Abstract
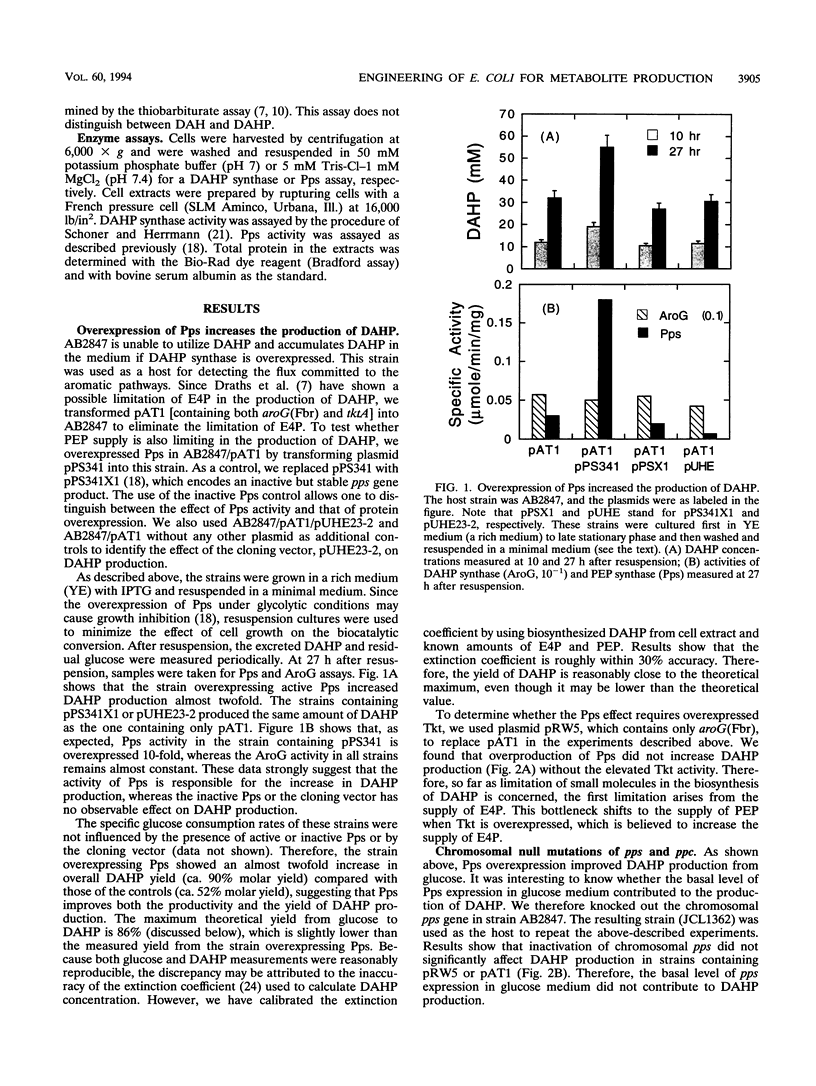
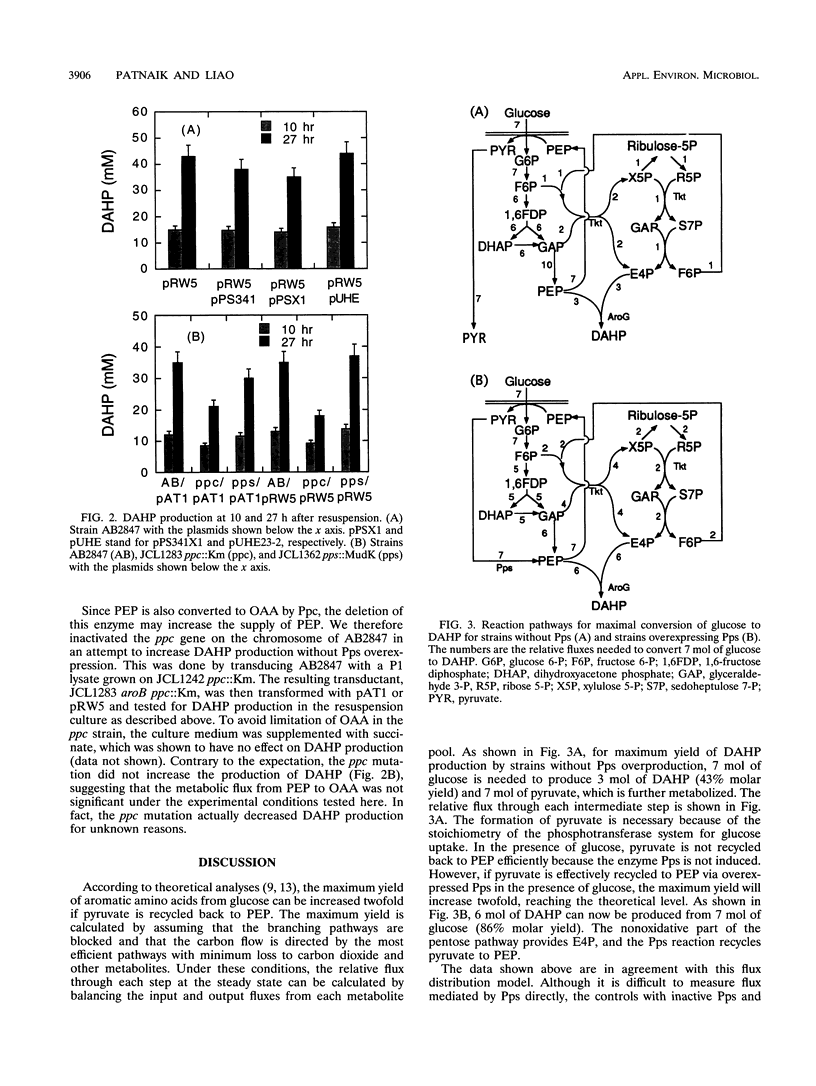
Escherichia coli and many other microorganisms synthesize aromatic amino acids through the condensation reaction between phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) and erythrose 4-phosphate to form 3-deoxy-D-arabinoheptulosonate 7-phosphate (DAHP). It has been shown that overexpression of transketolase increases the production of DAHP in an aroB mutant strain (unable to further metabolize DAHP) with elevated DAHP synthase. However, the yield (percent conversion) of DAHP from glucose is still low. Stoichiometric analysis shows that many enzymes compete for intracellular PEP. In particular, the phosphotransferase system, responsible for glucose transport in E. coli, uses PEP as a phosphate donor and converts it to pyruvate, which is less likely to recycle back to PEP. This stoichiometric limitation greatly reduces the yield of aromatic metabolites. To relieve this limitation, we overexpressed PEP synthase in the presence of glucose and showed that it increased the final concentration and the yield of DAHP by almost twofold, to a near theoretical maximum. The PEP synthase effect is not observed without overproduced transketolase, suggesting that erythrose 4-phosphate is the first limiting metabolite. This result demonstrates the utility of pathway analysis and the limitation of central metabolites in the high-level overproduction of desired metabolites.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiba S., Tsunekawa H., Imanaka T. New approach to tryptophan production by Escherichia coli: genetic manipulation of composite plasmids in vitro. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Feb;43(2):289–297. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.2.289-297.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey J. E. Toward a science of metabolic engineering. Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1668–1675. doi: 10.1126/science.2047876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron D. C., Tong I. T. Cellular and metabolic engineering. An overview. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 1993 Jan-Feb;38(1-2):105–140. doi: 10.1007/BF02916416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castilho B. A., Olfson P., Casadaban M. J. Plasmid insertion mutagenesis and lac gene fusion with mini-mu bacteriophage transposons. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):488–495. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.488-495.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao Y. P., Liao J. C. Alteration of growth yield by overexpression of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Dec;59(12):4261–4265. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.12.4261-4265.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao Y. P., Liao J. C. Metabolic responses to substrate futile cycling in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 18;269(7):5122–5126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensley B. D., Ratzkin B. J., Osslund T. D., Simon M. J., Wackett L. P., Gibson D. T. Expression of naphthalene oxidation genes in Escherichia coli results in the biosynthesis of indigo. Science. 