Abstract
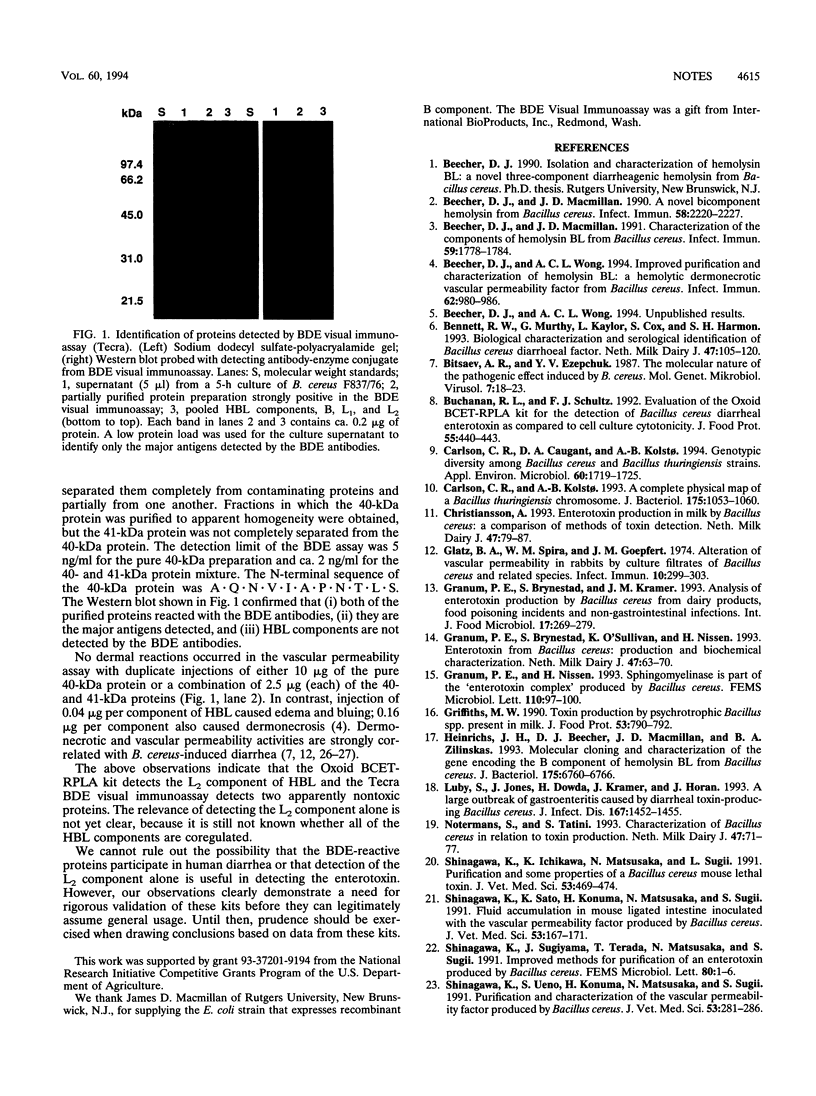
The usefulness of two commercial immunoassays for the detection of diarrheal enterotoxin of Bacillus cereus is unclear because the identity of the enterotoxin(s) has not been proven and the kits detect different proteins. We found that the Bacillus cereus Enterotoxin-Reversed Passive Latex Agglutination kit (Oxoid) detects the L2 component from hemolysin BL, and the Bacillus Diarrhoeal Enterotoxin Visual Immunoassay (Tecra) detects two apparently nontoxic proteins.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beecher D. J., MacMillan J. D. A novel bicomponent hemolysin from Bacillus cereus. Infect Immun. 1990 Jul;58(7):2220–2227. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.7.2220-2227.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beecher D. J., Macmillan J. D. Characterization of the components of hemolysin BL from Bacillus cereus. Infect Immun. 1991 May;59(5):1778–1784. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.5.1778-1784.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beecher D. J., Wong A. C. Improved purification and characterization of hemolysin BL, a hemolytic dermonecrotic vascular permeability factor from Bacillus cereus. Infect Immun. 1994 Mar;62(3):980–986. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.3.980-986.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bitsaev A. R., Ezepchuk Iu V. Molekuliarnaia priroda patogennogo deistviia, vyzyvaemogo B. cereus. Mol Gen Mikrobiol Virusol. 1987 Jul;(7):18–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson C. R., Caugant D. A., Kolstø A. B. Genotypic Diversity among Bacillus cereus and Bacillus thuringiensis Strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1994 Jun;60(6):1719–1725. doi: 10.1128/aem.60.6.1719-1725.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson C. R., Kolstø A. B. A complete physical map of a Bacillus thuringiensis chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1993 Feb;175(4):1053–1060. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.4.1053-1060.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glatz B. A., Spira W. M., Goepfert J. M. Alteration of vascular permeability in rabbits by culture filtrates of Bacillus cereus and related species. Infect Immun. 1974 Aug;10(2):299–303. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.2.299-303.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granum P. E., Brynestad S., Kramer J. M. Analysis of enterotoxin production by Bacillus cereus from dairy products, food poisoning incidents and non-gastrointestinal infections. Int J Food Microbiol. 1993 Feb;17(4):269–279. doi: 10.1016/0168-1605(93)90197-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granum P. E., Nissen H. Sphingomyelinase is part of the 'enterotoxin complex' produced by Bacillus cereus. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1993 Jun 1;110(1):97–100. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1993.tb06301.