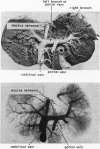
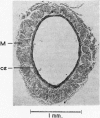
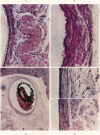
Full text
PDF
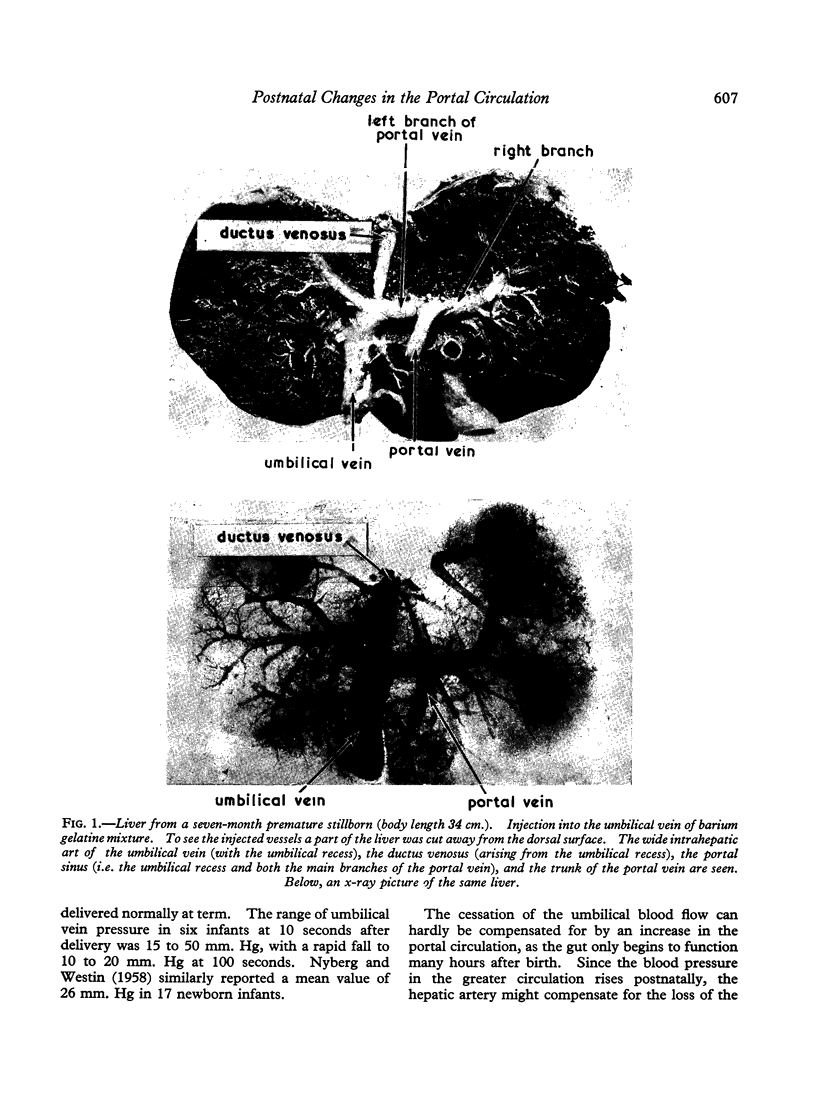
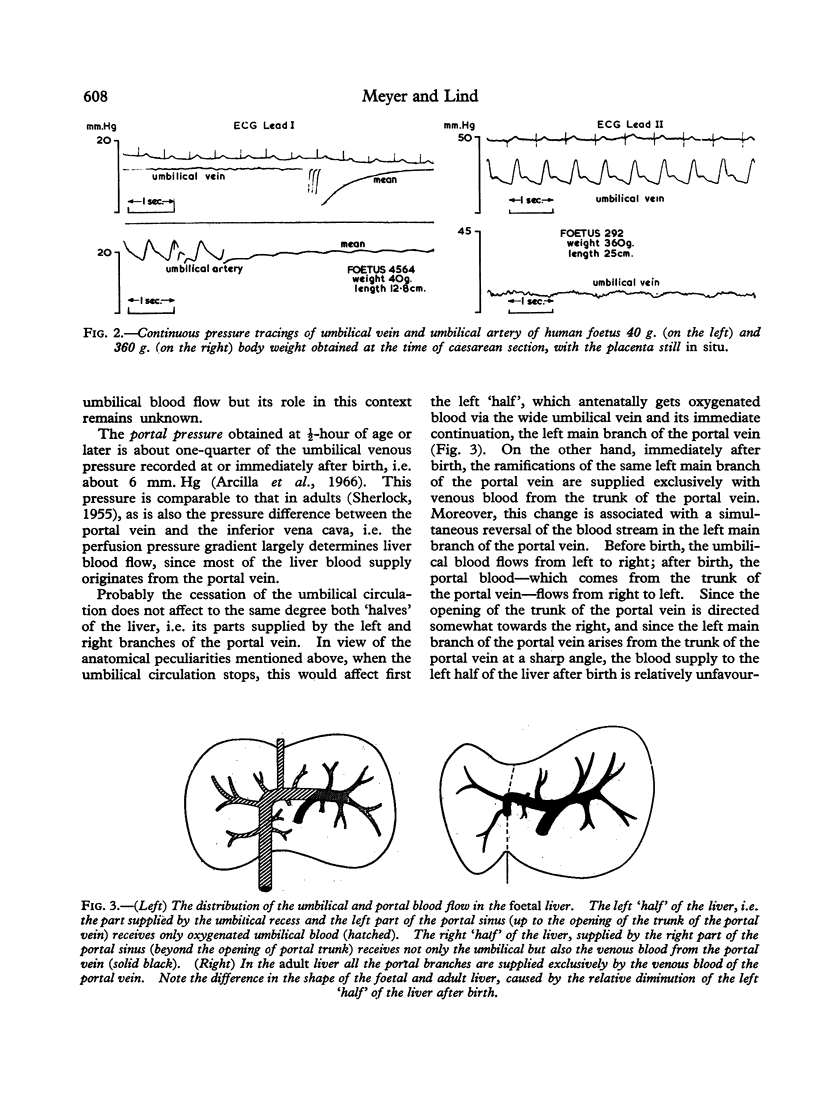




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- EMERY J. L. Degenerative changes in the left lobe of the liver in the newborn. Arch Dis Child. 1952 Dec;27(136):558–561. doi: 10.1136/adc.27.136.558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krenz G., Meyer W. W. Strukturveränderungen der Pfortaderwand bei Lebercirrhose. Untersuchungen am entfalteten Venenrohr. Frankf Z Pathol. 1966;75(5):375–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARGOLIS A. J., ORCUTT R. E. Pressures in human umbilical vessels in utero. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1960 Sep;80:573–576. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(16)36517-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEYER W. W. FUNKTIONELLE MORPHOLOGIE DES GEFAEBSYSTEMS IM KINDESALTER. Monatsschr Kinderheilkd. 1964 Feb;112:37–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEYER W. W., HENSCHEL E. Untersuchungen über die Schlängelung und Sklerose der Milzarterie. Virchows Arch Pathol Anat Physiol Klin Med. 1958;331(4):396–416. doi: 10.1007/BF00958022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEYER W. W., KLIEBSCH N. DIE STRUKTURABWANDLUNG DER PFORTADER NACH DER GEBURT IN IHRER BEZIEHUNG ZUR POSTNATALEN KREISLAUFUMSTELLUNG. Frankf Z Pathol. 1963 Nov 18;73:188–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NYBERG R., WESTIN B. The arterial blood pressure of the newborn infant. I. The blood pressure in the umbilical artery of the mature normal newborn infant. Acta Paediatr. 1958 Jul;47(4):357–360. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1958.tb07646.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALLGREN G., KARLBERG P., LIND J. Studies of the circulatory adaptation immediately after birth. Acta Paediatr. 1960 Nov;49:843–849. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1960.tb16094.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]