Abstract
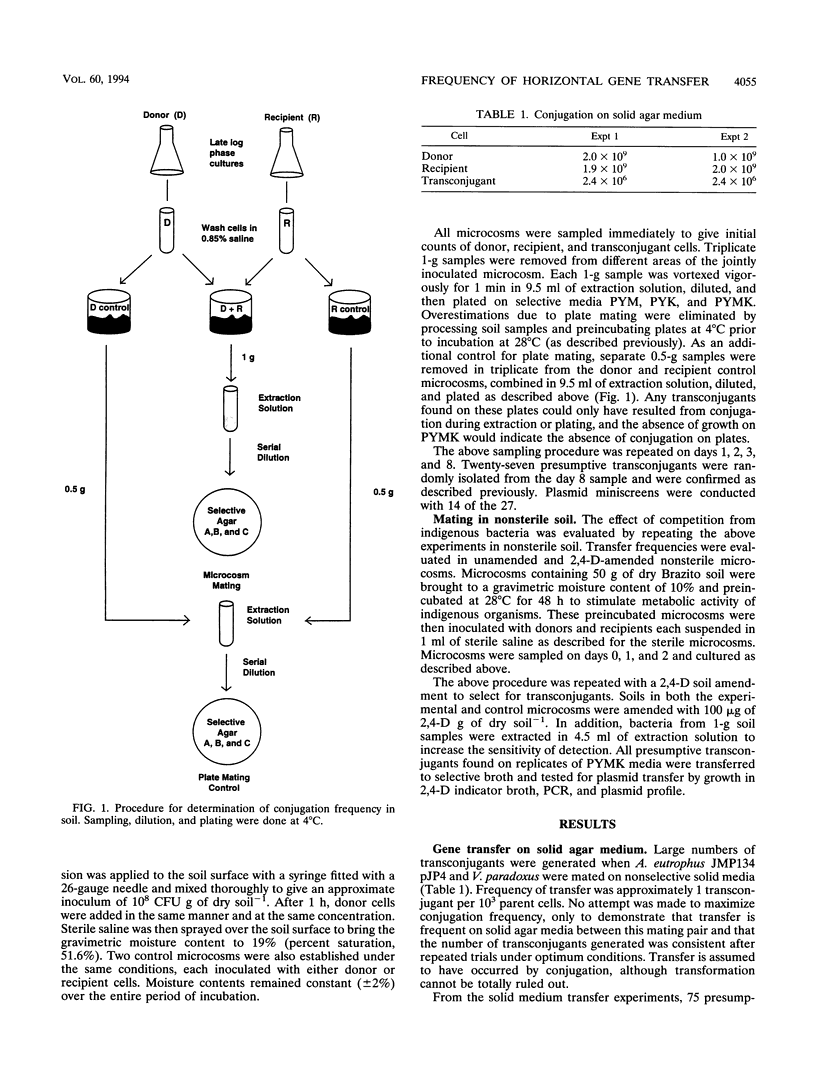
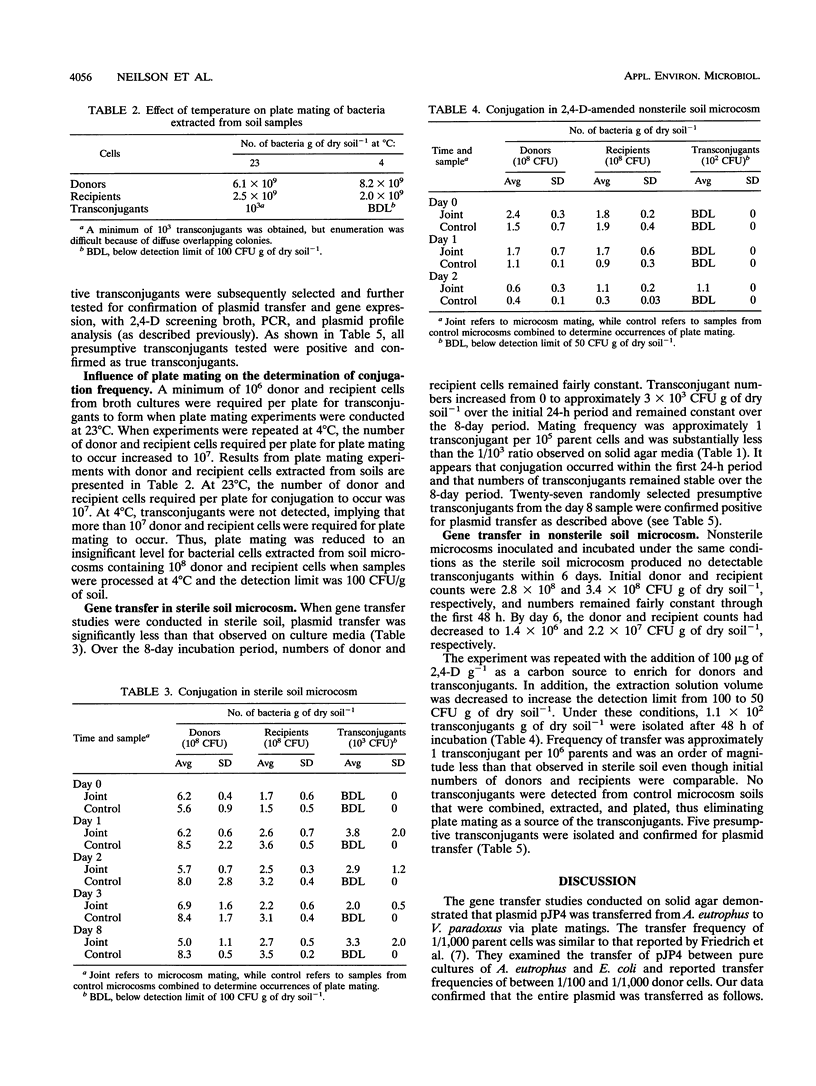
Limited work has been done to assess the bioremediation potential of transfer of plasmid-borne degradative genes from introduced to indigenous organisms in the environment. Here we demonstrate the transfer by conjugation of the catabolic plasmid pJP4, using a model system with donor and recipient organisms. The donor organism was Alcaligenes eutrophus JMP134 and the recipient organism was Variovorax paradoxus isolated from a toxic waste site. Plasmid pJP4 contains genes for mercury resistance and 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic (2,4-D) acid degradation. A transfer frequency of approximately 1/10(3) donor and recipient cells (parent cells) was observed on solid agar media, decreasing to 1/10(5) parent cells in sterile soil and finally 1/10(6) parent cells in 2,4-D-amended, nonsterile soil. Presumptive transconjugants were confirmed to be resistant to Hg, to be capable of degrading 2,4-D, and to contain a plasmid of size comparable to that of pJP4. In addition, we confirmed the transfer through PCR amplifications of the tfdB gene. Although transfer of pJP4 did occur at a high frequency in pure culture, the rate was significantly decreased by the introduction of abiotic (sterile soil) and biotic (nonsterile soil) stresses. An evaluation of the data from this model system implies that the reliance on plasmid transfer from a donor organism as a remediative strategy has limited potential.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Don R. H., Pemberton J. M. Genetic and physical map of the 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid-degradative plasmid pJP4. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):466–468. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.466-468.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Don R. H., Pemberton J. M. Properties of six pesticide degradation plasmids isolated from Alcaligenes paradoxus and Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):681–686. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.681-686.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich B., Meyer M., Schlegel H. G. Transfer and expression of the herbicide-degrading plasmid pJP4 in aerobic autotrophic bacteria. Arch Microbiol. 1983 Feb;134(2):92–97. doi: 10.1007/BF00407938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost L. S. Bacterial conjugation: everybody's doin' it. Can J Microbiol. 1992 Nov;38(11):1091–1096. doi: 10.1139/m92-179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulthorpe R. R., Wyndham R. C. Transfer and Expression of the Catabolic Plasmid pBRC60 in Wild Bacterial Recipients in a Freshwater Ecosystem. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 May;57(5):1546–1553. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.5.1546-1553.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosal D., You I. S., Chatterjee D. K., Chakrabarty A. M. Microbial degradation of halogenated compounds. Science. 1985 Apr 12;228(4696):135–142. doi: 10.1126/science.228.4696.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harker A. R., Olsen R. H., Seidler R. J. Phenoxyacetic acid degradation by the 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (TFD) pathway of plasmid pJP4: mapping and characterization of the TFD regulatory gene, tfdR. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):314–320. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.314-320.