Abstract
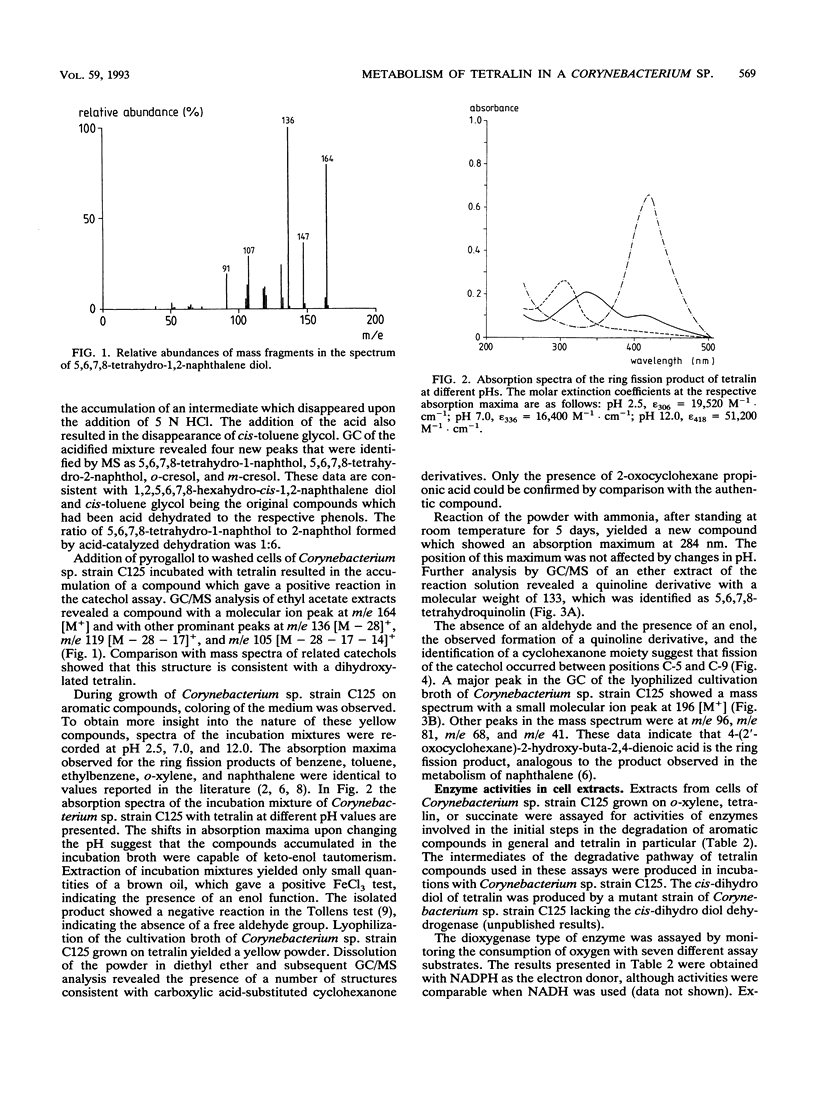
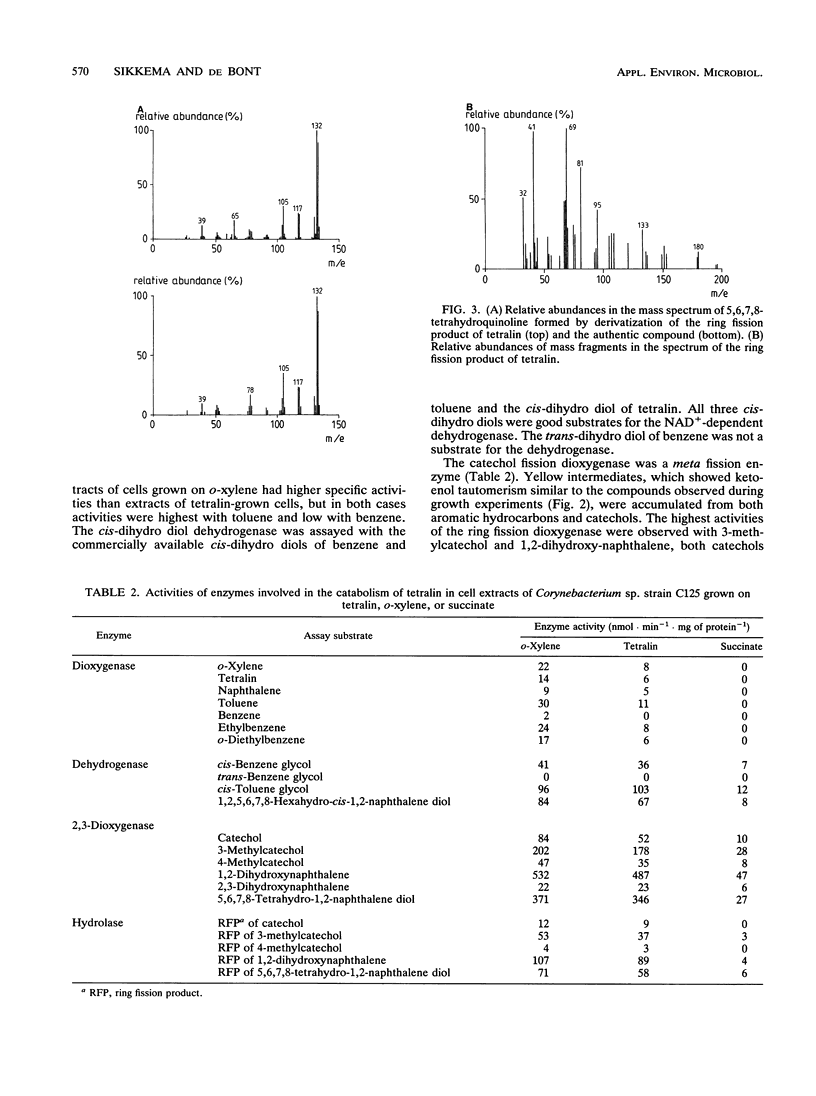
Corynebacterium sp. strain C125, originally isolated on o-xylene, was selected for its ability to grow on tetralin (1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalene) as the sole source of carbon and energy. The catabolism of tetralin in Corynebacterium sp. strain C125 was shown to proceed via initial hydroxylation of the benzene nucleus at positions C-5 and C-6, resulting in the formation of the corresponding cis-dihydro diol. Subsequently, the dihydro diol was dehydrogenated by a NAD-dependent dehydrogenase to 5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-1,2-naphthalene diol. The aromatic ring was cleaved in the extradiol position by a catechol-2,3-dioxygenase. The ring fission product was subject to a hydrolytic attack, resulting in the formation of a carboxylic acid-substituted cyclohexanone. This is the first report of the catabolism of tetralin via degradation of the aromatic moiety.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baggi G., Barbieri P., Galli E., Tollari S. Isolation of a Pseudomonas stutzeri strain that degrades o-xylene. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Sep;53(9):2129–2132. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.9.2129-2132.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarty A. M. Genetic basis of the biodegradation of salicylate in Pseudomonas. J Bacteriol. 1972 Nov;112(2):815–823. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.2.815-823.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. I., Evans W. C. Oxidative metabolism of naphthalene by soil pseudomonads. The ring-fission mechanism. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):251–261. doi: 10.1042/bj0910251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espejo R. T., Lebowitz J. A simple electrophoretic method for the determination of superhelix density of closed circular DNAs and for observation of their superhelix density heterogeneity. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:95–103. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90510-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganapathy K., Khanchandani K. S., Bhattacharyya P. K. Microbiological transformations of terpenes. VII. Further studies on the mechanism of fungal oxygenation reactions with the aid of model substrates. Indian J Biochem. 