Abstract
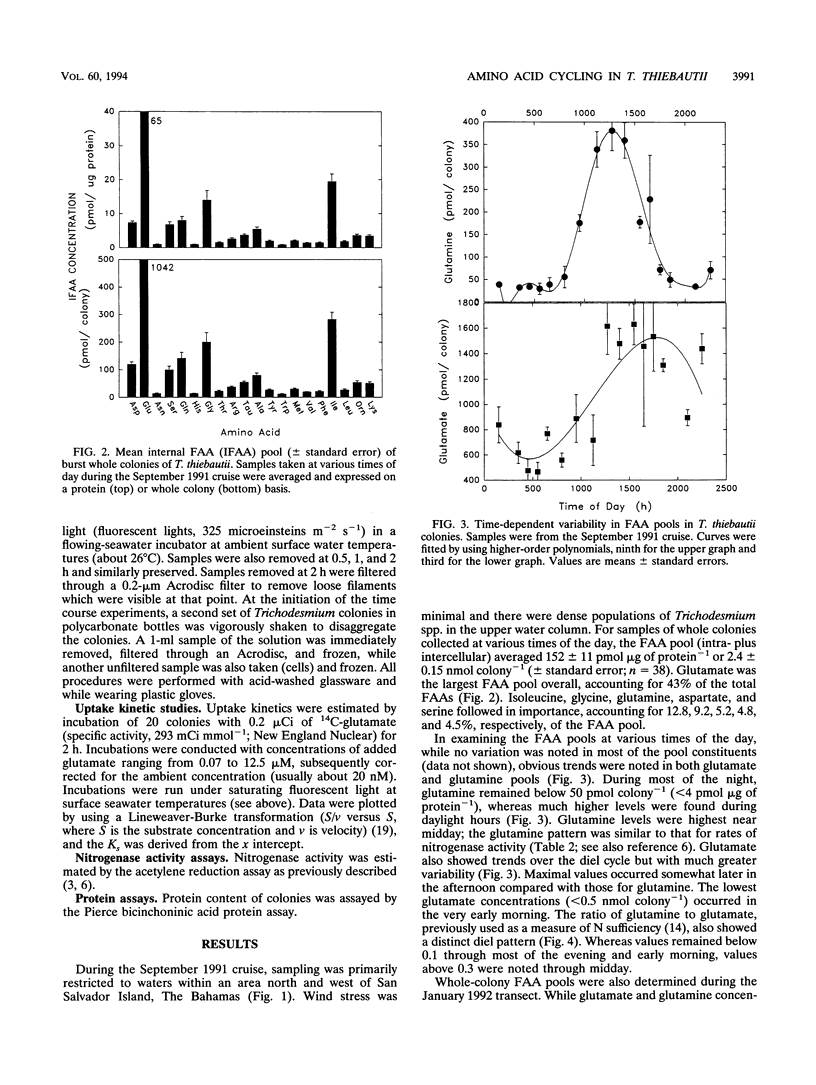
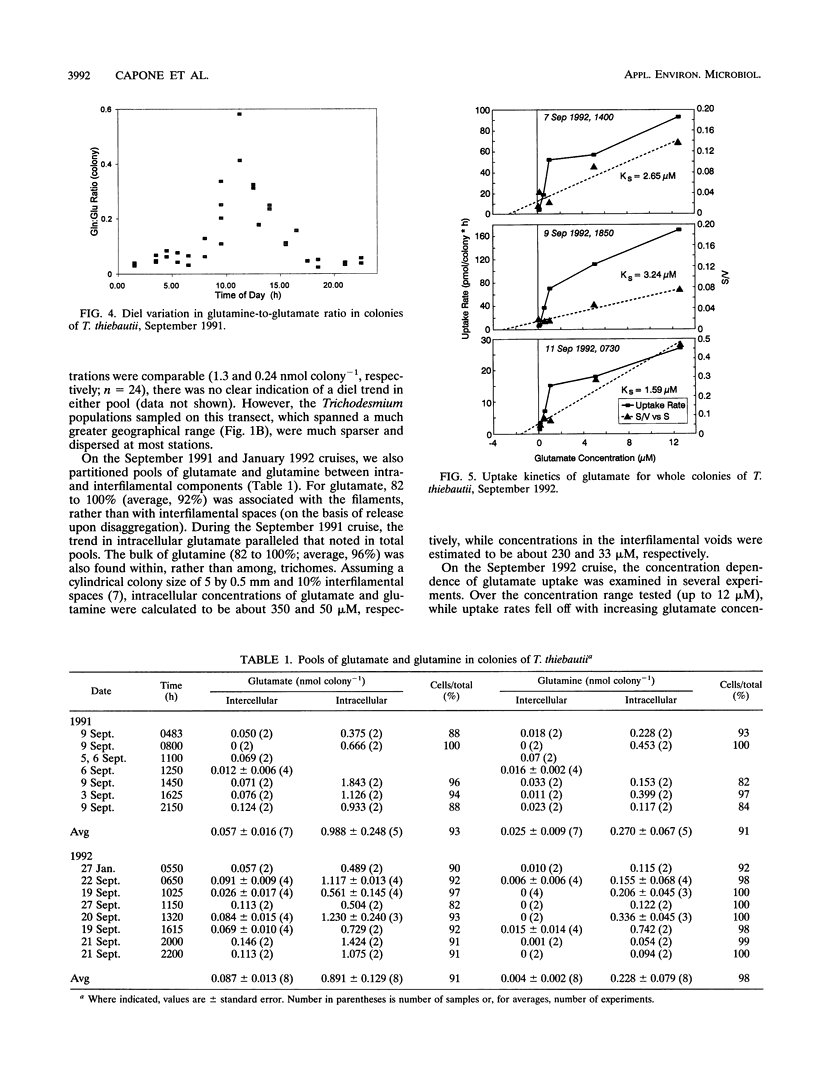
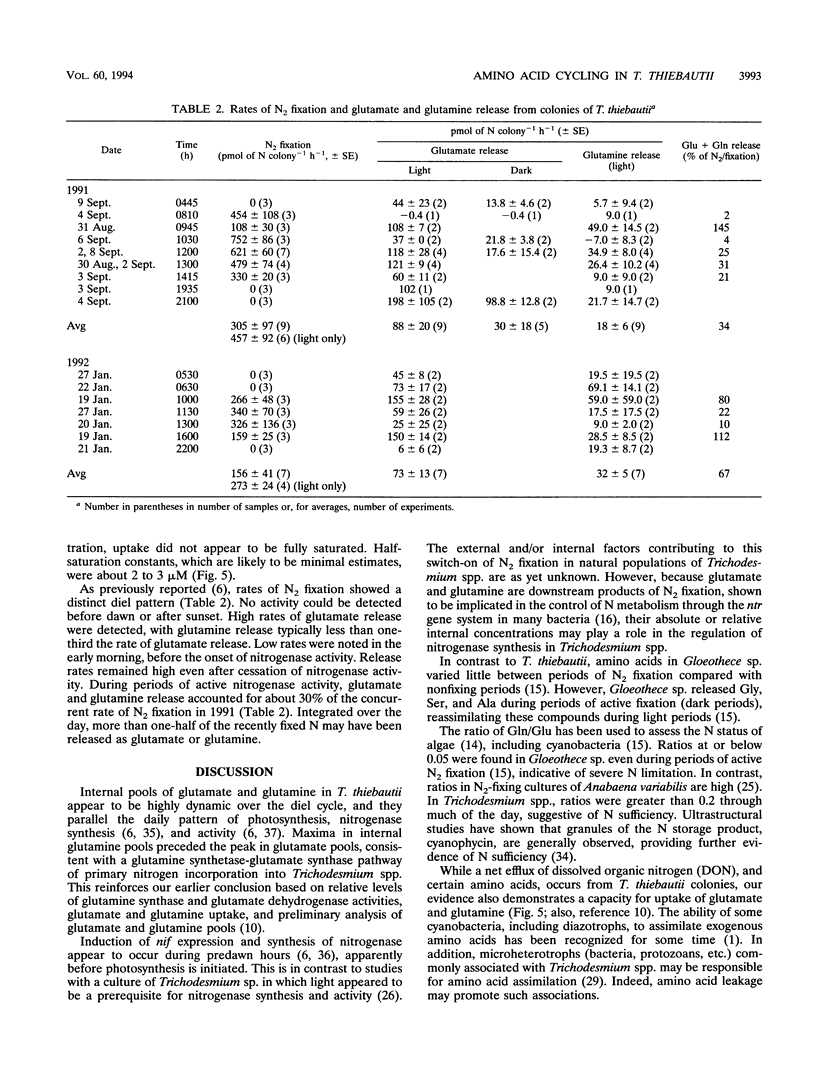
We examined diel trends in internal pools and net efflux of free amino acids in colonies of the nonheterocystous, diazotrophic cyanobacterium Trichodesmium thiebautii, freshly collected from waters of the Caribbean and the Bahamas. The kinetics of glutamate uptake by whole colonies were also examined. While intracolonial pools of most free amino acids were relatively constant through the day, pools of glutamate and glutamine varied over the diel cycle, with maxima during the early afternoon. This paralleled the daily cycle of nitrogenase activity. We also observed a large net release of these two amino acids from intact colonies. Glutamate release was typically 100 pmol of N colony-1 h-1. This is about one-fourth the concurrent rate of N2 fixation during the day. However, while nitrogenase activity only occurs during the day, net release of glutamate and glutamine persisted into the night and may therefore account for a greater loss of recently fixed N on a daily basis. This release may be an important route of new N input into tropical, oligotrophic waters. Whole colonies also displayed saturation kinetics with respect to glutamate uptake. The Ks for whole colonies varied from 1.6 to 3.2 μM, or about 100-fold greater than typical ambient