Abstract
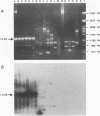
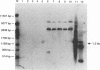
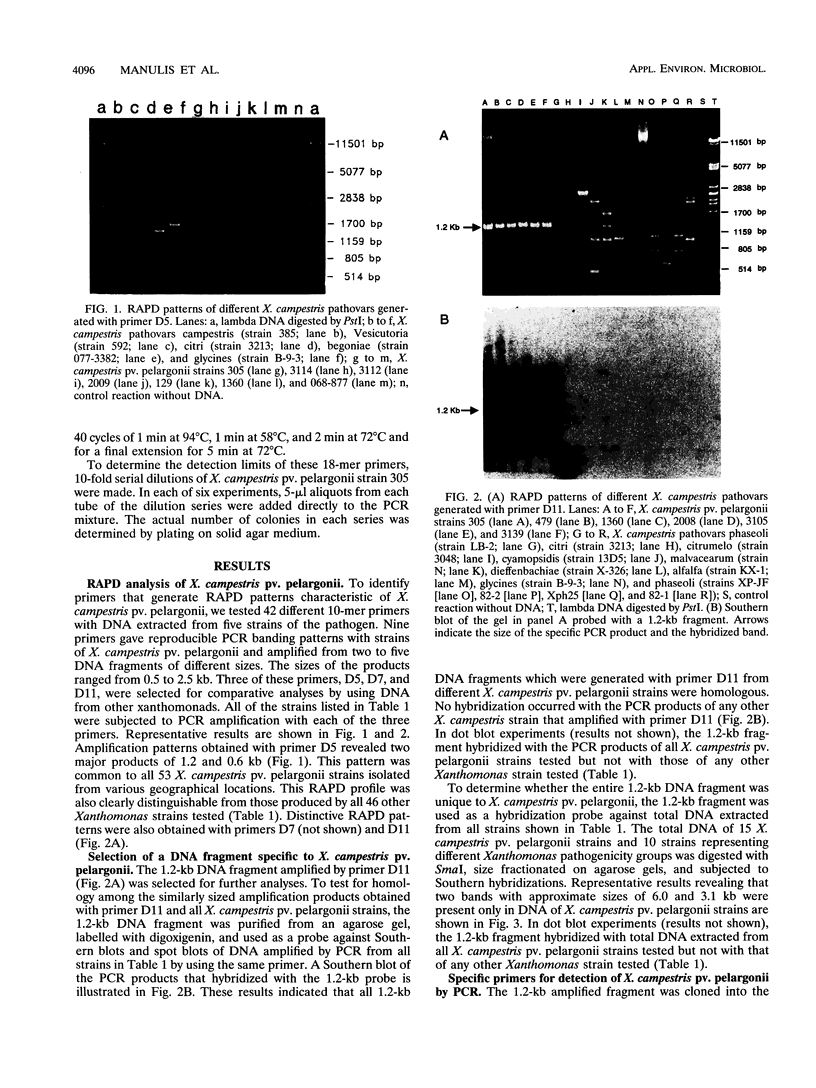
The random amplified polymorphic DNA method was used to distinguish strains of Xanthomonas campestris pv. pelargonii from 21 other Xanthomonas species and/or pathovars. Among the 42 arbitrarily chosen primers evaluated, 3 were found to reveal diagnostic polymorphisms when purified DNAs from compared strains were amplified by the PCR. The three primers revealed DNA amplification patterns which were conserved among all 53 strains tested of X. campestris pv. pelargonii isolated from various locations worldwide. The distinctive X. compestris pv. pelargonii patterns were clearly different from those obtained with any of 46 other Xanthomonas strains tested. An amplified 1.2-kb DNA fragment, apparently unique to X. campestris pv. pelargonii by these random amplified polymorphic DNA tests, was cloned and evaluated as a diagnostic DNA probe. It hybridized with total DNA from all 53 X. campestris pv. pelargonii strains tested and not with any of the 46 other Xanthomonas strains tested. The DNA sequence of the terminal ends of this 1.2-kb fragment was obtained and used to design a pair of 18-mer oligonucleotide primers specific for X. campestris pv. pelargonii. The custom-synthesized primers amplified the same 1.2-kb DNA fragment from all 53 X. campestris pv. pelargonii strains tested and failed to amplify DNA from any of the 46 other Xanthomonas strains tested. DNA isolated from saprophytes associated with the geranium plant also did not produce amplified DNA with these primers. The sensitivity of the PCR assay using the custom-synthesized primers was between 10 and 50 cells.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF

