Abstract
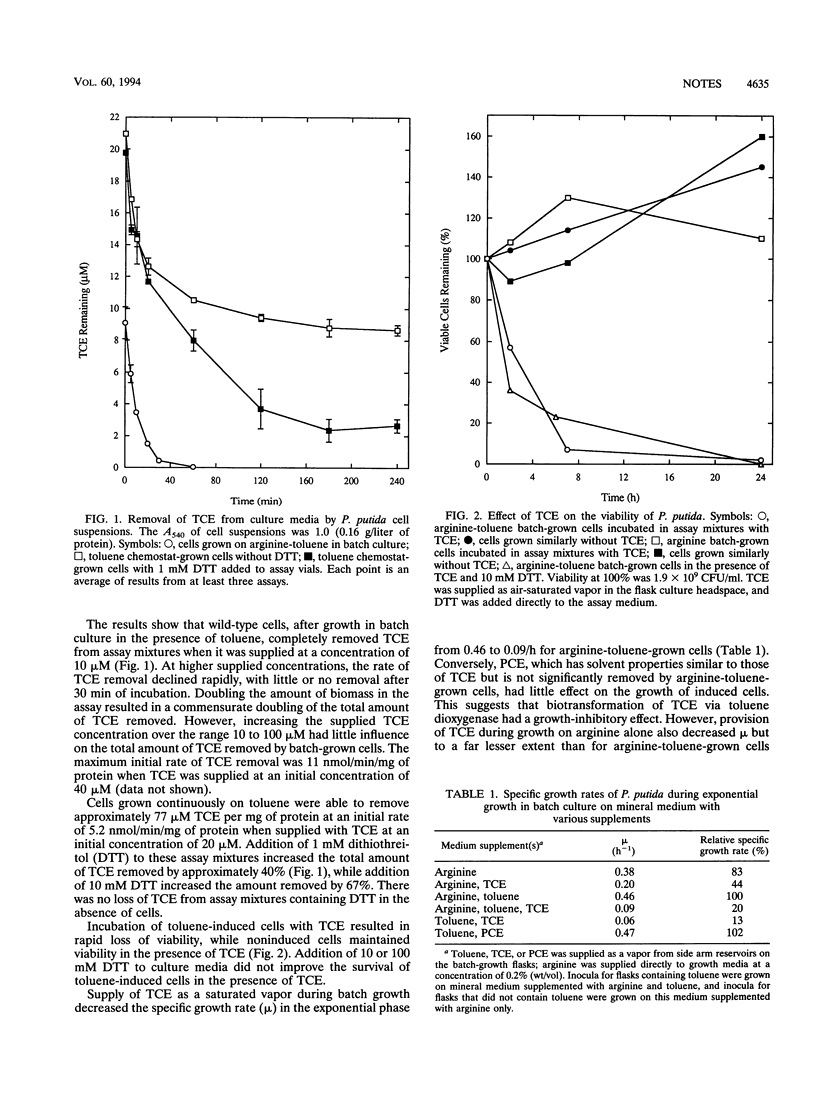
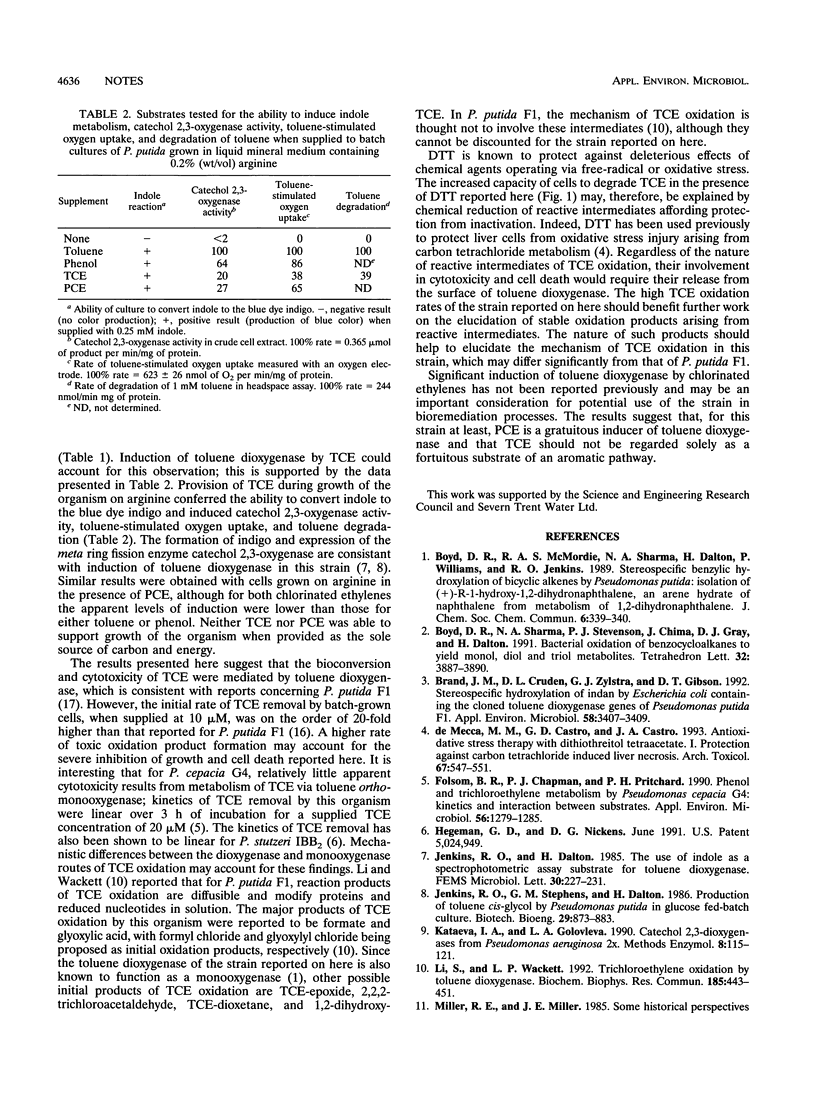
Whole cells of Pseudomonas putida containing toluene dioxygenase were able to remove all detectable trichloroethylene (TCE) from assay mixtures. The capacity of cells to remove TCE was 77 microM/mg of protein with an initial rate of removal of 5.2 nmol/min/ng of protein. TCE oxidation resulted in a decrease in the growth rate of cultures and caused rapid cell death. Addition of dithiothreitol to assay mixtures increased the TCE removal capacity of cells by up to 67% but did not prevent TCE-mediated cell death. TCE induced toluene degradation by whole cells to a rate approximately 40% of that induced by toluene itself.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brand J. M., Cruden D. L., Zylstra G. J., Gibson D. T. Stereospecific hydroxylation of indan by Escherichia coli containing the cloned toluene dioxygenase genes from Pseudomonas putida F1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Oct;58(10):3407–3409. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.10.3407-3409.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folsom B. R., Chapman P. J., Pritchard P. H. Phenol and trichloroethylene degradation by Pseudomonas cepacia G4: kinetics and interactions between substrates. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 May;56(5):1279–1285. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.5.1279-1285.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kataeva I. A., Golovleva L. A. Catechol 2,3-dioxygenases from Pseudomonas aeruginosa 2x. Methods Enzymol. 1990;188:115–121. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)88021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S., Wackett L. P. Trichloroethylene oxidation by toluene dioxygenase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 May 29;185(1):443–451. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps T. J., Niedzielski J. J., Schram R. M., Herbes S. E., White D. C. Biodegradation of trichloroethylene in continuous-recycle expanded-bed bioreactors. