Abstract
A method for the in situ fixation of human meninges for electron microscopic examination is described. It was found that the cranial meninges of humans do not include a subdural space. Instead there is a complex, tight layer of cells, the interface layer, composed in the innermost portion of the dura mater (the dural border cells) and the outermost portion of the arachnoid (the arachnoid barrier layer). The fusion of these components within the interface layer is much more intimate than is either the attachment of the dural border cells to the dura proper or that of the arachnoid barrier layer to the rest of the arachnoid. The fine structural characteristics of these layers are defined. The erroneous macroscopic impression of a subdural space results from an extraordinary lack of cohesion within the dura-arachnoid interface layer conditioned by a) a complete absence of a collagenous reinforcement within this zone, b) the presence of large extracellular cisterns between the dural border cells, and c) a paucity of intercellular contacts within that latter layer. An understanding of the fine structural organization of the interface layer is essential to any consideration of the pathogenesis of subdural lesions: these form within a sheet of torn dural border cells and not within a preexistent tissue compartment.
Full text
PDF










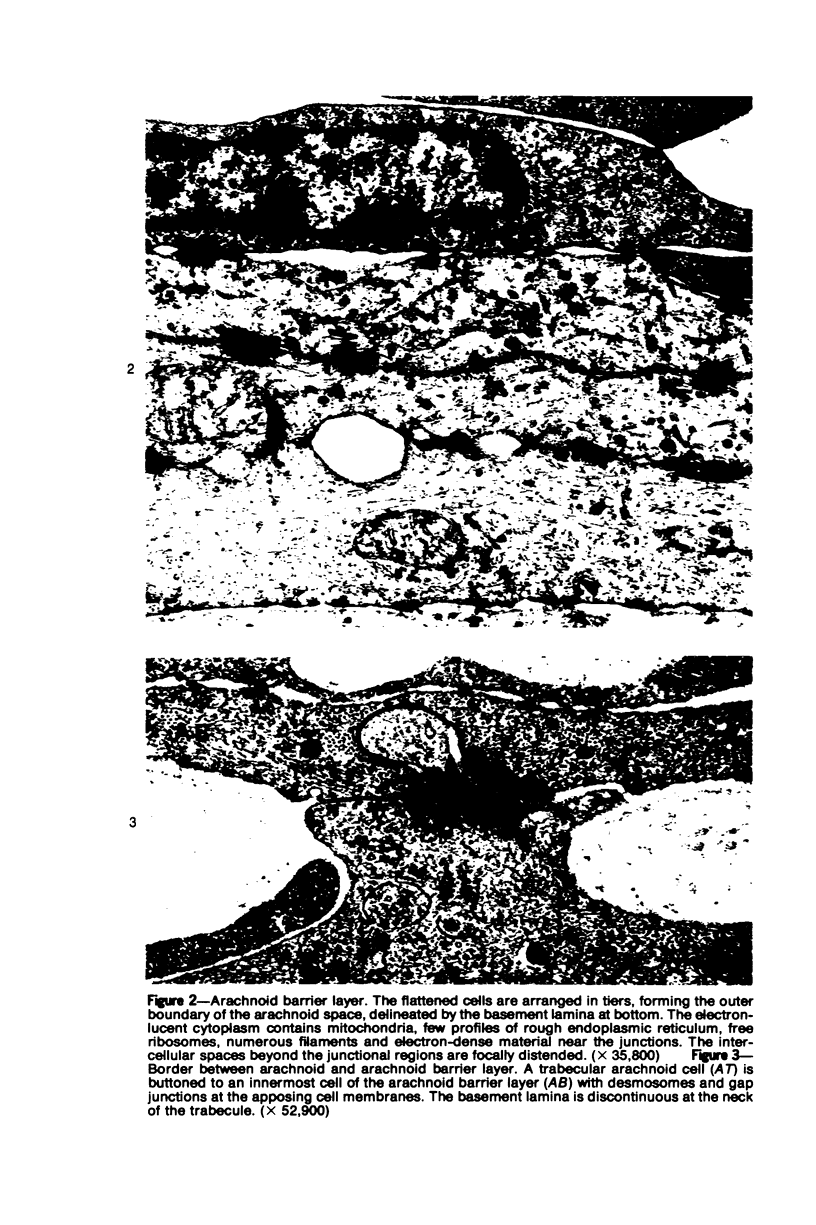
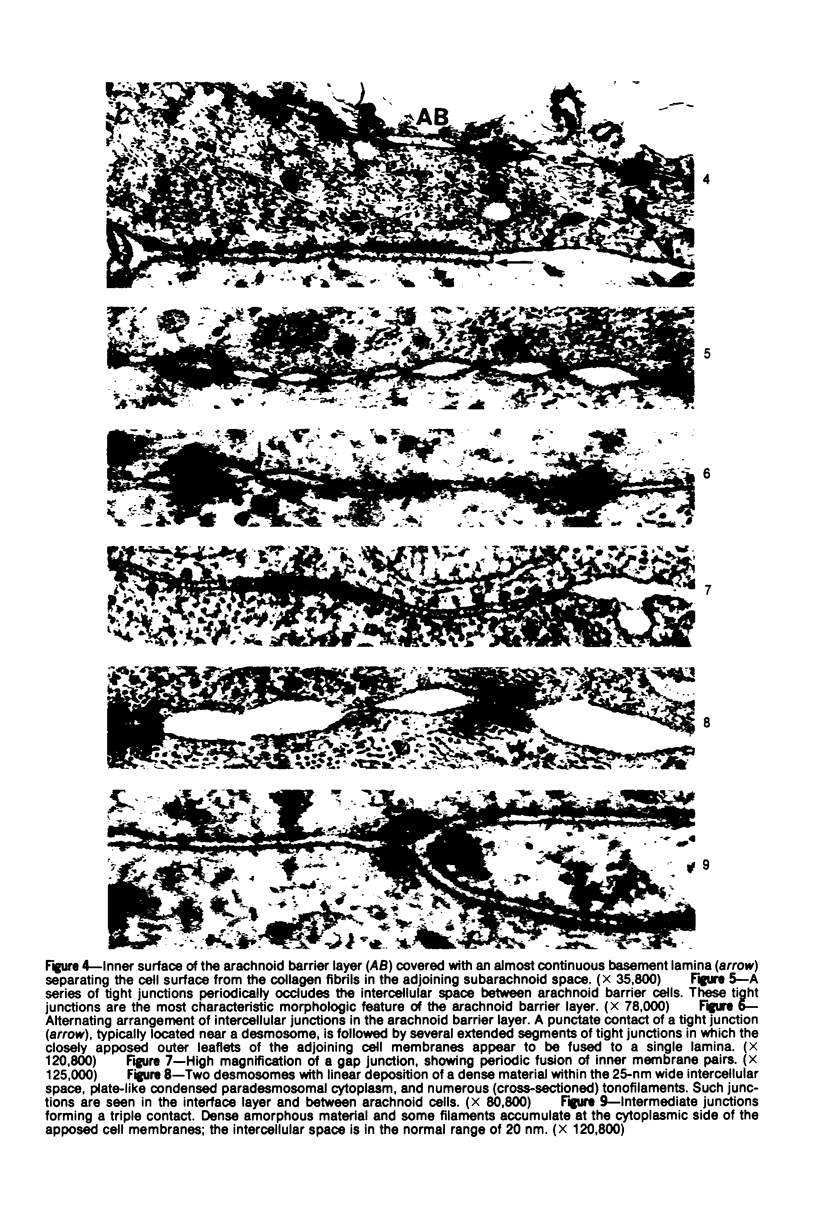
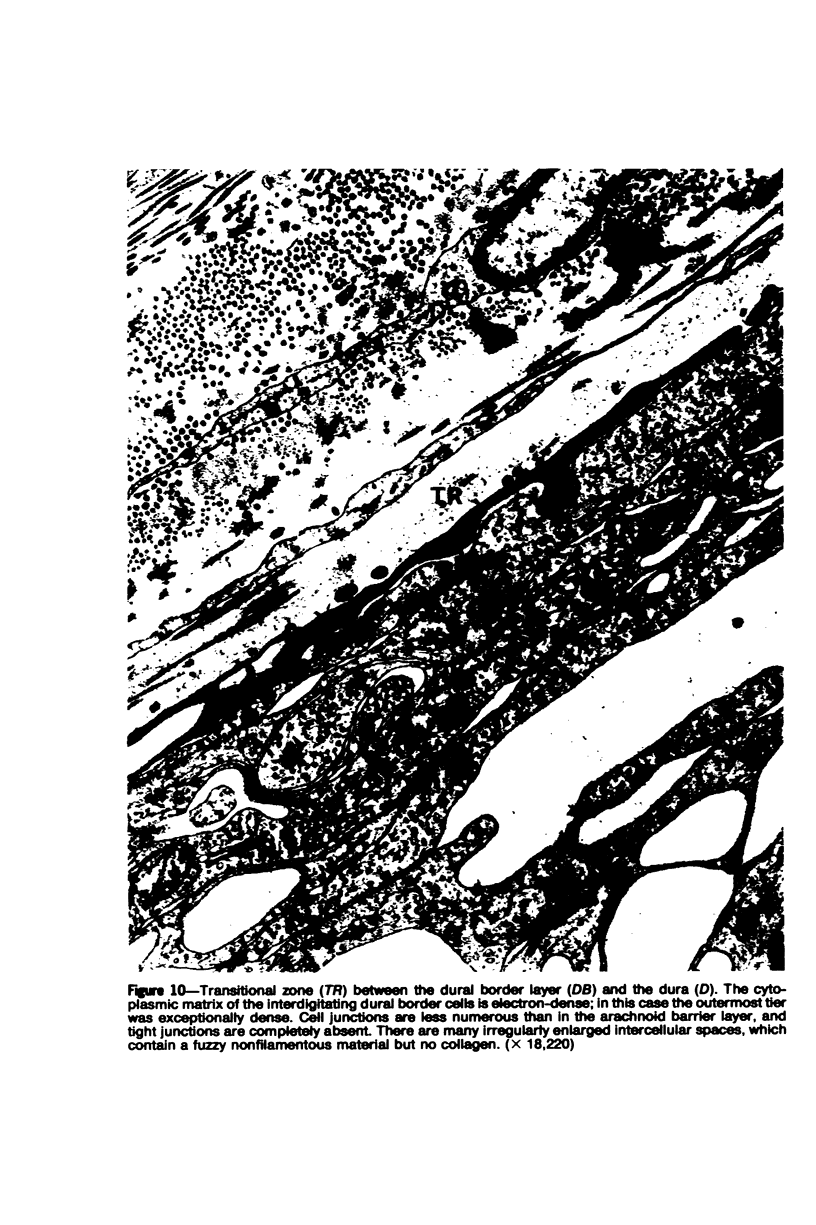