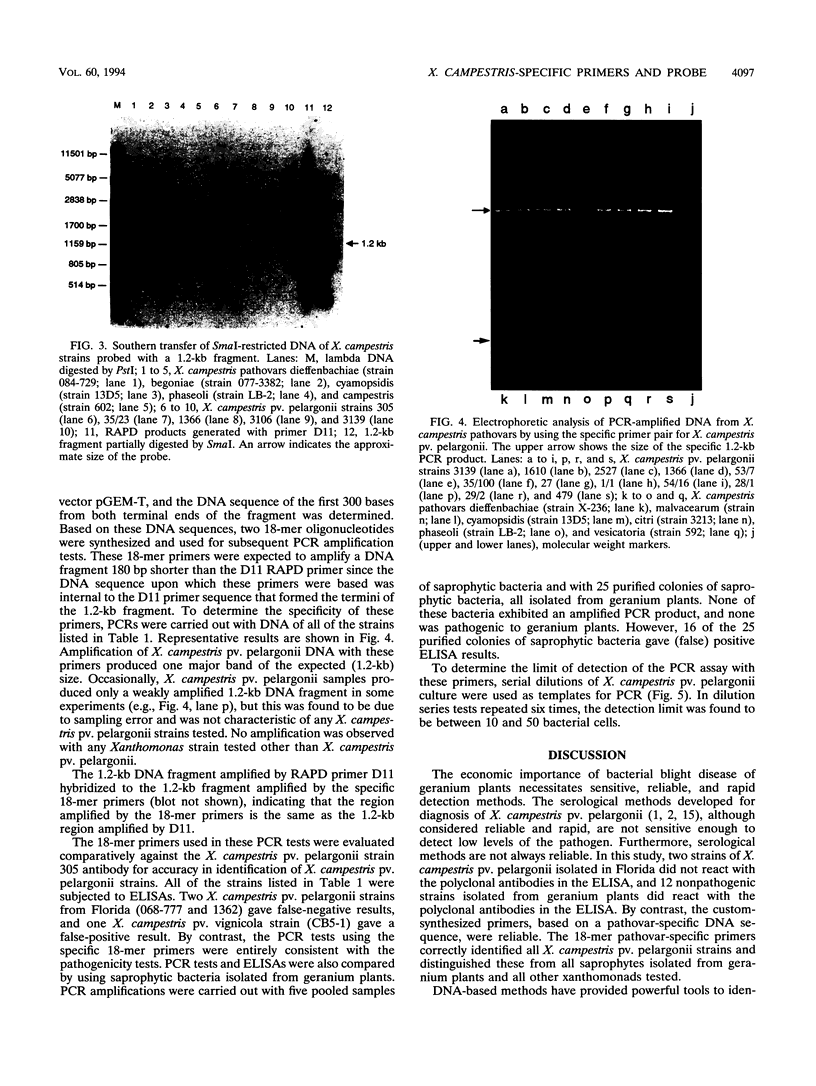


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benedict A. A., Alvarez A. M., Pollard L. W. Pathovar-Specific Antigens of Xanthomonas campestris pv. begoniae and X. campestris pv. pelargonii Detected with Monoclonal Antibodies. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Feb;56(2):572–574. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.2.572-574.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seal S. E., Jackson L. A., Daniels M. J. Isolation of a Pseudomonas solanacearum-specific DNA probe by subtraction hybridization and construction of species-specific oligonucleotide primers for sensitive detection by the polymerase chain reaction. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Nov;58(11):3751–3758. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.11.3751-3758.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh J., McClelland M. Fingerprinting genomes using PCR with arbitrary primers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 25;18(24):7213–7218. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.24.7213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. G., Kubelik A. R., Livak K. J., Rafalski J. A., Tingey S. V. DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 25;18(22):6531–6535. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.22.6531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]