Abstract
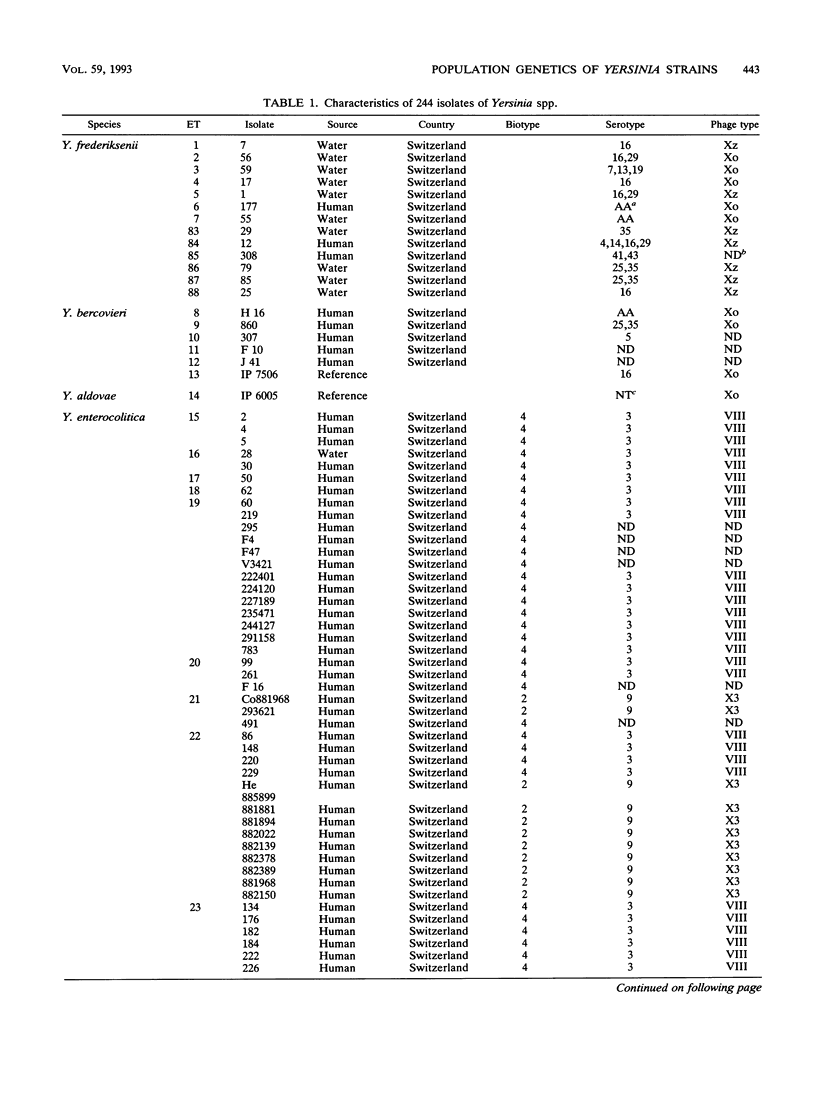
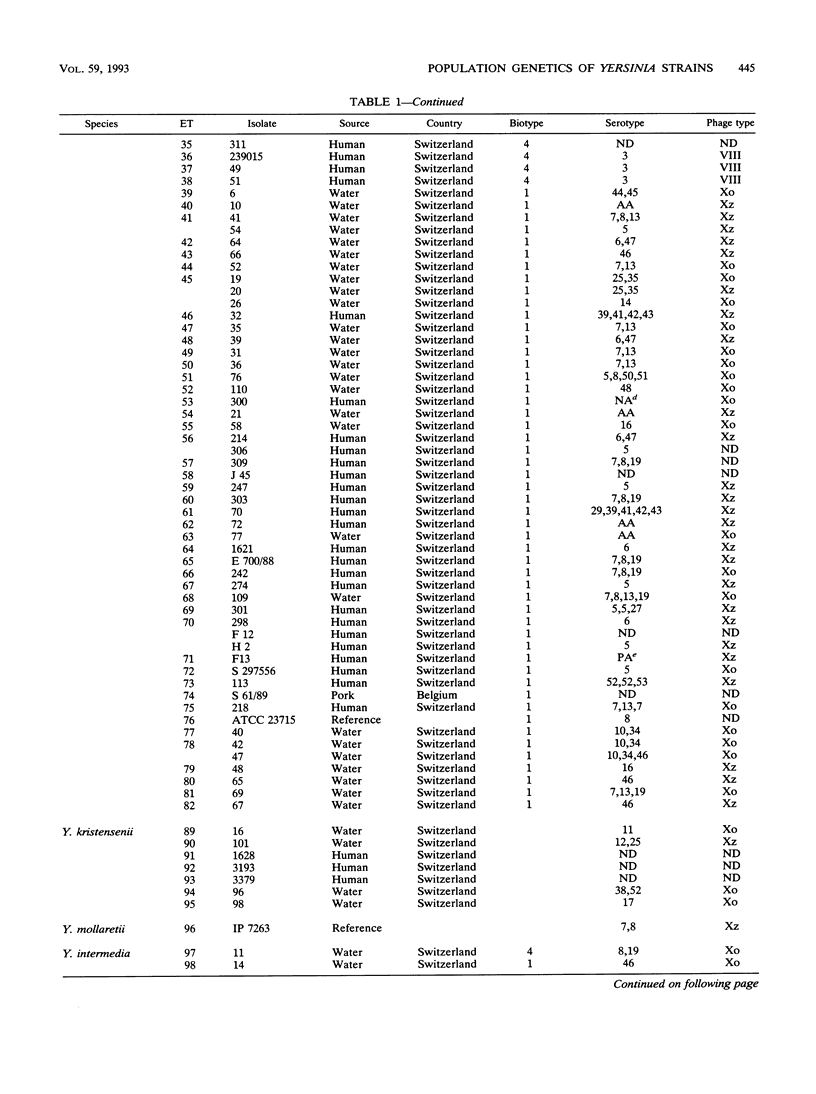
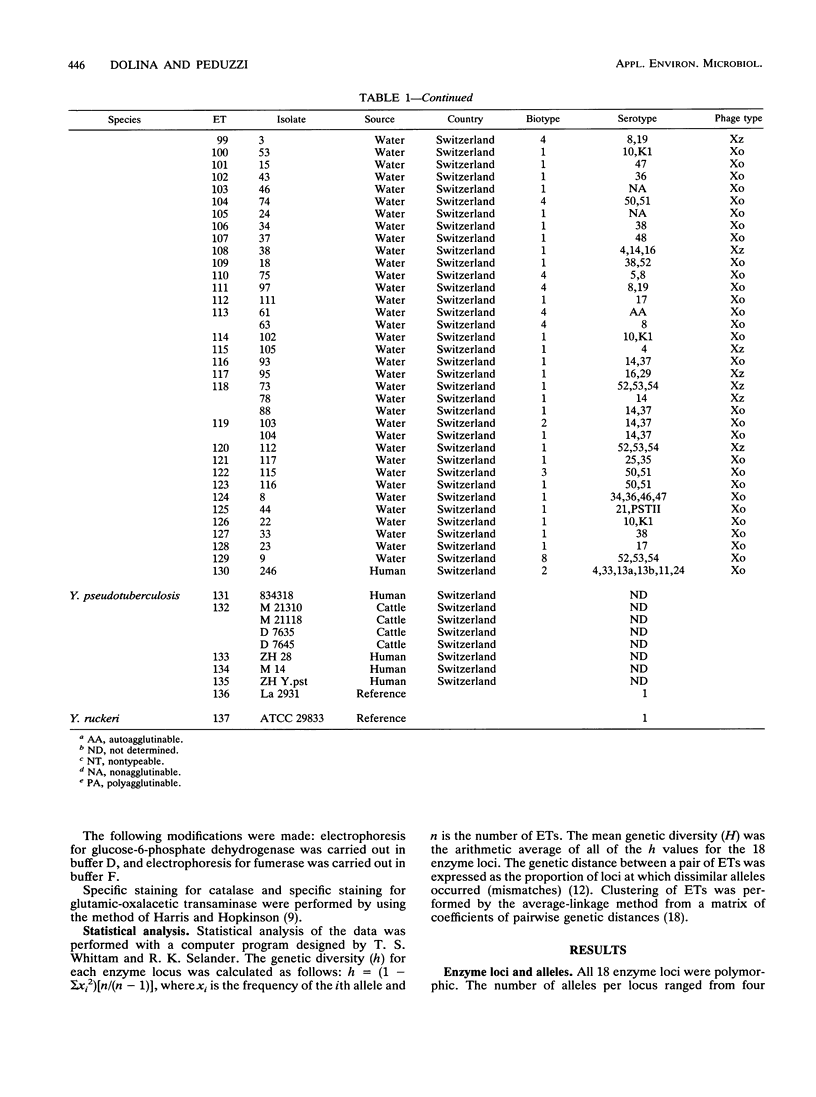
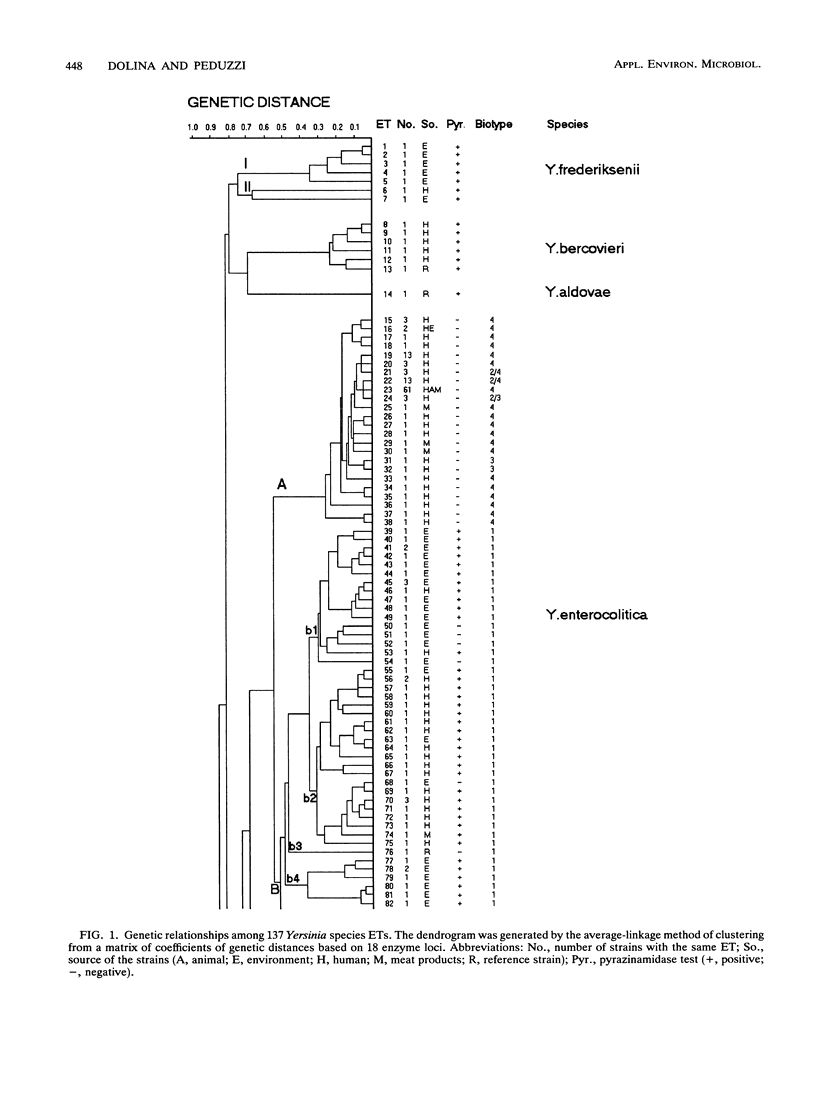
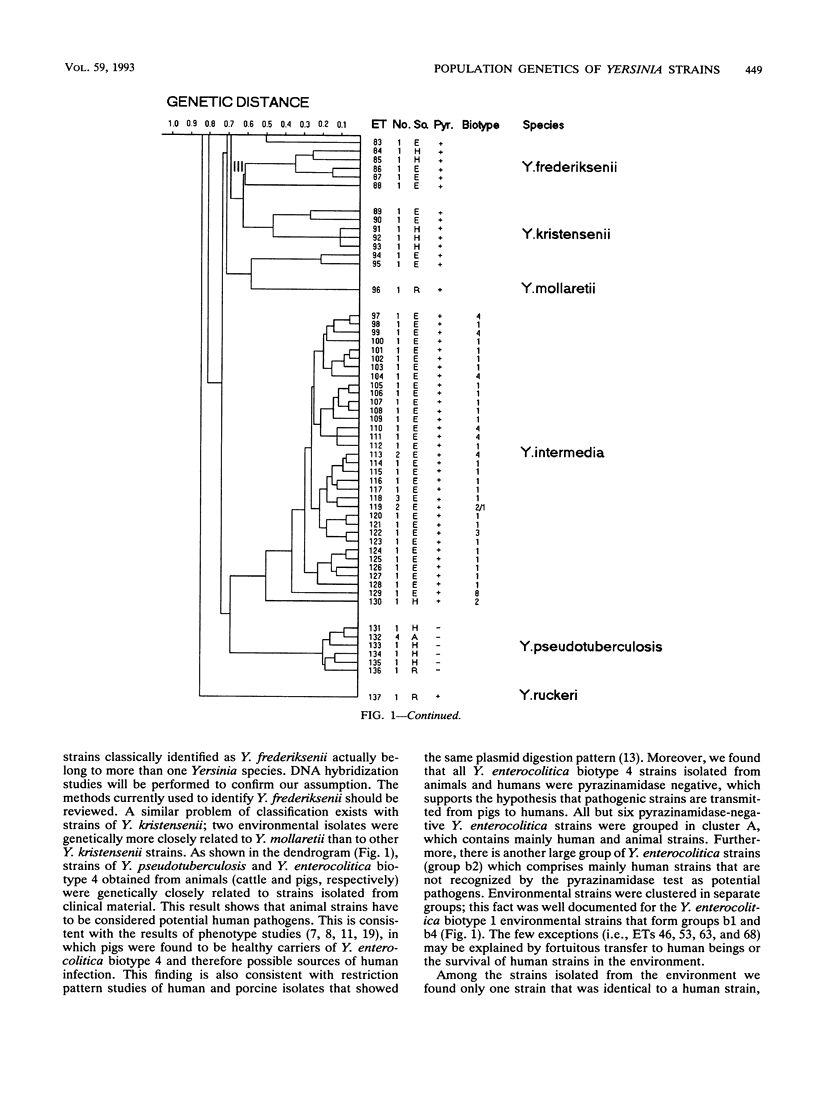
Multilocus enzyme electrophoresis was used to analyze 244 strains of nine Yersinia species isolated from the environment, animals, and humans at 18 genes encoding metabolic enzymes. All 18 enzymes were polymorphic. Among the 137 electrophoretic types (ETs) distinguished, the mean allelic diversity per locus was 0.531. Yersinia frederiksenii ETs were divided into three major clusters that were separated by a large genetic distance, and one ET was more closely related to Yersinia enterocolitica. Thus, strains classically identified as Y. frederiksenii may represent more than one species. Furthermore, two strains identified as Yersinia kristensenii proved to be more closely related to Yersinia mollaretii. Environmental strains formed independent groups. A very interesting ET consisting of as many as 61 isolates of Yersinia enterocolitica was detected, and the epidemiologic relevance of this ET is discussed. Human strains of Y. enterocolitica biotype 4 and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis