Abstract
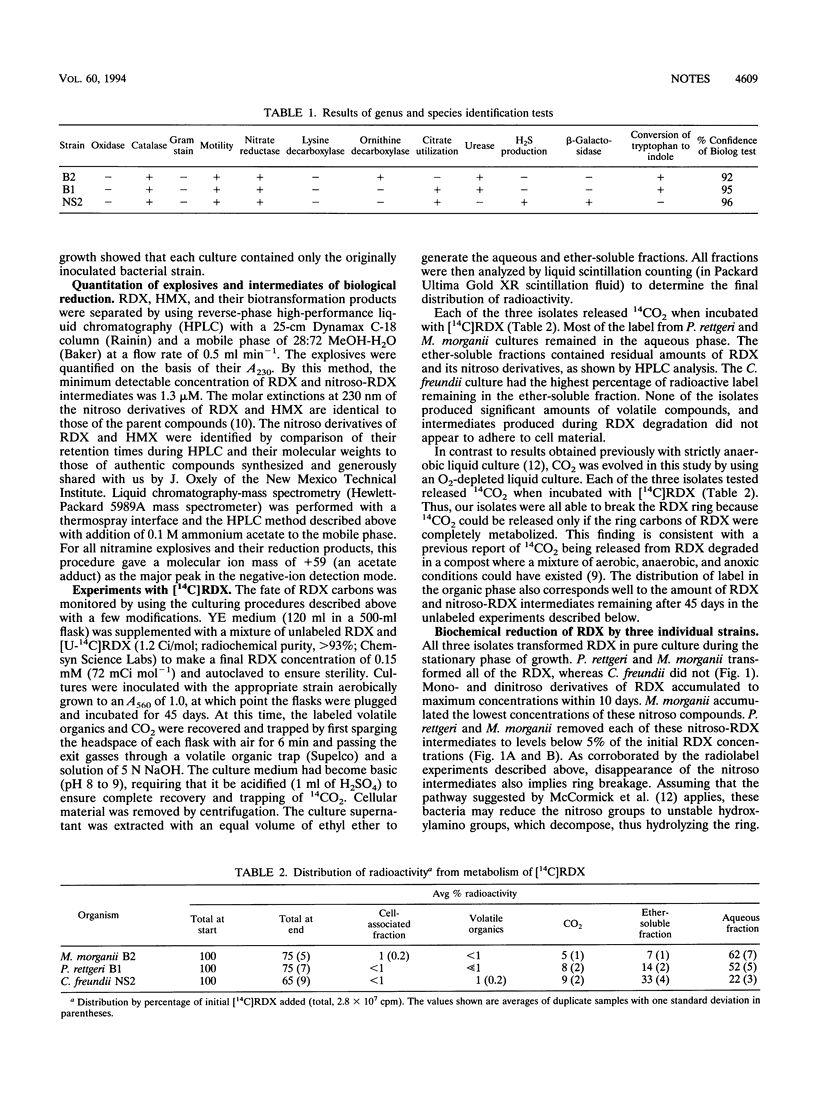
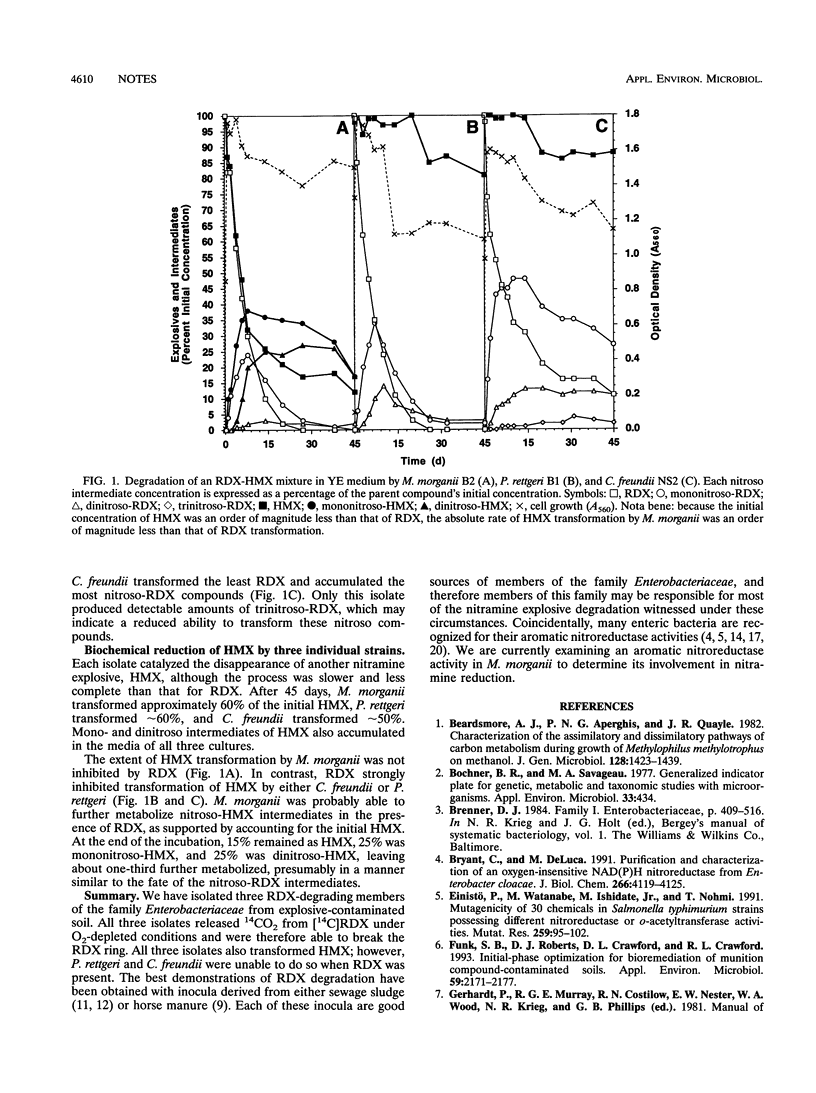
Three species of the family Enterobacteriaceae that biochemically reduced hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine (RDX) and octahydro-1,3,5,7-tetranitro-1,3,5,7-tetrazocine (HMX) were isolated from nitramine explosive-contaminated soil. Two isolates, identified as Morganella morganii and Providencia rettgeri, completely transformed both RDX and the nitroso-RDX reduction intermediates. The third isolate, identified as Citrobacter freundii, partially transformed RDX and generated high concentrations of nitroso-RDX intermediates. All three isolates produced 14CO2 from labeled RDX under O2-depleted culture conditions. While all three isolates transformed HMX, only M. morganii transformed HMX in the presence of RDX.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bochner B. R., Savageau M. A. Generalized indicator plate for genetic, metabolic, and taxonomic studies with microorganisms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Feb;33(2):434–444. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.2.434-444.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant C., DeLuca M. Purification and characterization of an oxygen-insensitive NAD(P)H nitroreductase from Enterobacter cloacae. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 5;266(7):4119–4125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einistö P., Watanabe M., Ishidate M., Jr, Nohmi T. Mutagenicity of 30 chemicals in Salmonella typhimurium strains possessing different nitroreductase or O-acetyltransferase activities. Mutat Res. 1991 Jan;259(1):95–102. doi: 10.1016/0165-1218(91)90113-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funk S. B., Roberts D. J., Crawford D. L., Crawford R. L. Initial-phase optimization for bioremediation of munition compound-contaminated soils. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Jul;59(7):2171–2177. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.7.2171-2177.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick N. G., Cornell J. H., Kaplan A. M. Biodegradation of hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Nov;42(5):817–823. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.5.817-823.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori M., Miyahara T., Hasegawa Y., Kudo Y., Kozuka H. Metabolism of dinitrotoluene isomers by Escherichia coli isolated from human intestine. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1984 Oct;32(10):4070–4075. doi: 10.1248/cpb.32.4070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson F. J., Mason R. P., Hovsepian J., Holtzman J. L. Oxygen-sensitive and -insensitive nitroreduction by Escherichia coli and rat hepatic microsomes. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):4009–4014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. B., Tomfohrde K. M., Rhoden D. L., Balows A. API system: a multitube micromethod for identification of Enterobacteriaceae. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Sep;24(3):449–452. doi: 10.1128/am.24.3.449-452.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