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain R. K., Sayler G. S., Wilson J. T., Houston L., Pacia D. Maintenance and stability of introduced genotypes in groundwater aquifer material. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):996–1002. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.996-1002.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinkle B. K., Sadowsky M. J., Schmidt E. L., Koskinen W. C. Plasmids pJP4 and r68.45 Can Be Transferred between Populations of Bradyrhizobia in Nonsterile Soil. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Jun;59(6):1762–1766. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.6.1762-1766.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loos M. A. Indicator media for microorganisms degrading chlorinated pesticides. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Jan;21(1):104–107. doi: 10.1139/m75-016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilson J. W., Josephson K. L., Pillai S. D., Pepper I. L. Polymerase chain reaction and gene probe detection of the 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid degradation plasmid, pJP4. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Apr;58(4):1271–1275. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.4.1271-1275.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins E. J., Gordon M. P., Caceres O., Lurquin P. F. Organization and sequence analysis of the 2,4-dichlorophenol hydroxylase and dichlorocatechol oxidative operons of plasmid pJP4. J Bacteriol. 1990 May;172(5):2351–2359. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.5.2351-2359.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richaume A., Angle J. S., Sadowsky M. J. Influence of soil variables on in situ plasmid transfer from Escherichia coli to Rhizobium fredii. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jul;55(7):1730–1734. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.7.1730-1734.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stotzky G., Babich H. Survival of, and genetic transfer by, genetically engineered bacteria in natural environments. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1986;31:93–138. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(08)70440-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streber W. R., Timmis K. N., Zenk M. H. Analysis, cloning, and high-level expression of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetate monooxygenase gene tfdA of Alcaligenes eutrophus JMP134. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):2950–2955. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.2950-2955.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Top E., Mergeay M., Springael D., Verstraete W. Gene escape model: transfer of heavy metal resistance genes from Escherichia coli to Alcaligenes eutrophus on agar plates and in soil samples. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Aug;56(8):2471–2479. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.8.2471-2479.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trevors J. T., Oddie K. M. R-plasmid transfer in soil and water. Can J Microbiol. 1986 Jul;32(7):610–613. doi: 10.1139/m86-114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter M. V., Porteous A., Seidler R. J. Measuring genetic stability in bacteria of potential use in genetic engineering. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Jan;53(1):105–109. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.1.105-109.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