1966 Jun;3(2):66–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson D. T., Gschwendt B., Yeh W. K., Kobal V. M. Initial reactions in the oxidation of ethylbenzene by Pseudomonas putida. Biochemistry. 1973 Apr 10;12(8):1520–1528. doi: 10.1021/bi00732a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYAISHI O., KATAGIRI M., ROTHBERG S. Studies on oxygenases; pyrocatechase. J Biol Chem. 1957 Dec;229(2):905–920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmans S., Smits J. P., van der Werf M. J., Volkering F., de Bont J. A. Metabolism of Styrene Oxide and 2-Phenylethanol in the Styrene-Degrading Xanthobacter Strain 124X. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Nov;55(11):2850–2855. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.11.2850-2855.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Högn T., Jaenicke L. Benzene metabolism of Moraxella species. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Oct;30(2):369–375. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb02107.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffrey A. M., Yeh H. J., Jerina D. M., Patel T. R., Davey J. F., Gibson D. T. Initial reactions in the oxidation of naphthalene by Pseudomonas putida. Biochemistry. 1975 Feb 11;14(3):575–584. doi: 10.1021/bi00674a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOJIMA Y., ITADA N., HAYAISHI O. Metapyrocatachase: a new catechol-cleaving enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1961 Aug;236:2223–2228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAIR P. M., VAIDYANATHAN C. S. A COLORIMETRIC METHOD FOR DETERMINATION OF PYROCATECHOL AND RELATED SUBSTANCES. Anal Biochem. 1964 Mar;7:315–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel T. R., Gibson D. T. Purification and propeties of (plus)-cis-naphthalene dihydrodiol dehydrogenase of Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):879–888. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.879-888.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J. E., Gibson D. T. Purification and properties of cis-toluene dihydrodiol dehydrogenase from Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jun;130(3):1117–1124. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.3.1117-1124.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sala-Trepat J. M., Evans W. C. The meta cleavage of catechol by Azotobacter species. 4-Oxalocrotonate pathway. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Jun 11;20(3):400–413. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01406.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sala-Trepat J. M., Murray K., Williams P. A. The metabolic divergence in the meta cleavage of catechols by Pseudomonas putida NCIB 10015. Physiological significance and evolutionary implications. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jul 24;28(3):347–356. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01920.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schraa G., Bethe B. M., van Neerven A. R., Van den Tweel W. J., Van der Wende E., Zehnder A. J. Degradation 1,2-dimethylbenzene by Corynebacterium strain C125. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1987;53(3):159–170. doi: 10.1007/BF00393844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikkema J., Poolman B., Konings W. N., de Bont J. A. Effects of the membrane action of tetralin on the functional and structural properties of artificial and bacterial membranes. J Bacteriol. 1992 May;174(9):2986–2992. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.9.2986-2992.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. R. The biodegradation of aromatic hydrocarbons by bacteria. Biodegradation. 1990;1(2-3):191–206. doi: 10.1007/BF00058836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soli G., Bens E. M. Bacteria which attack petroleum hydrocarbons in a saline medium. Biotechnol Bioeng. 1972 May;14(3):319–330. doi: 10.1002/bit.260140305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubbs C. M., Trezise D., Connor H. E., Feniuk W. Vasodilator effect of 8-OH-DPAT in the isolated perfused mesenteric bed of the rat: no evidence for involvement of 5-HT1A receptors. J Auton Pharmacol. 1991 Aug;11(4):237–245. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1991.tb00321.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigmore G. J., Bayly R. C., Di Berardino D. Pseudomonas putida mutants defective in the metabolism of the products of meta fission of catechol and its methyl analogues. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):31–37. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.31-37.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bont J. A., Vorage M. J., Hartmans S., van den Tweel W. J. Microbial degradation of 1,3-dichlorobenzene. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Oct;52(4):677–680. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.4.677-680.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


