Abstract
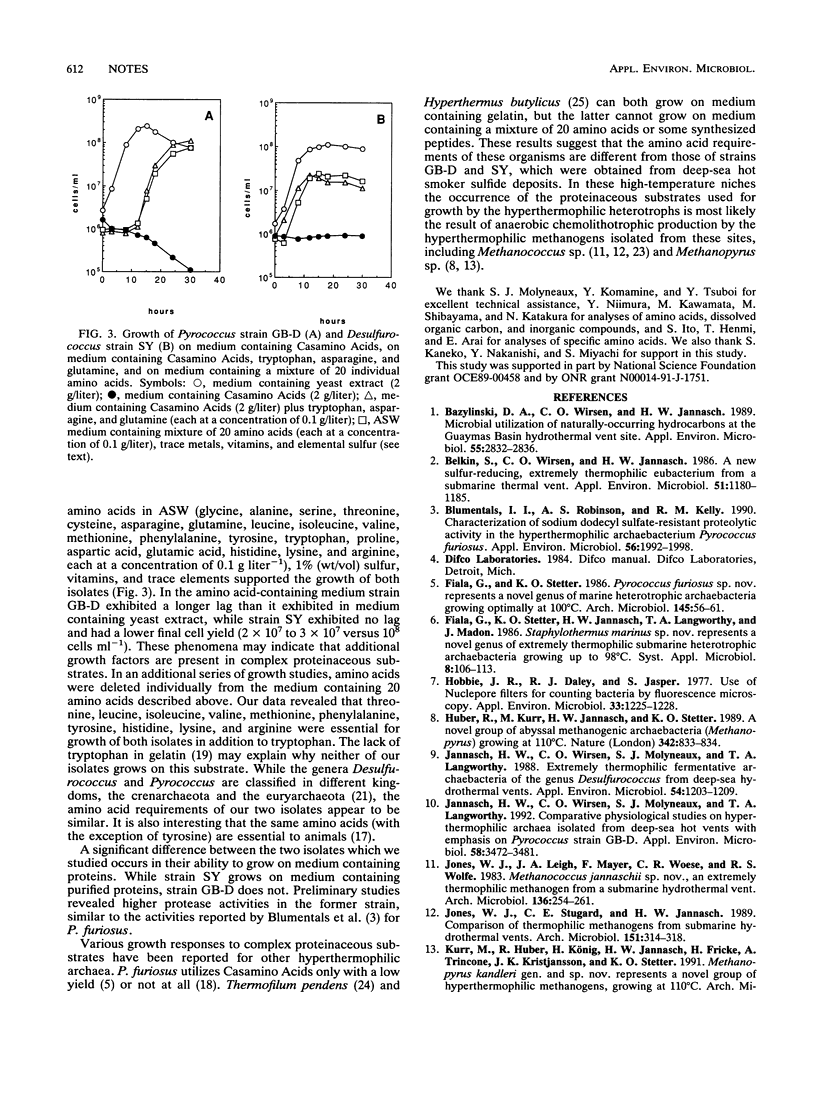
Two sulfur-dependent hyperthermophilic archaea, Desulfurococcus strain SY and Pyrococcus strain GB-D, which were isolated from deep-sea hydrothermal vents, utilized free amino acids and peptides obtained from various molecular size fractions of yeast extract. It was found that 11 amino acids were essential for growth. The metabolic products were acetate, i-butyrate, and i-valerate.