concentrations. Thus, uptake systems appear to be adapted to the higher concentrations of glutamate found within the intracellular spaces of the colonies. This suggests that glutamate may be a vehicle for N exchange among trichomes in the colony.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Capone D. G., Carpenter E. J. Nitrogen fixation in the marine environment. Science. 1982 Sep 17;217(4565):1140–1142. doi: 10.1126/science.217.4565.1140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capone D. G., O'neil J. M., Zehr J., Carpenter E. J. Basis for Diel Variation in Nitrogenase Activity in the Marine Planktonic Cyanobacterium Trichodesmium thiebautii. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Nov;56(11):3532–3536. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.11.3532-3536.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter E. J., Bergman B., Dawson R., Siddiqui P. J., Söderbäck E., Capone D. G. Glutamine synthetase and nitrogen cycling in colonies of the marine diazotrophic cyanobacteria Trichodesmium spp. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Sep;58(9):3122–3129. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.9.3122-3129.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter E. J., Romans K. Major role of the cyanobacterium trichodesmium in nutrient cycling in the north atlantic ocean. Science. 1991 Nov 29;254(5036):1356–1358. doi: 10.1126/science.254.5036.1356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glibert P. M., Bronk D. A. Release of Dissolved Organic Nitrogen by Marine Diazotrophic Cyanobacteria, Trichodesmium spp. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1994 Nov;60(11):3996–4000. doi: 10.1128/aem.60.11.3996-4000.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paerl H. W. Ecophysiological and trophic implications of light-stimulated amino Acid utilization in marine picoplankton. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Feb;57(2):473–479. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.2.473-479.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paerl H. W., Priscu J. C., Brawner D. L. Immunochemical localization of nitrogenase in marine trichodesmium aggregates: relationship to n(2) fixation potential. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Nov;55(11):2965–2975. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.11.2965-2975.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zehr J. P., Wyman M., Miller V., Duguay L., Capone D. G. Modification of the Fe Protein of Nitrogenase in Natural Populations of Trichodesmium thiebautii. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Mar;59(3):669–676. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.3.669-676.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