were recognized as being closely related to animal strains of the same species. Therefore, animal strains of these two species may be considered potential human pathogens.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Caugant D. A., Aleksic S., Mollaret H. H., Selander R. K., Kapperud G. Clonal diversity and relationships among strains of Yersinia enterocolitica. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Dec;27(12):2678–2683. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.12.2678-2683.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelis G., Laroche Y., Balligand G., Sory M. P., Wauters G. Yersinia enterocolitica, a primary model for bacterial invasiveness. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Jan-Feb;9(1):64–87. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.1.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle M. P., Hugdahl M. B., Taylor S. L. Isolation of virulent Yersinia enterocolitica from porcine tongues. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Oct;42(4):661–666. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.4.661-666.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima H. Direct isolation of Yersinia enterocolitica and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis from meat. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Sep;50(3):710–712. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.3.710-712.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandolo K., Wauters G. Pyrazinamidase activity in Yersinia enterocolitica and related organisms. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jun;21(6):980–982. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.6.980-982.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nei M. Estimation of average heterozygosity and genetic distance from a small number of individuals. Genetics. 1978 Jul;89(3):583–590. doi: 10.1093/genetics/89.3.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesbakken T., Kapperud G., Sørum H., Dommarsnes K. Structural variability of 40-50 Mdal virulence plasmids from Yersinia enterocolitica. Geographical and ecological distribution of plasmid variants. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1987 Jun;95(3):167–173. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1987.tb03107.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schill W. B., Phelps S. R., Pyle S. W. Multilocus Electrophoretic Assessment of the Genetic Structure and Diversity of Yersinia ruckeri. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Nov;48(5):975–979. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.5.975-979.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., Caugant D. A., Ochman H., Musser J. M., Gilmour M. N., Whittam T. S. Methods of multilocus enzyme electrophoresis for bacterial population genetics and systematics. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 May;51(5):873–884. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.5.873-884.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., Musser J. M., Caugant D. A., Gilmour M. N., Whittam T. S. Population genetics of pathogenic bacteria. Microb Pathog. 1987 Jul;3(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90032-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tauxe R. V., Vandepitte J., Wauters G., Martin S. M., Goossens V., De Mol P., Van Noyen R., Thiers G. Yersinia enterocolitica infections and pork: the missing link. Lancet. 1987 May 16;1(8542):1129–1132. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91683-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