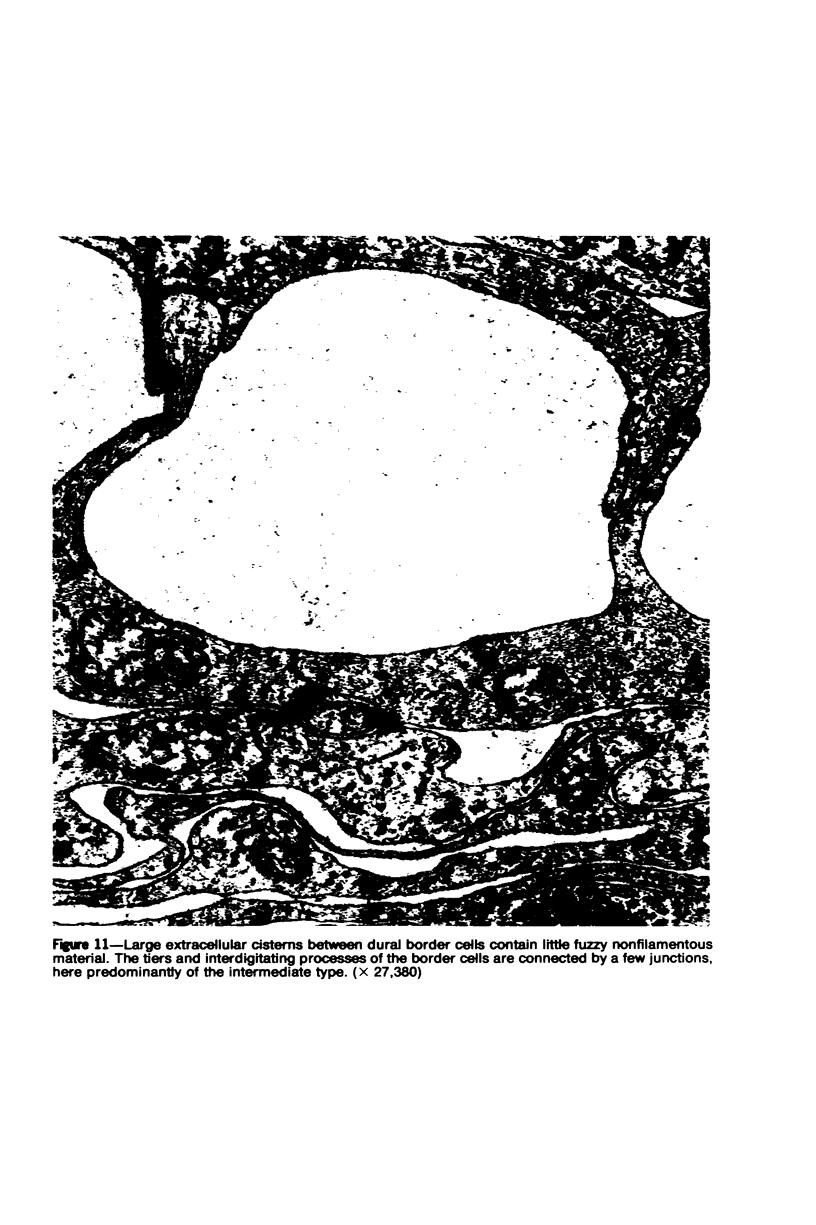
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akashi Y. [Electron microscopic studies on the fine structure of the arachnoid membrane at the base of the rabbit brain]. Kaibogaku Zasshi. 1972 Aug;47(4):285–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. R. ltrastructure of meningeal sheaths. Normal human and monkey optic nerves. Arch Ophthalmol. 1969 Nov;82(5):659–674. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1969.00990020653015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andres K. H. Uber die Feinstruktur der Arachnoidea und Dura mater von Mammalia. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1967;79(2):272–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andres K. H. Zur Feinstuktur der Arachnoidalzotten bei Mammalia. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1967;82(1):92–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brightman M. W., Reese T. S. Junctions between intimately apposed cell membranes in the vertebrate brain. J Cell Biol. 1969 Mar;40(3):648–677. doi: 10.1083/jcb.40.3.648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friede R. L., Schachenmayr W. The origin ofsubdural neomembranes. II. Fine structural of neomembranes. Am J Pathol. 1978 Jul;92(1):69–84. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himango W. A., Low F. N. The fine structure of a lateral recess of the subarachnoid space in the rat. Anat Rec. 1971 Sep;171(1):1–19. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091710102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klika E. The ultrastructure of meninges in vertebrates. Acta Univ Carol Med (Praha) 1967;13(1):53–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopes C. A., Mair W. G. Ultrastructure of the arachnoid membrane in man. Acta Neuropathol. 1974;28(2):167–173. doi: 10.1007/BF00710326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLone D. G., Bondareff W. Developmental morphology of the subarachnoid space and contiguous structures in the mouse. Am J Anat. 1975 Mar;142(3):273–293. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001420302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabeshima S., Reese T. S., Landis D. M., Brightman M. W. Junctions in the meninges and marginal glia. J Comp Neurol. 1975 Nov 15;164(2):127–169. doi: 10.1002/cne.901640202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEASE D. C., SCHULTZ R. L. Electron microscopy of rat cranial meninges. Am J Anat. 1958 Mar;102(2):301–321. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001020207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsey H. J. Fine structure of the surface of the cerebral cortex of human brain. J Cell Biol. 1965 Aug;26(2):323–334. doi: 10.1083/jcb.26.2.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rascol M. M., Izard J. Y. The subdural neurothelium of the cranial meninges in man. Anat Rec. 1976 Nov;186(3):429–436. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091860308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rascol M., Izard J. La jonction cortico-pie-mérienne et la pénétration des vaisseaux dans le cortex cérébral chez l'Homme. Structure et ultrastructure. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1972;123(3):337–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reese T. S., Karnovsky M. J. Fine structural localization of a blood-brain barrier to exogenous peroxidase. J Cell Biol. 1967 Jul;34(1):207–217. doi: 10.1083/jcb.34.1.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simionescu M., Simionescu N. Organization of cell junctions in the peritoneal mesothelium. J Cell Biol. 1977 Jul;74(1):98–110. doi: 10.1083/jcb.74.1.98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staehelin L. A. Structure and function of intercellular junctions. Int Rev Cytol. 1974;39:191–283. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60940-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade J. B., Karnovsky M. J. The structure of the zonula occludens. A single fibril model based on freeze-fracture. J Cell Biol. 1974 Jan;60(1):168–180. doi: 10.1083/jcb.60.1.168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waggener J. D., Beggs J. The membranous coverings of neural tissues: an electron microscopy study. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1967 Jul;26(3):412–426. doi: 10.1097/00005072-196707000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]