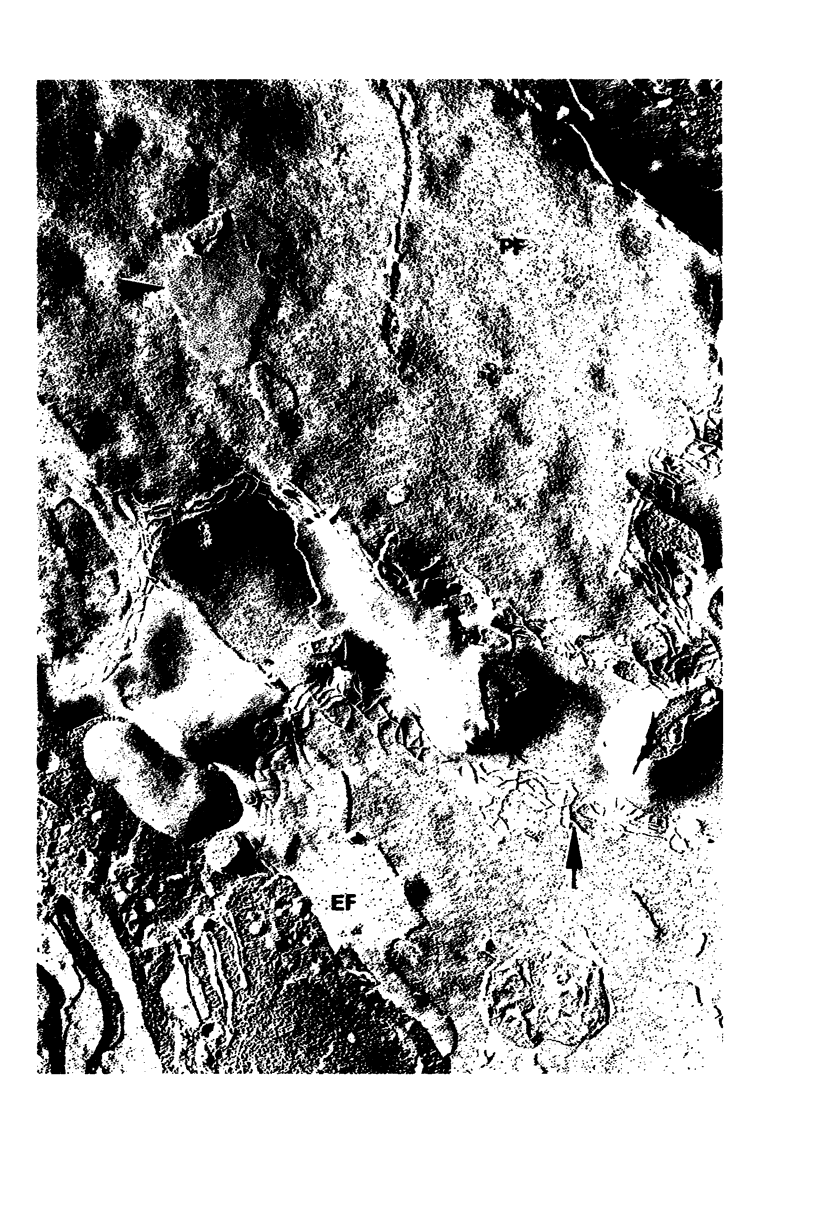
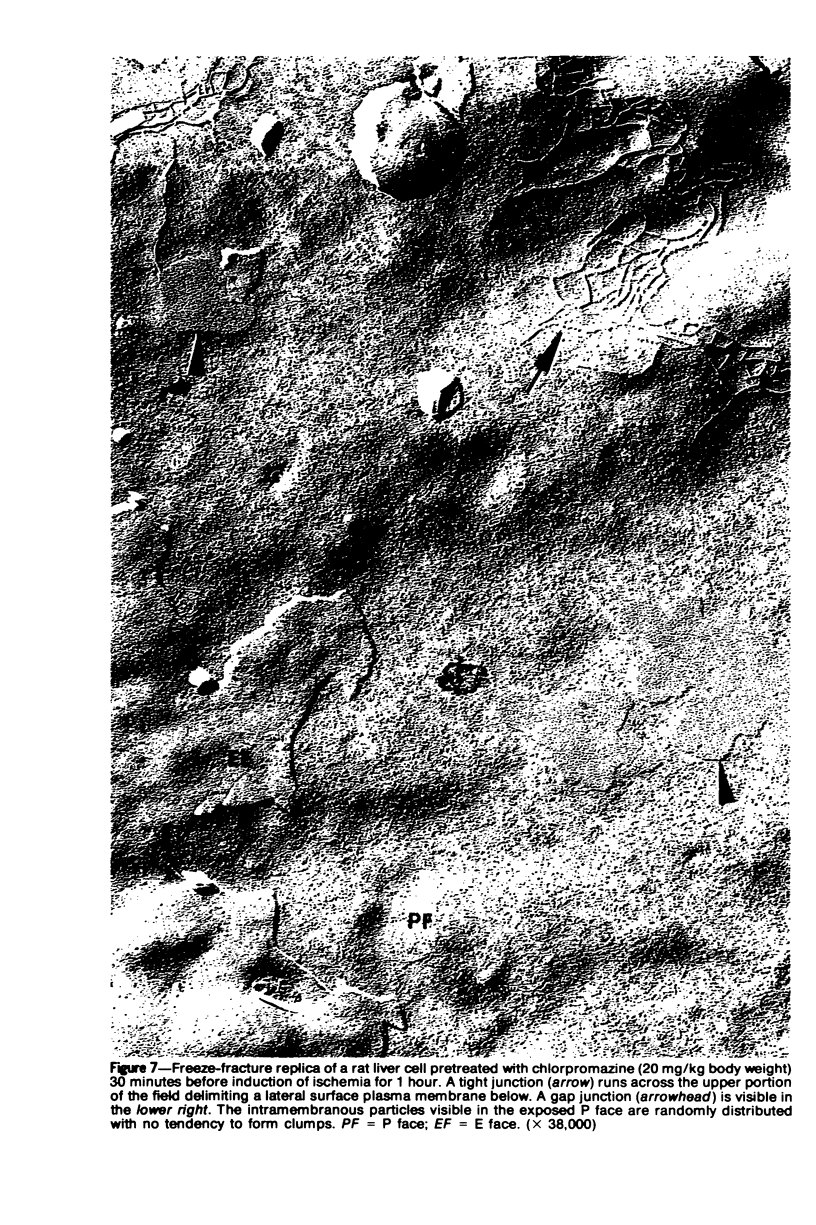


















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahkong Q. F., Fisher D., Tampion W., Lucy J. A. Mechanisms of cell fusion. Nature. 1975 Jan 17;253(5488):194–195. doi: 10.1038/253194a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahkong Q. F., Tampion W., Lucy J. A. Promotion of cell fusion by divalent cation ionophores. Nature. 1975 Jul 17;256(5514):208–209. doi: 10.1038/256208a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashraf M., Halverson C. A. Structural changes in the freeze-fractured sarcolemma of ischemic myocardium. Am J Pathol. 1977 Sep;88(3):583–594. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee D., Redman C. M. Effect of local anesthetics on plasma protein secretion by rat hepatocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Nov 7;500(1):49–60. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(77)90045-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branton D., Bullivant S., Gilula N. B., Karnovsky M. J., Moor H., Mühlethaler K., Northcote D. H., Packer L., Satir B., Satir P. Freeze-etching nomenclature. Science. 1975 Oct 3;190(4209):54–56. doi: 10.1126/science.1166299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. S., Hubbell W. L. Temperature- and light-dependent structural changes in rhodopsin-lipid membranes. Exp Eye Res. 1973 Dec 24;17(6):517–532. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(73)90082-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chien K. R., Abrams J., Pfau R. G., Farber J. L. Prevention by chlorpromazine of ischemic liver cell death. Am J Pathol. 1977 Sep;88(3):539–557. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chien K. R., Abrams J., Serroni A., Martin J. T., Farber J. L. Accelerated phospholipid degradation and associated membrane dysfunction in irreversible, ischemic liver cell injury. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jul 10;253(13):4809–4817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chien K. R., Farber J. L. Microsomal membrane dysfunction in ischemic rat liver cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Apr 15;180(1):191–198. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90025-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman S. E., Duggan J., Hackett R. L. Plasma membrane changes in freeze-fractured rat kidney cortex following renal ischemia. Lab Invest. 1976 Jul;35(1):63–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duppel W., Dahl G. Effect of phase transition on the distribution of membrane-associated particles in microsomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Mar 19;426(3):408–417. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90386-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenzel J., Arnold K., Nuhn P. Calorimetric, 13C NMR, and 31P NMR studies on the interaction of some phenothiazine derivatives with dipalmitoyl phosphatidylcholine model membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Feb 21;507(2):185–197. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90415-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giddon D. B., Lindhe J. In vivo quantitation of local anesthetic suppression of leukocyte adherence. Am J Pathol. 