1983 Oct 14;222(4620):167–169. doi: 10.1126/science.6353574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imanaka T., Tsunekawa H., Aiba S. Phenotypic stability of trp operon recombinant plasmids in Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 May;118(1):253–261. doi: 10.1099/00221287-118-1-253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingram L. O., Conway T., Clark D. P., Sewell G. W., Preston J. F. Genetic engineering of ethanol production in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Oct;53(10):2420–2425. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.10.2420-2425.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowry O. H., Carter J., Ward J. B., Glaser L. The effect of carbon and nitrogen sources on the level of metabolic intermediates in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1971 Nov;246(21):6511–6521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazur R. H., Schlatter J. M., Goldkamp A. H. Structure-taste relationships of some dipeptides. J Am Chem Soc. 1969 May 7;91(10):2684–2691. doi: 10.1021/ja01038a046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patnaik R., Roof W. D., Young R. F., Liao J. C. Stimulation of glucose catabolism in Escherichia coli by a potential futile cycle. J Bacteriol. 1992 Dec;174(23):7527–7532. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.23.7527-7532.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittard J., Wallace B. J. Distribution and function of genes concerned with aromatic biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1966 Apr;91(4):1494–1508. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.4.1494-1508.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SRINIVASAN P. R., SPRINSON D. B. 2-Keto-3-deoxy-D-arabo-heptonic acid 7-phosphate synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1959 Apr;234(4):716–722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoner R., Herrmann K. M. 3-Deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonate 7-phosphate synthase. Purification, properties, and kinetics of the tyrosine-sensitive isoenzyme from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 25;251(18):5440–5447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer M., Baker T. A., Schnitzler G., Deischel S. M., Goel M., Dove W., Jaacks K. J., Grossman A. D., Erickson J. W., Gross C. A. A collection of strains containing genetically linked alternating antibiotic resistance elements for genetic mapping of Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Mar;53(1):1–24. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.1.1-24.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprenger G. A. Location of the transketolase (tkt) gene on the Escherichia coli physical map. J Bacteriol. 1992 Mar;174(5):1707–1708. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.5.1707-1708.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh K., Koshland D. E., Jr Characterization of rate-controlling steps in vivo by use of an adjustable expression vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3577–3581. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winans S. C., Elledge S. J., Krueger J. H., Walker G. C. Site-directed insertion and deletion mutagenesis with cloned fragments in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):1219–1221. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.1219-1221.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


