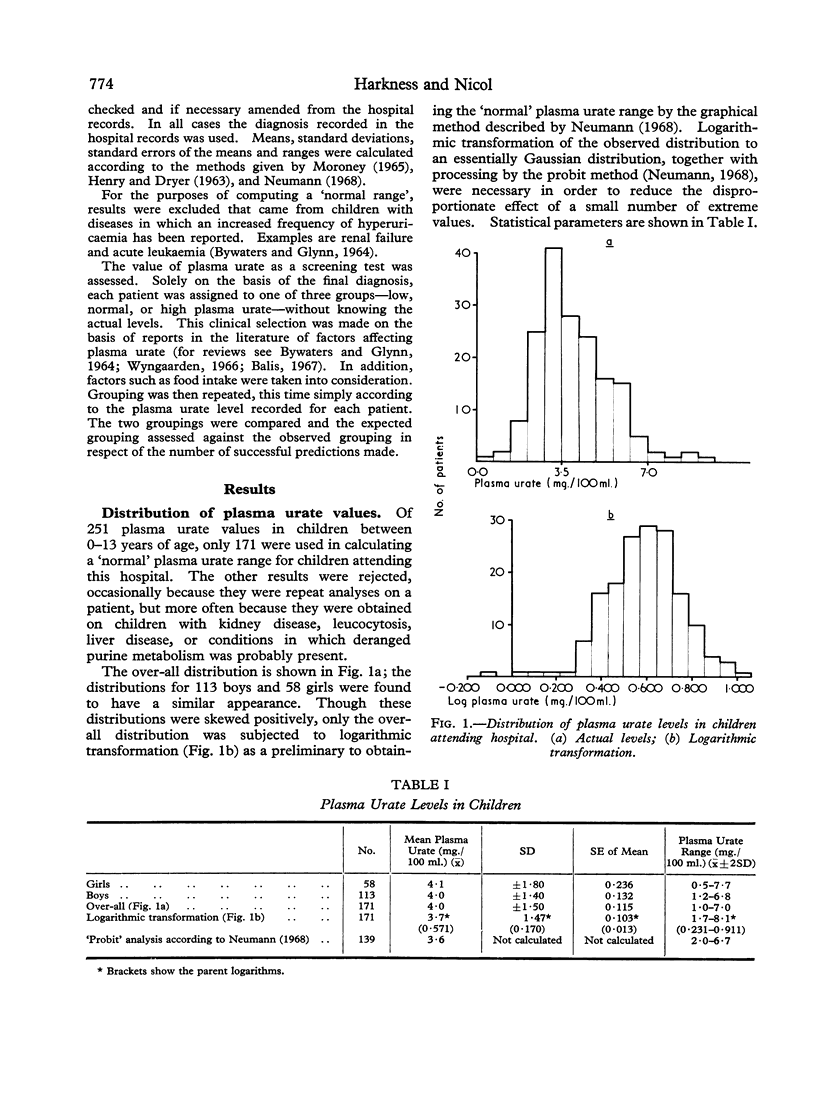
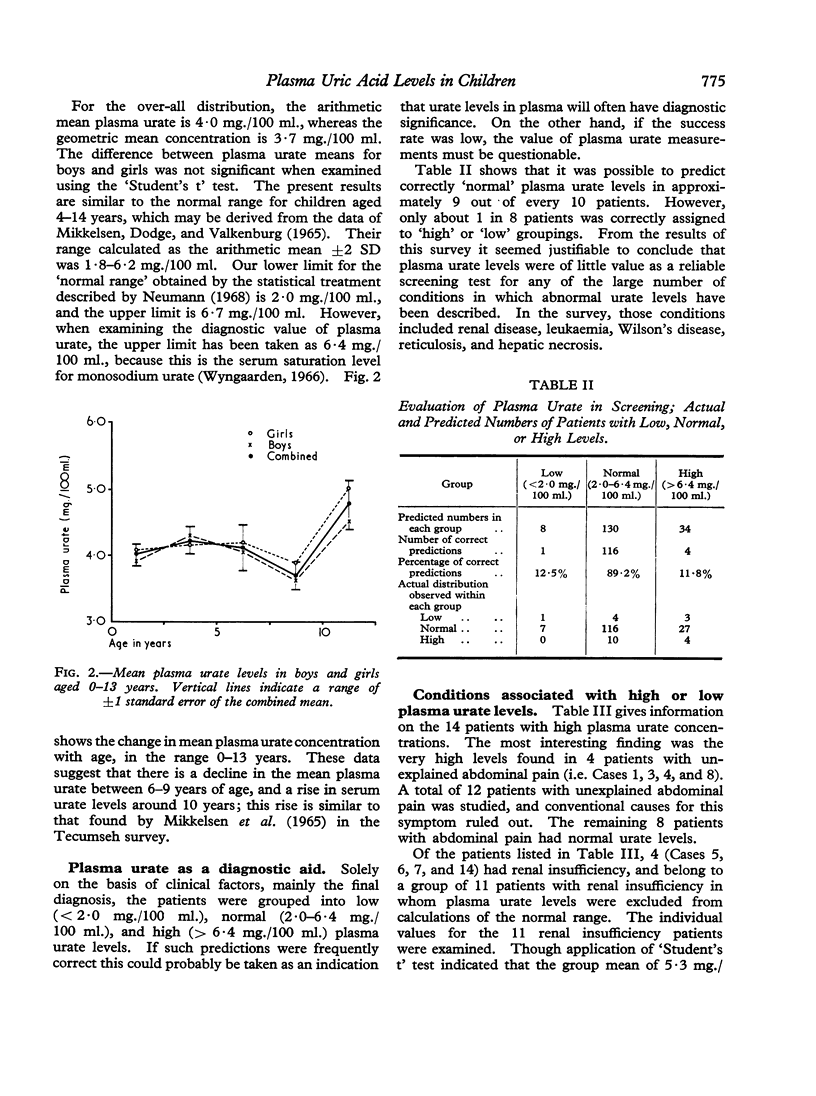
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CLARK L. C., Jr, THOMPSON H. L., BECK E. I., JACOBSON W. Excretion of creatine and creatinine by children. AMA Am J Dis Child. 1951 Jun;81(6):774–783. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1951.02040030788004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman J. M., Greene M. L., Seegmiller J. E. Urine uric acid to creatinine rtio--a screening test for inherited disorders of purine metabolism. Phosphoribosyltransferase (PRT) deficiency in X-linked cerebral palsy and in a variant of gout. J Pediatr. 1968 Oct;73(4):583–592. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(68)80274-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley W. N., Levy R. I., Rosenbloom F. M., Henderson J. F., Seegmiller J. E. Adenine phosphoribosyltransferase deficiency: a previously undescribed genetic defect in man. J Clin Invest. 1968 Oct;47(10):2281–2289. doi: 10.1172/JCI105913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein F., Lafeber G. J. Improvements of the uricase-u.v. method for the determination of uric acid in serum and urine. Clin Chim Acta. 1966 Nov;14(5):708–710. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(66)90200-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LESCH M., NYHAN W. L. A FAMILIAL DISORDER OF URIC ACID METABOLISM AND CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM FUNCTION. Am J Med. 1964 Apr;36:561–570. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(64)90104-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIDDLE L., SEEGMILLER J. E., LASTER L. The enzymatic spectrophotometric method for determination of uric acid. J Lab Clin Med. 1959 Dec;54:903–913. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAHLER H. R., HUBSCHER G., BAUM R. Studies on uricase. I. Preparation, purification, and properties of a cuproprotein. J Biol Chem. 1955 Oct;216(2):625–641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIKKELSEN W. M., DODGE H. J., VALKENBURG H. THE DISTRIBUTION OF SERUM URIC ACID VALUES IN A POPULATION UNSELECTED AS TO GOUT OR HYPERURICEMIA: TECUMSEH, MICHIGAN 1959-1960. Am J Med. 1965 Aug;39:242–251. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(65)90048-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maclachlan M. J., Rodnan G. P. Effect of food, fast and alcohol on serum uric acid and acute attacks of gout. Am J Med. 1967 Jan;42(1):38–57. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(67)90005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann G. J. The determination of normal ranges from routine laboratory data. Clin Chem. 1968 Oct;14(10):979–988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyhan W. L. Lesch-Nyhan syndrome. Summary of clinical features. Fed Proc. 1968 Jul-Aug;27(4):1034–1041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCOTT J. T., MCCALLUM F. M., HOLLOWAY V. P. STARVATION, KETOSIS AND URIC ACID EXCRETION. Clin Sci. 1964 Oct;27:209–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seegmiller J. E., Rosenbloom F. M., Kelley W. N. Enzyme defect associated with a sex-linked human neurological disorder and excessive purine synthesis. Science. 1967 Mar 31;155(3770):1682–1684. doi: 10.1126/science.155.3770.1682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


