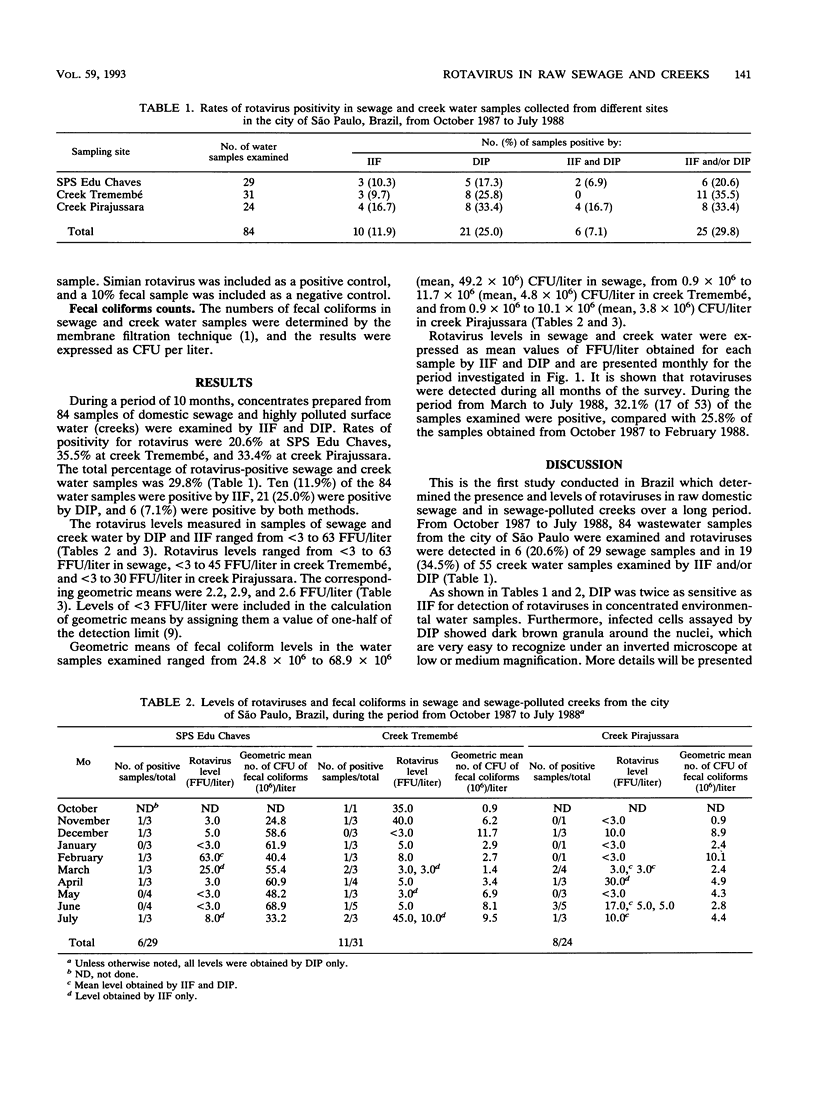
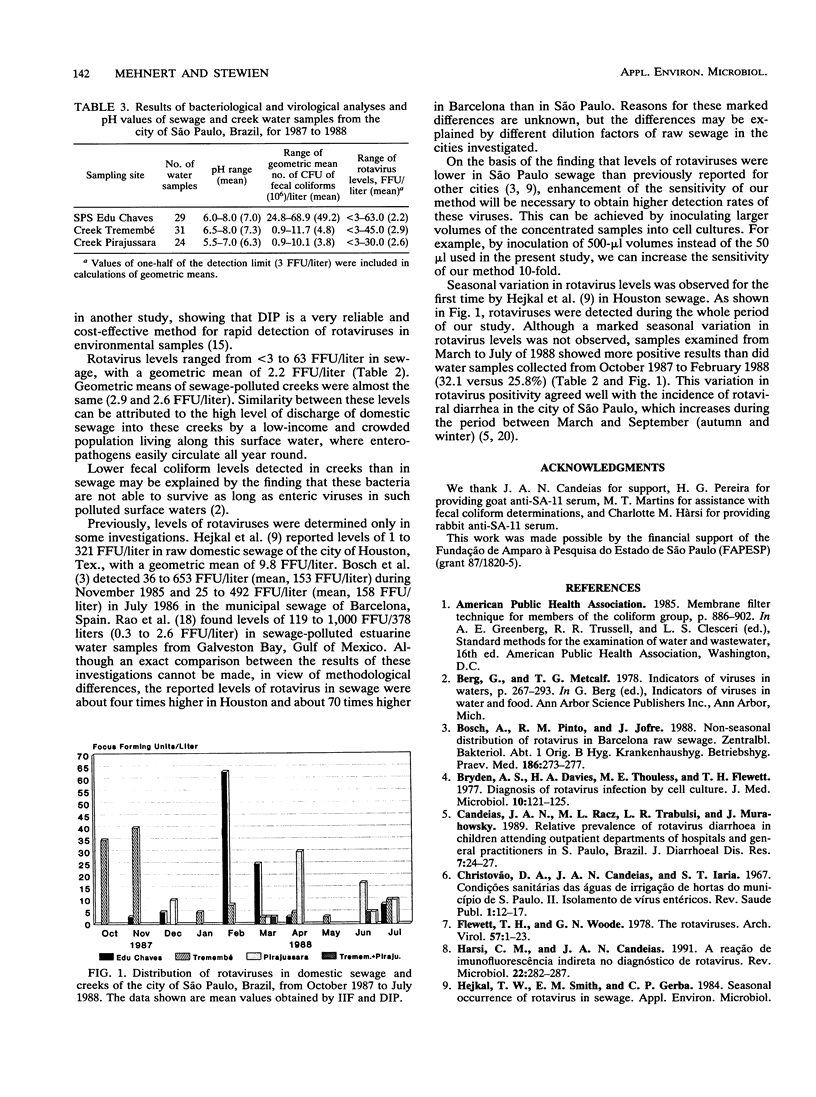
Abstract
Rotaviruses were concentrated from 8-liter samples of raw domestic sewage and sewage-polluted creek water by adsorption to and elution from positively charged microporous filters (Zeta Plus 60S), followed by ultracentrifugation of the filter eluates. Indirect immunofluorescence and direct immunoperoxidase methods allowed detection and enumeration of rotavirus in 6 (20.6%) of 29 sewage samples and in 19 (34.5%) of 55 creek water samples. Levels of rotaviruses ranged from < 3 to 63 focus-forming units (FFU)/liter, and the geometric means were 2.2 FFU/liter in sewage, 2.9 FFU/liter at creek Tremembé, and 2.6 FFU/liter at creek Pirajussara. Wastewater samples examined during autumn and winter months showed a higher rate positivity for rotavirus than those collected in spring and summer, corresponding to the seasonal variation of rotaviral diarrhea in the city of São Paulo.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bosch A., Pinto R. M., Jofre J. Non-seasonal distribution of rotavirus in Barcelona raw sewage. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg B. 1988 Jun;186(3):273–277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryden A. S., Davies H. A., Thouless M. E., Flewitt T. H. Diagnosis of rotavirus infection by cell culture. J Med Microbiol. 1977 Feb;10(1):121–125. doi: 10.1099/00222615-10-1-121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Candeias J. A., Racz M. L., Travulsi L. R., Murahowsky J. Relative prevalence of rotavirus diarrhoea in children attending outpatient departments of hospitals and general practitioners in Sao Paulo, Brazil. J Diarrhoeal Dis Res. 1989 Mar-Jun;7(1-2):24–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christovão D. de A., Iaria S. T., Candeias J. A. Condiçes sanitárias das águas de irrigaço de hortas do municípo de São Paulo. II. Isolamento de virus entéricos. Rev Saude Publica. 1967 Jun;1(1):12–17. doi: 10.1590/s0034-89101967000100003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flewett T. H., Woode G. N. The rotaviruses. Arch Virol. 1978;57(1):1–23. doi: 10.1007/BF01315633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins R. S., Gaspard G. B., Williams F. P., Jr, Karlin R. J., Cukor G., Blacklow N. R. A community waterborne gastroenteritis outbreak: evidence for rotavirus as the agent. Am J Public Health. 