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinrichs J. H., Beecher D. J., MacMillan J. D., Zilinskas B. A. Molecular cloning and characterization of the hblA gene encoding the B component of hemolysin BL from Bacillus cereus. J Bacteriol. 1993 Nov;175(21):6760–6766. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.21.6760-6766.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luby S., Jones J., Dowda H., Kramer J., Horan J. A large outbreak of gastroenteritis caused by diarrheal toxin-producing Bacillus cereus. J Infect Dis. 1993 Jun;167(6):1452–1455. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.6.1452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinagawa K., Ichikawa K., Matsusaka N., Sugii S. Purification and some properties of a Bacillus cereus mouse lethal toxin. J Vet Med Sci. 1991 Jun;53(3):469–474. doi: 10.1292/jvms.53.469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinagawa K., Sato K., Konuma H., Matsusaka N., Sugii S. Fluid accumulation in mouse ligated intestine inoculated with the vascular permeability factor produced by Bacillus cereus. J Vet Med Sci. 1991 Apr;53(2):167–171. doi: 10.1292/jvms.53.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinagawa K., Sugiyama J., Terada T., Matsusaka N., Sugii S. Improved methods for purification of an enterotoxin produced by Bacillus cereus. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 May 1;64(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90199-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinagawa K., Ueno S., Konuma H., Matsusaka N., Sugii S. Purification and characterization of the vascular permeability factor produced by Bacillus cereus. J Vet Med Sci. 1991 Apr;53(2):281–286. doi: 10.1292/jvms.53.281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland A. D., Limond A. M. Influence of pH and sugars on the growth and production of diarrhoeagenic toxin by Bacillus cereus. J Dairy Res. 1993 Nov;60(4):575–580. doi: 10.1017/s0022029900027928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland A. D. Toxin production by Bacillus cereus in dairy products. J Dairy Res. 1993 Nov;60(4):569–574. doi: 10.1017/s0022029900027916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson N. E., Ketterhagen M. J., Bergdoll M. S., Schantz E. J. Isolation and some properties of an enterotoxin produced by Bacillus cereus. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):887–894. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.887-894.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnbull P. C., Kramer J. M., Jørgensen K., Gilbert R. J., Melling J. Properties and production characteristics of vomiting, diarrheal, and necrotizing toxins of Bacillus cereus. Am J Clin Nutr. 1979 Jan;32(1):219–228. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/32.1.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Netten P., van De Moosdijk A., van Hoensel P., Mossel D. A., Perales I. Psychrotrophic strains of Bacillus cereus producing enterotoxin. J Appl Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;69(1):73–79. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1990.tb02913.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]