Abstract
A method for the measurement of specific levels of gene expression that combines target mRNA and target DNA quantitation has been developed. The use of target gene dose as a normalizing factor for mRNA provides an alternative to 16S or 23S rRNA, which are unsuitable for use in the environment because of their presence in nontarget organisms. Both target mRNA and DNA are recovered from replicate samples and detected by using antisense and sense single-stranded RNA gene probes. For efficient mRNA recovery, the use of Millipore Durapore filters and multiple extractions was necessary. Quantitation was performed by radiometric detection by using a β-scanner and comparison of the sample signal against target mRNA and DNA standard curves. This method enabled the measurement of expression of the catechol-2,3-dioxygenase gene (xylE) contained on the thermoregulated plasmid pLV1013 in a marine Vibrio strain in culture and in the environment. In studies of the relationship between mRNA levels and enzyme activities, the appearance of enzyme activity lagged behind xylE mRNA synthesis by an hour after temperature induction. This suggests that mRNA analysis is well suited for determining rapid regulation of microbial gene expression at the transcriptional level in water column microbial populations.
Full text
PDF

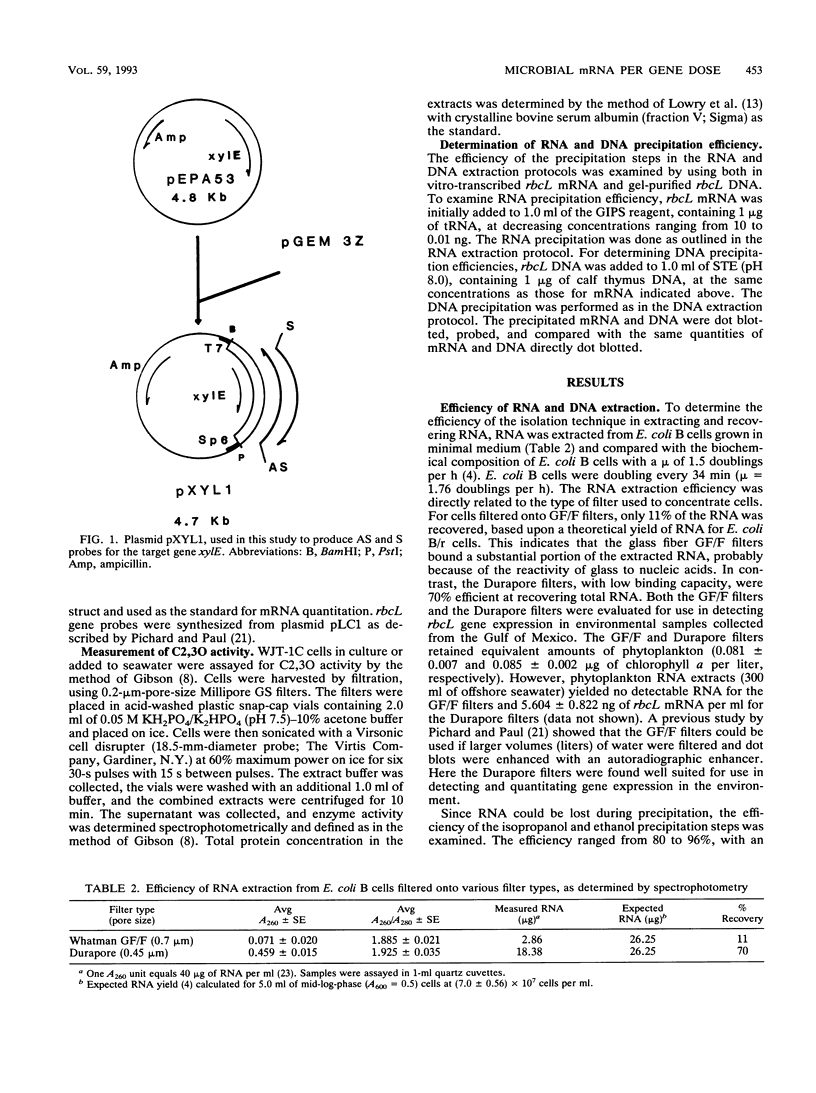
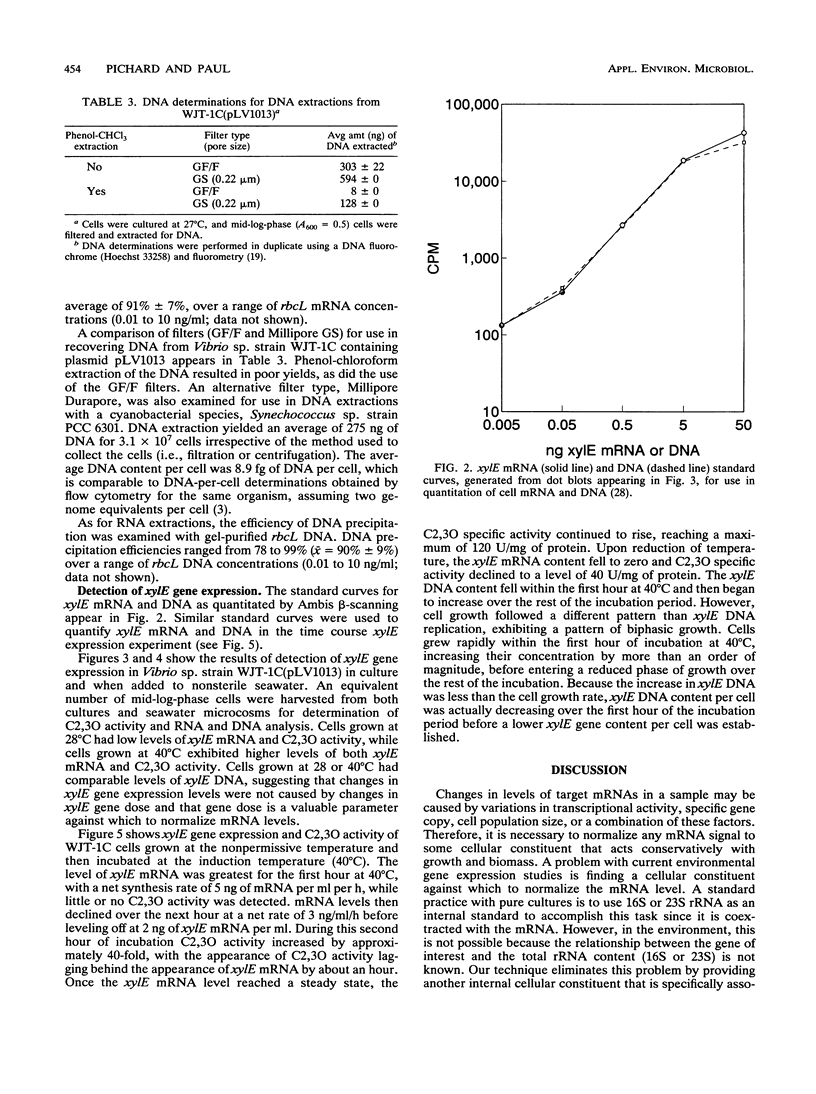
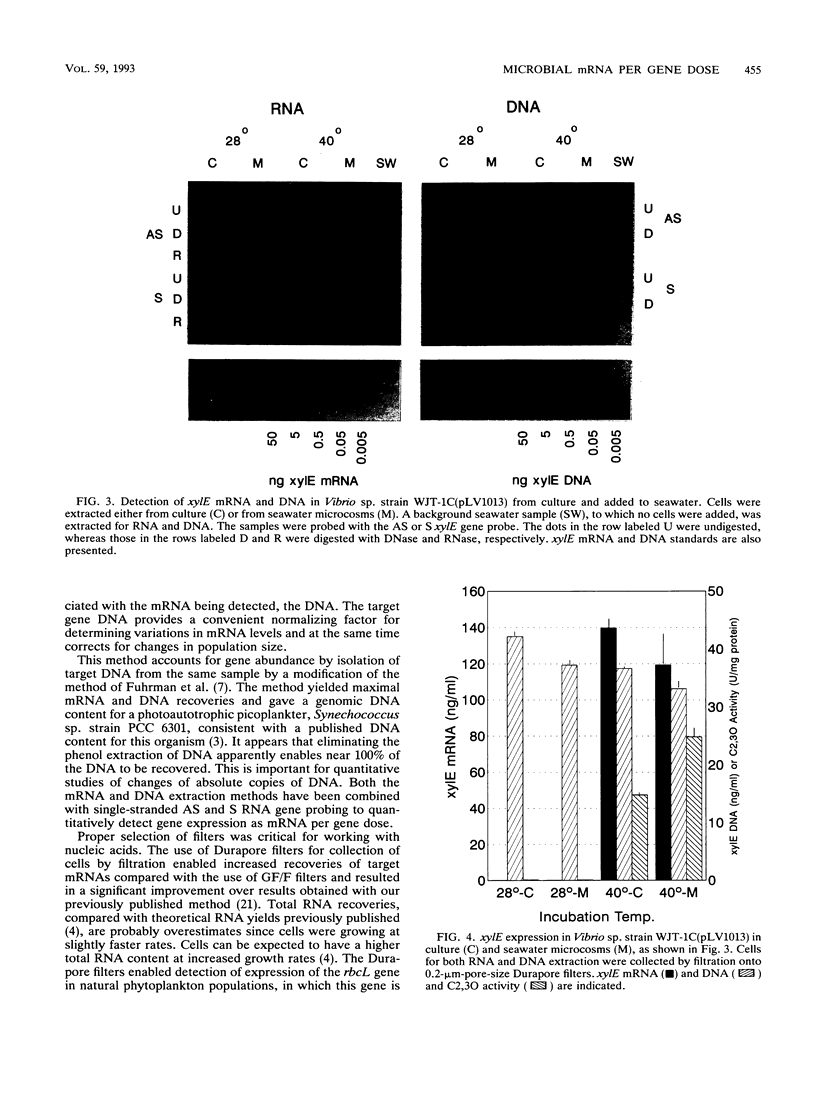
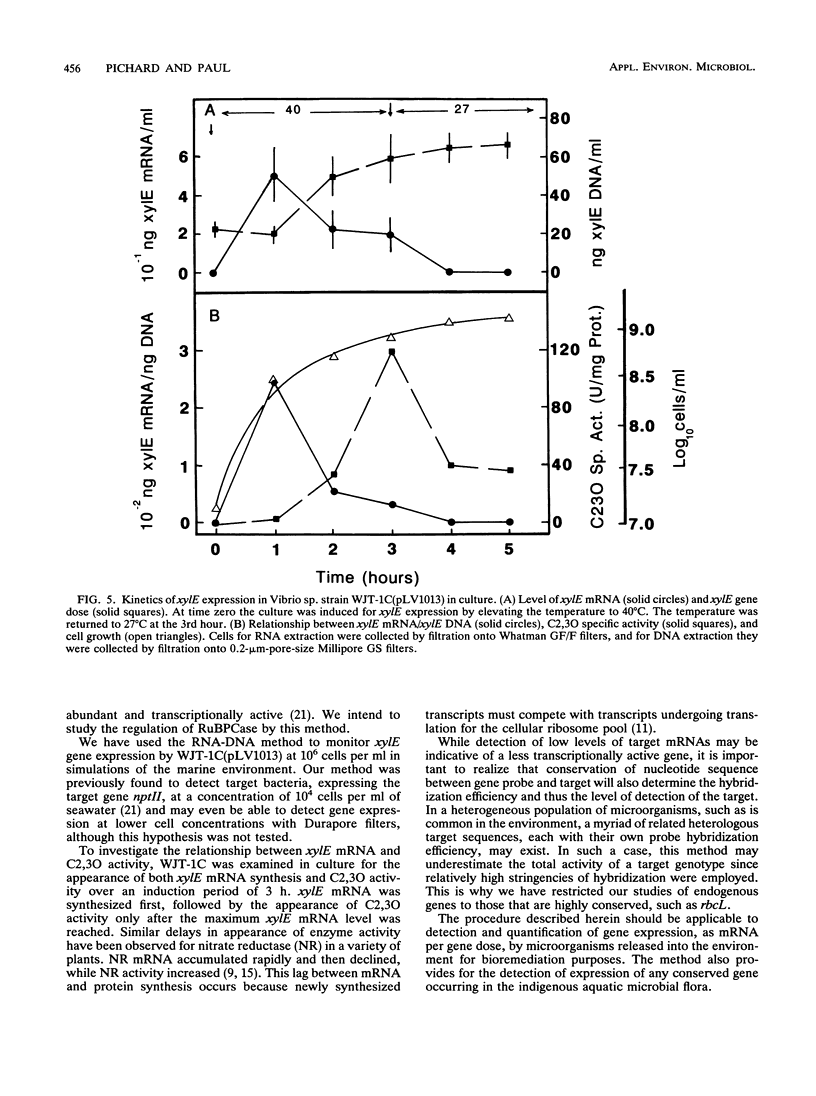