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jun;56(6):1702–1709. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.6.1702-1709.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shields M. S., Montgomery S. O., Chapman P. J., Cuskey S. M., Pritchard P. H. Novel pathway of toluene catabolism in the trichloroethylene-degrading bacterium g4. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jun;55(6):1624–1629. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.6.1624-1629.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien H. C., Brusseau G. A., Hanson R. S., Waclett L. P. Biodegradation of trichloroethylene by Methylosinus trichosporium OB3b. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Dec;55(12):3155–3161. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.12.3155-3161.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel T. M., McCarty P. L. Biotransformation of tetrachloroethylene to trichloroethylene, dichloroethylene, vinyl chloride, and carbon dioxide under methanogenic conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 May;49(5):1080–1083. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.5.1080-1083.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wackett L. P., Gibson D. T. Degradation of trichloroethylene by toluene dioxygenase in whole-cell studies with Pseudomonas putida F1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jul;54(7):1703–1708. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.7.1703-1708.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wackett L. P., Householder S. R. Toxicity of Trichloroethylene to Pseudomonas putida F1 Is Mediated by Toluene Dioxygenase. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Oct;55(10):2723–2725. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.10.2723-2725.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Mecca M. M., Castro G. D., Castro J. A. Antioxidative stress therapy with dithiothreitol tetraacetate. I. Protection against carbon tetrachloride induced liver necrosis. Arch Toxicol. 1993;67(8):547–551. doi: 10.1007/BF01969267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