1972 Aug;68(2):327–338. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodenough D. A., Revel J. P. A fine structural analysis of intercellular junctions in the mouse liver. J Cell Biol. 1970 May;45(2):272–290. doi: 10.1083/jcb.45.2.272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant C. W., McConnell H. M. Glycophorin in lipid bilayers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4653–4657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gratzl M., Dahl G. Ca2+-induced fusion of golgi-derived secretory vesicles isolated from rat liver. FEBS Lett. 1976 Feb 15;62(2):142–145. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80038-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höchli M., Hackenbrock C. R. Thermotropic lateral translational motion of intramembrane particles in the inner mitochondrial membrane and its inhibition by artificial peripheral proteins. J Cell Biol. 1977 Feb;72(2):278–291. doi: 10.1083/jcb.72.2.278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson K., Papahadjopoulos D. Phase transitions and phase separations in phospholipid membranes induced by changes in temperature, pH, and concentration of bivalent cations. Biochemistry. 1975 Jan 14;14(1):152–161. doi: 10.1021/bi00672a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James R., Branton D. Lipid- and temperature-dependent structural changes in Acholeplasma laidlawii cell membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Oct 25;323(3):378–390. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90183-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleemann W., McConnell H. M. Lateral phase separations in Escherichia coli membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Apr 29;345(2):220–230. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90260-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunze H., Nahas N., Traynor J. R., Wurl M. Effects of local anaesthetics on phospholipases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jul 20;441(1):93–102. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(76)90284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson D., Raff M. C., Gomperts B., Fewtrell C., Gilula N. B. Molecular events during membrane fusion. A study of exocytosis in rat peritoneal mast cells. J Cell Biol. 1977 Feb;72(2):242–259. doi: 10.1083/jcb.72.2.242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachbaur J., Colbeau A., Vignais P. M. Distribution of membrane-confined phospholipases A in the rat hepatocyte. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 9;274(2):426–446. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90189-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville D. M., Jr Isolation of an organ specific protein antigen from cell-surface membrane of rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Apr 9;154(3):540–552. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(68)90014-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newkirk J. D., Waite M. Identification of a phospholipase A1 in plasma membranes of rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Feb 2;225(2):224–233. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90215-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newkirk J. D., Waite M. Phospholipid hydrolysis by phospholipase A 1 and A 2 in plasma membranes and microsomes of rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Mar 29;298(3):562–576. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90074-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'BRIEN J. R. The adhesiveness of native platelets and its prevention. J Clin Pathol. 1961 Mar;14:140–149. doi: 10.1136/jcp.14.2.140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'brien J. R. Platelet aggregation: Part I Some effects of the adenosine phosphates, thrombin, and cocaine upon platelet adhesiveness. J Clin Pathol. 1962 Sep;15(5):446–452. doi: 10.1136/jcp.15.5.446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onishi S., Ito T. Calcium-induced phase separations in phosphatidylserine--phosphatidylcholine membranes. Biochemistry. 1974 Feb 26;13(5):881–887. doi: 10.1021/bi00702a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinto da Silva P., Nogueira M. L. Membrane fusion during secretion. A hypothesis based on electron microscope observation of Phytophthora Palmivora zoospores during encystment. J Cell Biol. 1977 Apr;73(1):161–181. doi: 10.1083/jcb.73.1.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poste G., Reeve P. Inhibition of cell fusion by local anaesthetics and tranquillizers. Exp Cell Res. 1972 Jun;72(2):556–560. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(72)90029-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth S., Seeman P. All lipid-soluble anaesthetics protect red cells. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 30;231(26):284–285. doi: 10.1038/newbio231284a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottem S., Yashouv J., Ne'eman Z., Razin S. Cholesterol in mycoplasma membranes. Composition, ultrastructure and biological properties of membranes from Mycoplasma mycoides var. capri cells adapted to grow with low cholesterol concentrations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Nov 16;323(4):495–508. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90158-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satir B., Schooley C., Satir P. Membrane fusion in a model system. Mucocyst secretion in Tetrahymena. J Cell Biol. 1973 Jan;56(1):153–176. doi: 10.1083/jcb.56.1.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherphof G. L., Scarpa A., van Toorenenbergen A. The effect of local anesthetics on the hydrolysis of free and membrane-bound phospholipids catalyzed by various phospholipases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jun 19;270(2):226–240. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(72)90234-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schober R., Nitsch C., Rinne U., Morris S. J. Calcium-induced displacement of membrane-associated particles upon aggregation of chromaffin granules. Science. 1977 Feb 4;195(4277):495–497. doi: 10.1126/science.835010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiner G. F., Unanue E. R. The disruption of immunoglobulin caps by local anesthetics. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1976 Sep;6(2):264–269. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(76)90118-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman P. The membrane actions of anesthetics and tranquilizers. Pharmacol Rev. 1972 Dec;24(4):583–655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shechter E., Letellier L., Gulik-Krzywicki G. Relations between structure and function in cytoplasmic membrane vesicles isolated from an Escherichia coli fatty-acid auxotroph. High-angle x-ray diffraction, freeze-etch electron microscopy and transport studies. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Nov 1;49(1):61–76. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03811.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speth V., Wunderlich F. Membranes of Tetrahymena. II. Direct visualization of reversible transitions in biomembrane structure induced by temperature. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 16;291(3):621–628. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90467-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stowell R. E., Gill T. J., 3rd, Trump B. F., Scarpelli D. G. Conference on the future of academic pathology. September 22-24, 1976, College Park, Maryland. Am J Pathol. 1977 Aug;88(2):431–464. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunderman F. W., Jr Carcinogenic effects of metals. Fed Proc. 1978 Jan;37(1):40–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toister Z., Loyter A. The mechanism of cell fusion. II. Formation of chicken erythrocyte polykaryons. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 25;248(2):422–432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verkleij A. J., Ververgaert P. H., van Deenen L. L., Elbers P. F. Phase transitions of phospholipid bilayers and membranes of Acholeplasma laidlawii B visualized by freeze fracturing electron microscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 2;288(2):326–332. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90253-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vos J., Ahkong Q. F., Botham G. M., Quirk S. J., Lucy J. A. Changes in the distribution of intramembranous particles in hen erythrocytes during cell fusion induced by the bivalent-cation ionophore A23187. Biochem J. 1976 Sep 15;158(3):651–653. doi: 10.1042/bj1580651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade J. B., Kachadorian W. A., DiScala V. A. Freeze-fracture electron microscopy: relationship of membrane structural features to transport physiology. Am J Physiol. 1977 Feb;232(2):F77–F83. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1977.232.2.F77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wunderlich F., Wallach D. F., Speth V., Fischer H. Differential effects of temperature on the nuclear and plasma membranes of lymphoid cells. A study by freeze-etch electron microscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Nov 27;373(1):34–43. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90102-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Bosch H. Phosphoglyceride metabolism. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):243–277. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.001331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]