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Binder B. J., Chisholm S. W. Relationship between DNA cycle and growth rate in Synechococcus sp. strain PCC 6301. J Bacteriol. 1990 May;172(5):2313–2319. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.5.2313-2319.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frischer M. E., Thurmond J. M., Paul J. H. Natural plasmid transformation in a high-frequency-of-transformation marine Vibrio strain. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Nov;56(11):3439–3444. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.11.3439-3444.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrman J. A., Comeau D. E., Hagström A., Chan A. M. Extraction from natural planktonic microorganisms of DNA suitable for molecular biological studies. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jun;54(6):1426–1429. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.6.1426-1429.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iyobe S., Kono M., Oara K., Hashimoto H., Mitsuhashi S. Relationship between chloramphenicol acetyltransferase activity and the number of resistance genes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Jan;5(1):68–74. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.1.68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen K. F., Pedersen S. Metabolic growth rate control in Escherichia coli may be a consequence of subsaturation of the macromolecular biosynthetic apparatus with substrates and catalytic components. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Jun;54(2):89–100. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.2.89-100.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King J. M., Digrazia P. M., Applegate B., Burlage R., Sanseverino J., Dunbar P., Larimer F., Sayler G. S. Rapid, sensitive bioluminescent reporter technology for naphthalene exposure and biodegradation. Science. 1990 Aug 17;249(4970):778–781. doi: 10.1126/science.249.4970.778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordström K., Ingram L. C., Lundbäck A. Mutations in R factors of Escherichia coli causing an increased number of R-factor copies per chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):562–569. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.562-569.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odakura Y., Hashimoto H., Mitsuhashi S. R-factor mutant capable of specifying hypersynthesis of penicillinase. J Bacteriol. 1974 Dec;120(3):1260–1267. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.3.1260-1267.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogunseitan O. A., Delgado I. L., Tsai Y. L., Olson B. H. Effect of 2-hydroxybenzoate on the maintenance of naphthalene-degrading pseudomonads in seeded and unseeded soil. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Oct;57(10):2873–2879. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.10.2873-2879.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul J. H., Myers B. Fluorometric determination of DNA in aquatic microorganisms by use of hoechst 33258. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jun;43(6):1393–1399. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.6.1393-1399.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippidis G. P., Malmberg L. H., Hu W. S., Schottel J. L. Effect of gene amplification on mercuric ion reduction activity of Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Dec;57(12):3558–3564. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.12.3558-3564.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pichard Scott L., Paul John H. Detection of Gene Expression in Genetically Engineered Microorganisms and Natural Phytoplankton Populations in the Marine Environment by mRNA Analysis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Jun;57(6):1721–1727. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.6.1721-1727.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai Y. L., Olson B. H. Effects of Hg, CH(3)-Hg, and Temperature on the Expression of Mercury Resistance Genes in Environmental Bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Nov;56(11):3266–3272. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.11.3266-3272.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai Y. L., Park M. J., Olson B. H. Rapid method for direct extraction of mRNA from seeded soils. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Mar;57(3):765–768. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.3.765-768.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winstanley C., Morgan J. A., Pickup R. W., Jones J. G., Saunders J. R. Differential regulation of lambda pL and pR promoters by a cI repressor in a broad-host-range thermoregulated plasmid marker system. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Apr;55(4):771–777. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.4.771-777.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