Full text
PDF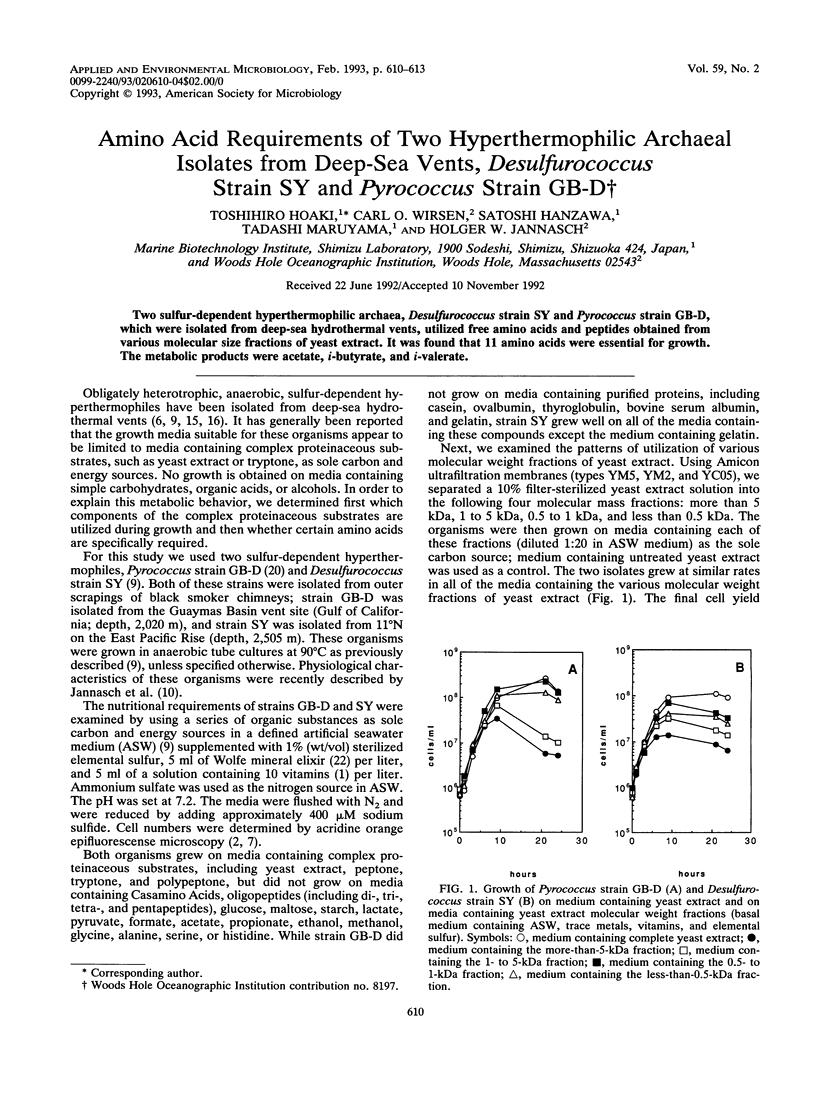


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bazylinski D. A., Wirsen C. O., Jannasch H. W. Microbial utilization of naturally occurring hydrocarbons at the guaymas basin hydrothermal vent site. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Nov;55(11):2832–2836. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.11.2832-2836.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belkin S., Wirsen C. O., Jannasch H. W. A new sulfur-reducing, extremely thermophilic eubacterium from a submarine thermal vent. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Jun;51(6):1180–1185. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.6.1180-1185.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumentals I. I., Robinson A. S., Kelly R. M. Characterization of sodium dodecyl sulfate-resistant proteolytic activity in the hyperthermophilic archaebacterium Pyrococcus furiosus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jul;56(7):1992–1998. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.7.1992-1998.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbie J. E., Daley R. J., Jasper S. Use of nuclepore filters for counting bacteria by fluorescence microscopy. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 May;33(5):1225–1228. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.5.1225-1228.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jannasch H. W., Wirsen C. O., Molyneaux S. J., Langworthy T. A. Comparative Physiological Studies on Hyperthermophilic Archaea Isolated from Deep-Sea Hot Vents with Emphasis on Pyrococcus Strain GB-D. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Nov;58(11):3472–3481. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.11.3472-3481.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jannasch H. W., Wirsen C. O., Molyneaux S. J., Langworthy T. A. Extremely thermophilic fermentative archaebacteria of the genus desulfurococcus from deep-sea hydrothermal vents. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 May;54(5):1203–1209. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.5.1203-1209.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snowden L. J., Blumentals I. I., Kelly R. M. Regulation of Proteolytic Activity in the Hyperthermophile Pyrococcus furiosus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Apr;58(4):1134–1141. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.4.1134-1141.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRISTRAM G. R., SMITH R. H. THE AMINO ACID COMPOSITION OF SOME PURIFIED PROTEINS. Adv Protein Chem. 1963;18:227–318. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60270-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLIN E. A., WOLIN M. J., WOLFE R. S. FORMATION OF METHANE BY BACTERIAL EXTRACTS. J Biol Chem. 1963 Aug;238:2882–2886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Kandler O., Wheelis M. L. Towards a natural system of organisms: proposal for the domains Archaea, Bacteria, and Eucarya. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4576–4579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zillig W., Holz I., Janekovic D., Klenk H. P., Imsel E., Trent J., Wunderl S., Forjaz V. H., Coutinho R., Ferreira T. Hyperthermus butylicus, a hyperthermophilic sulfur-reducing archaebacterium that ferments peptides. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):3959–3965. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.3959-3965.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