1984 Mar;74(3):263–265. doi: 10.2105/ajph.74.3.263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linhares A. C., Gabbay Y. B., Mascarenhas J. D., Freitas R. B., Flewett T. H., Beards G. M. Epidemiology of rotavirus subgroups and serotypes in Belem, Brazil: a three-year study. Ann Inst Pasteur Virol. 1988 Jan-Mar;139(1):89–99. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2617(88)80009-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linhares A. C., Pinheiro F. P., Freitas R. B., Gabbay Y. B., Shirley J. A., Beards G. M. An outbreak of rotavirus diarrhea among a nonimmune, isolated South American Indian community. Am J Epidemiol. 1981 Jun;113(6):703–710. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNulty M. S. Rotaviruses. J Gen Virol. 1978 Jul;40(1):1–18. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-40-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauli G., Gregersen J. P., Ludwig H. Plaque/focus immunoassay: a simple method for detecting antiviral monoclonal or other antibodies and viral antigens in cells. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Nov 30;74(2):337–344. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90301-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira H. G., Azeredo R. S., Leite J. P., Candeias J. A., Rácz M. L., Linhares A. C., Gabbay Y. B., Trabulsi J. R. Electrophoretic study of the genome of human rotaviruses from Rio de Janeiro, São Paulo and Pará, Brazil. J Hyg (Lond) 1983 Feb;90(1):117–125. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400063919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao V. C., Metcalf T. G., Melnick J. L. Development of a method for concentration of rotavirus and its application to recovery of rotaviruses from estuarine waters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Sep;52(3):484–488. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.3.484-488.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutmoller F., Azeredo R. S., Lacerda M. D., Barth O. M., Pereira H. G., Hoffer E., Schatzmayr H. G. An outbreak of gastroenteritis caused by both rotavirus and Shigella sonnei in a private school in Rio de Janeiro. J Hyg (Lond) 1982 Apr;88(2):285–293. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400070145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


